MMS • RSS
Article originally posted on Data Science Central. Visit Data Science Central
Today’s Artificial Intelligence (AI) discussions remind me of a Steve Martin skit from the early Saturday Night Live days (1979). In the skit titled “What the Hell is that?”, Steve Martin, later joined by Bill Murray, is looking in the distance at something, repeatedly asking the question “What the hell is that?” The skit reminds me of today’s AI discussions about “What the hell is AI?”, which distracts from the more important conversation about how we should be leveraging AI to derive and drive business value.
Folks are spending too much time trying to define“AI” and not enough time trying to exploitAI to optimize key business and operational processes, mitigate compliance and security risks, uncover new sources of revenue and create a more compelling, differentiated customer experience.
We’ve seen this “focus on definition and not on exploitation” problem before. I wrote a blog titled “Data Lake, Data Reservoir, Data Dump…Blah, Blah, Blah…” that described the Data Lake versus Data Reservoir (a term that I’m happy to see has faded) debate:
Who cares what it’s called. The fact that every technology vendor and IT analyst is out there trying to coin their own favorite term only dooms us to delaying the most important discussion – how do we leverage this “data thingie” to uncover customer, product and operational insights that we can use to differentiate our customer engagements, optimize key business processes and uncover new monetization opportunities?
Bottom-line: Understand the capabilities of AI well enough so you can envision and prototype how to exploitthe AI capabilities to deliver material business value.
Understanding AI Capabilities, Not AI Definition
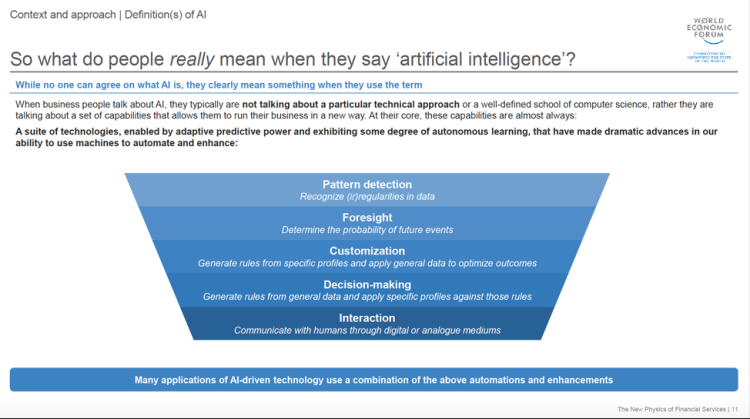
My friends at Deloitte (yes, I have friends…some…) shared with me this marvelous report titled “The New Physics of Financial Services – How artificial intelligence is transforming the financial ecosystem.” The report provides some interesting insights into the challenges and opportunities that financial services organizations are going to face with respect to how AI is likely to disrupt their business models and customer relationships. The report does a nice job of focusing not on the definition but instead on the capabilities of AI (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Understanding AI Capabilities
For me, the simplest way to describe AI (and Data Science) is that “AI and Data Science is about identifying those variables and metrics that might be better predictors of performance”. That means twisting, stretching, bending and torturing the data to identify and codify patterns and relationshipsburied in the data that I can use to predict the performance and behaviors of both humans and machines/devices.
Data Science and AI is about identifying and codifying the patterns and relationships buried in the data so one can predict future performance and behaviors
This is the discussion I have with my University of San Francisco and National University of Ireland-Galway students in helping them to understand how analytics can transform an organization’s business models. In the blog “Artificial Intelligence is not ‘Fake’ Intelligence”, I try to frame the entire analytics space, of which AI is only a portion, and how to think about analytics from a business application perspective:
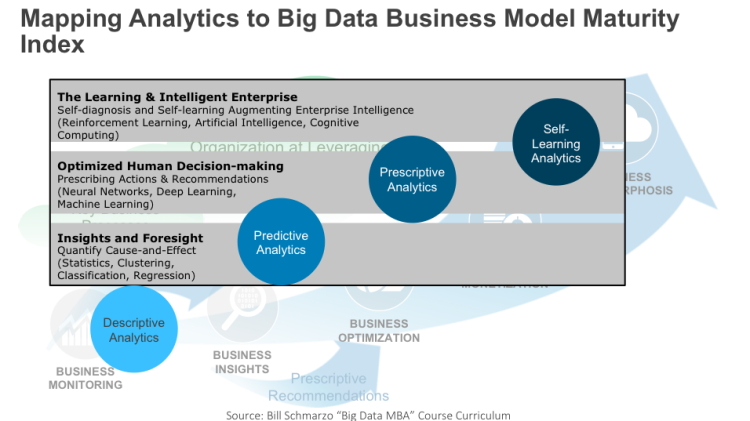
- Level 1: Insights and Foresight. This is the foundational level that includes statistical analytics as well as the broad categories of predictive analytics (e.g., clustering, classification, regression) and data mining. The goal of the level 1 is to quantify cause-and-effect, establish confidence levels and measure goodness of fit.
- Level 2: Optimized Human-decision Making. This level includes machine learning, deep learning and neural networks. The goal of these advanced analytic algorithms is to enable computers to learn on their own; to identify patterns in data, build models that explain the data, and predict outcomes without having pre-programmed rules and analytic models.
- Level 3: The Learning and Intelligent Enterprise. This level includes artificial intelligence, reinforcement learning and cognitive computing. These advanced analytic algorithms self-monitor, self-diagnose, self-adjust and self-learn. These analytics perceive the world around them, create goals, make decisions towards those goals, measure decision effectiveness, and learn in order to refine the decisions that advance towards the goals (maximize rewards while minimizing costs).
I then map these 3 levels of analytics to the Big Data Business Model Maturity Index to provide a framework to help organizations become more effective at leveraging Big Data, IOT and advanced analytics to power their business models (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Mapping Advanced Analytics to Big Data Business Model Maturity Index
AI Drives Business Model Disruption
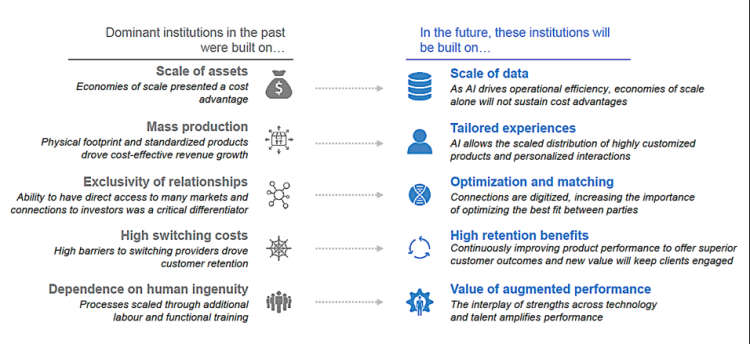
The Deloitte report also does a nice job of outlining how the AI capabilities can empower or threaten business models (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: Areas where AI is Altering Successful Business Models
To summarize Figure 3, in the future, successful institutions will be built on:
- Scale of data where organizations have mastered Big Data and IoT to derive and drive new sources of customer, product, service and operational value.
- Tailored, differentiated customer experiences based upon an intimate knowledge of an individual customer’s propensities, tendencies, inclinations, behaviors, interests, relationships and associations.
- Optimized and matching of products and services to the unique needs and life stage of each customer; the ultimate realization of 1-to-1 marketing.
- Continuously-learning interactions with customers which will enable organizations to continuously morph the individual’s personal experience to drive retention, loyalty and ultimately advocacy.
- Employee and operational “augmented performance” where customer, product, service and operational insights enable better customer and operational decisions.
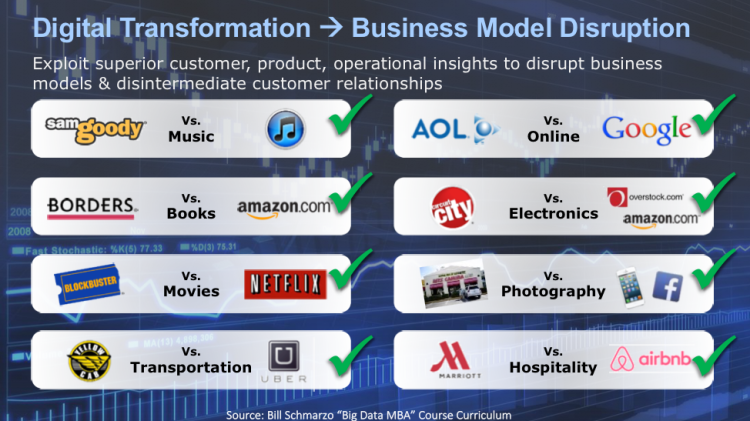
AI will drive business model disruption and will disintermediate customer relationships. Leading digital organizations will leverage AI to operationalize superior customer, product, operational insights to disrupt business models and disintermediate customer relationships (see Figure 4).
Figure 4: Superior Customer, Product, Operational Insights Driving Business Model Disruption
Across multiple industries, leading organizations are coupling new Big Data technologies and new sources of data with advanced analytics (data science) to uncover new customer, product, operational and market insights in order to disintermediate existing customer relationships and disrupt existing business models. Here are some organizations that are leveraging superior customer, product and operational insights to challenge long-held business models:
- Uber: The world’s largest taxi company owns 0 taxis
- Airbnb: The largest accommodation provider does not own real estate
- TripAdvisor: The world’s largest travel company owns 0 inventory
- Skype, Whatsapp, WeChat: The largest phone companies do not own any telco infrastructure
- Amazon: The world’s most valuable retailer has no inventory
- Apple & Google: The largest software vendors don’t write the apps
- Facebook: The most popular media owner does not create content
- Netflix: The world’s largest movie house does not own any cinemas
AI Drives Digital Transformation
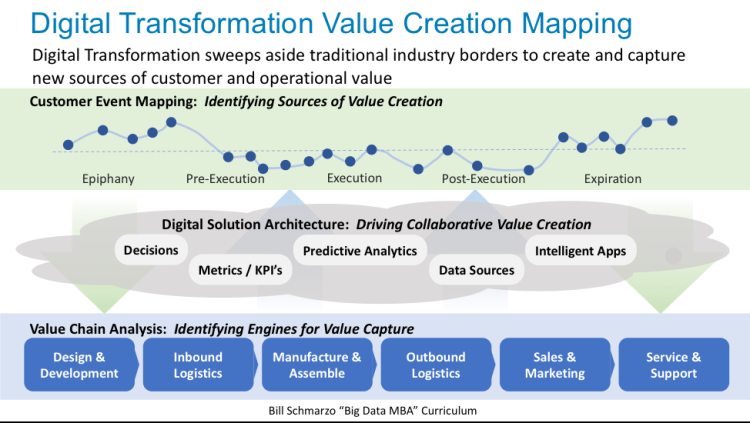
Leading organizations are not getting caught up on the AI definition debate, and instead they are focusing AI, coupled with Big Data and IOT, to (see Figure 5):
- Identifying Sources of Value Creation. Identifying the sources of value creation is a customer-centric perspective (think “outside-in”) that focuses on identifying, validating, valuing and prioritizing the sources of customer (and market) value creation.
- Identifying Engines of Value Capture. Identifying the engines of value capture is a production-centric perspective (think “inside-out”) that focuses on identifying and prioritizing the organizational capabilities or functions necessary to capture the sources of value creation.
Figure 5: Digital Transformation Value Creation Mapping
In the end, it really doesn’t matter “What the Hell is AI?” as long as we understand enough about what it can do – its capabilities – to exploit AI to derive and drive new sources of customer and market value.
“A rose by any other name would still be a rose”
=====
To learn more about the Digital Transformation journey, check out these videos and blogs;
Digital Transformation Introduction video:
https://www.youtube.com/edit?o=U&video_id=7IQw4N5zric
It’s Not Digital Transformation; It’s Digital “Business” Transformation! – Part I
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/its-digital-transformation-business-part-i-bill-schmarzo/
It’s Not Digital Transformation; It’s Digital “Business” Transformation – Part II
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/its-digital-transformation-business-part-ii-bill-schmarzo/
It’s Not Digital Transformation; It’s Digital “Business” Transformation – Part III
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/its-digital-transformation-business-part-iii-bill-schmarzo/
Digital Transformation Law #6: It’s About Monetizing the Pain
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/digital-transformation-law-6-its-monetizing-pain-bill-schmarzo/
The Customer Journey Digital Transformation Workbook
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/customer-journey-digital-transformation-workbook-bill-schmarzo/