Month: November 2023

MMS • RSS
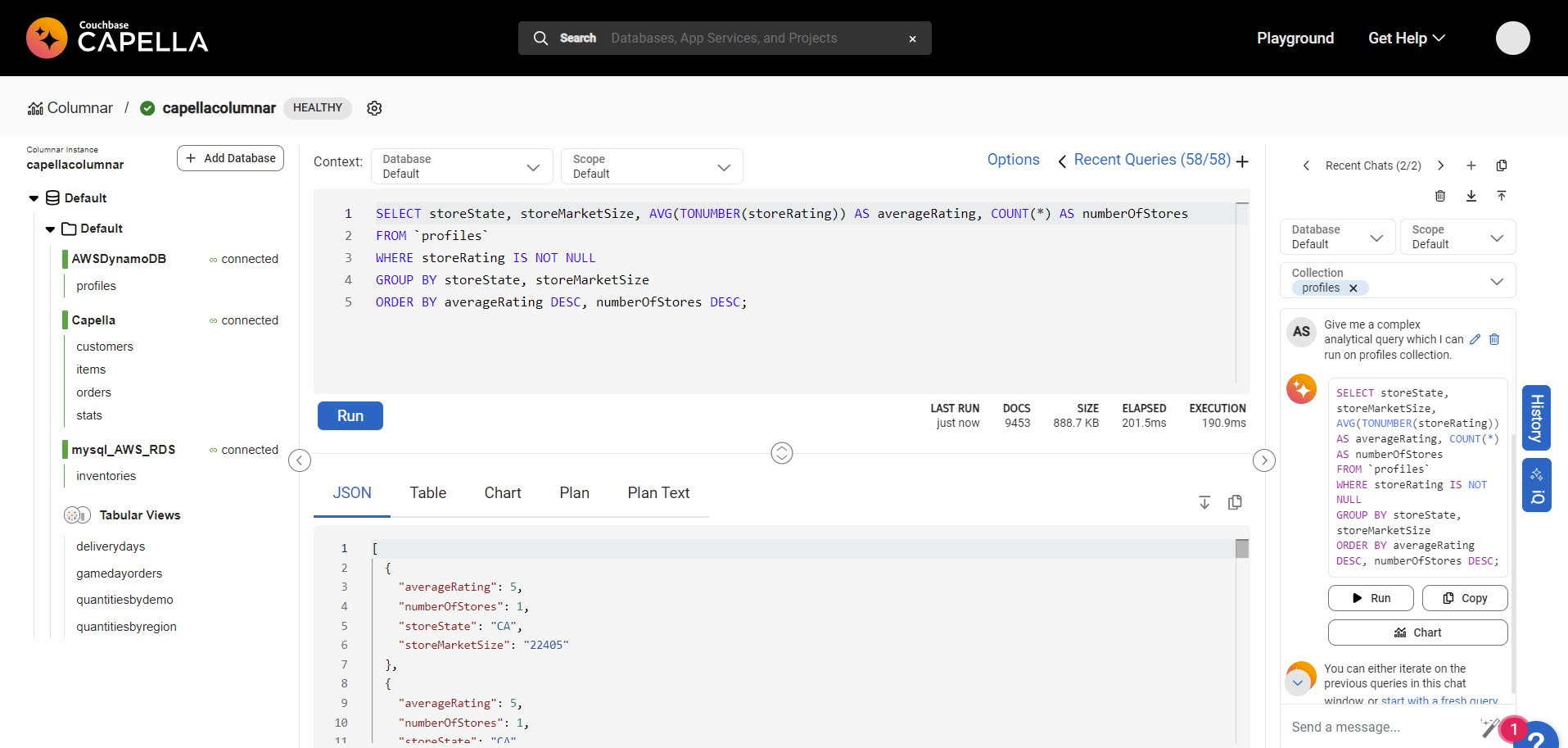
At the AWS re:Invent 2023 conference today, Couchbase, Inc. announced it added a columnar database based on the JSON file format to its database-as-a-service (DBaaS) portfolio to enable organizations to build real-time analytics applications.
Scott Anderson, senior vice president for product management and business operations at Couchbase, said the Capella columnar database is designed to be integrated with the company’s JSON-based document database via a database change protocol (DCP) that Couchbase has embedded within its DBaaS environment.
Deployed on cloud services from Amazon Web Services (AWS), the overall goal is to reduce the level of friction that IT teams would otherwise encounter when integrating a document database with a columnar database optimized to process analytics using columns rather than the rows typically associated with a relational database.
That approach gives IT teams the ability to use a schemaless database architecture that provides an alternative to employing disparate databases that would need to be deployed and then integrated using extract, transform and load (ETL) processes to move data from one database to the other, noted Anderson.
Capella columnar also uses the same SQL++ language as the company’s document database to streamline queries in addition to supporting Capella iQ, a copilot based on generative artificial intelligence (AI) that enables queries to be crafted in natural language.
In addition, Capella columnar provides connectors to move data from Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon DocumentDB, Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) and other data sources deployed on the AWS cloud.
In the longer term, Couchbase is also planning to add vector capabilities to its DBaaS environment to make it simpler to securely extend generative AI models, said Anderson.
In general, document databases have been widely adopted because they provide developers with an alternative to legacy database platforms that they can download and deploy themselves. The Capella DBaaS platform further simplifies that process via a managed service through which Couchbase assumes operational responsibility for managing databases. The columnar database extends that capability using a columnar database that can drive analytics capabilities to deliver a more personalized application experience, noted Anderson.
It’s not clear to what degree organizations will ultimately wind up relying on as-a-service platforms, but since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the shift to this approach to consuming IT resources has increased significantly. As a result, the way internal IT teams are organized is shifting as lower-level tasks are either automated or handled by an external IT team that works for a vendor.
Regardless of how databases are managed, however, there remains a need to integrate the data operations (DataOps) processes used to manage them with the DevOps workflows used to build modern applications. Each organization will need to determine how much economic sense it makes for them to manage that data versus relying on an external services provider. The challenge when relying on an external service provider is, as always, integrating that service into an existing IT environment.
Couchbase announces columnar service for Capella on AWS to power adaptive, real-time …

MMS • RSS

Cloud database-as-a-service provider Couchbase Inc. today launched a new columnar service for its Capella platform on Amazon Web Services Inc.’s public cloud platform.
The company says the new service, announced at AWS re:Invent 2023, makes it easier for companies to leverage real-time analytics to build more adaptive software applications.
Capella’s columnar service brings a columnar store and data integration into the Capella DaaS platform, enabling the real-time analysis of data on the same cloud platform where enterprises run many of their operational workloads, the company said. This convergence of operational and real-time analytics capabilities within one data platform will help to reduce friction and ensure superior application user experiences, it added.
Couchbase Capella is a cloud-hosted version of the Couchbase NoSQL database that is used to power complex business applications. Unlike traditional databases, such as Oracle Database, Capella can process both structured and unstructured data at the same time, making it a more flexible choice for certain kinds of apps.
The ability to handle multiple kinds of data means Capella can serve as a data cache, too. So companies can use just one system in Capella, rather than using three separate systems — a database for structured data, a data store for unstructured information, and a data cache.
With the addition of the columnar service, Couchbase said, it’s eliminating the need for organizations to process, reformat and move data, first from transactional to operational systems, and from there, to analytical systems. The company cites a report from Forrester Research about the need for this capability. It said the need for data movement is a serious hindrance to the development of applications that can make decisions in real time. “Disparate data stacks also compromise the delivery of timely data to various applications, operational systems and into the analytics workflow, resulting in missed business opportunities,” Forrester’s report said.
Moreover, with the growing adoption of artificial intelligence systems and applications, the use of disparate data platforms adds further complexity and often confuses AI models, the company said. Capella columnar solves these headaches by performing operational and real-time analytics on data within a single platform, reducing latency to deliver enhanced experiences for end users.
The company cited a number of benefits to customers, including improved agility and performance for applications, and stream ingestion from enterprise data sources in real-time. The integrated data platform also makes life much easier for developers, Couchbase promised, as it uses the same SQL++ query language across operational and analytical applications.
It means developers with knowledge of the Structured Query Language can build simplified apps using a single query language, rather than two different ones. Not least, the company said the convergence of operational and real-time analytics in a single platform will significantly reduce the cost and complexity of applications.
Scott Anderson, Couchbase’s senior vice president of product management and management and business operations, said real-time analytics is key to the delivery of more intelligent, adaptive and hyper-personalized applications. “With columnar in our Capella DBaaS, for the first time organizations can easily build adaptive applications powered by real-time analytics in a single JSON-based platform,” he said. “We are eliminating the latency gap that has forever existed between analytics and operational databases.”
The Capella columnar service is said to leverage a number of AWS services that form the basis of its product architecture, and will provide connectors to data sources such as Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Document DB, Amazon Relational Database Service and Amazon SageMaker for AI development.
Image: Couchbase
Your vote of support is important to us and it helps us keep the content FREE.
One click below supports our mission to provide free, deep, and relevant content.
Join our community on YouTube
Join the community that includes more than 15,000 #CubeAlumni experts, including Amazon.com CEO Andy Jassy, Dell Technologies founder and CEO Michael Dell, Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger, and many more luminaries and experts.
THANK YOU

MMS • RSS

© Reuters. (MDB) – Analyzing MongoDB’s Short Interest
Benzinga – by Benzinga Insights, Benzinga Staff Writer.
MongoDB’s (NYSE:MDB) short percent of float has risen 16.28% since its last report. The company recently reported that it has 3.67 million shares sold short, which is 6.0% of all regular shares that are available for trading. Based on its trading volume, it would take traders 3.72 days to cover their short positions on average.
Why Short Interest Matters
Short interest is the number of shares that have been sold short but have not yet been covered or closed out. Short selling is when a trader sells shares of a company they do not own, with the hope that the price will fall. Traders make money from short selling if the price of the stock falls and they lose if it rises.
Short interest is important to track because it can act as an indicator of market sentiment towards a particular stock. An increase in short interest can signal that investors have become more bearish, while a decrease in short interest can signal they have become more bullish.
MongoDB Short Interest Graph (3 Months)
As you can see from the chart above the percentage of shares that are sold short for MongoDB has grown since its last report. This does not mean that the stock is going to fall in the near-term but traders should be aware that more shares are being shorted.
Comparing MongoDB’s Short Interest Against Its Peers
Peer comparison is a popular technique amongst analysts and investors for gauging how well a company is performing. A company’s peer is another company that has similar characteristics to it, such as industry, size, age, and financial structure. You can find a company’s peer group by reading its 10-K, proxy filing, or by doing your own similarity analysis.
According to Benzinga Pro, MongoDB’s peer group average for short interest as a percentage of float is 5.46%, which means the company has more short interest than most of its peers.
Did you know that increasing short interest can actually be bullish for a stock? This post by Benzinga Money explains how you can profit from it.
This article was generated by Benzinga’s automated content engine and was reviewed by an editor.
© 2023 Benzinga.com. Benzinga does not provide investment advice. All rights reserved.

MMS • RSS

Sundry Photography
MongoDB (NASDAQ:MDB) is slated to report fiscal third-quarter results on December 5 and while revenue growth is expected to slow, all eyes will be on the database company’s Atlas service, investment firm Monness, Crespi, Hardt said on Monday.
Analyst Brian White, who has a neutral rating on MongoDB (MDB) shares, said he is expecting 33% revenue growth to come in at $443M, down from 47% in the year-ago quarter. However, White said Wall Street estimates are “absurdly low” at $403.7M and the company is likely to “steamroll over analyst projections.”
“In fact, the Street’s [third-quarter] revenue estimate reflects the weakest sequential revenue performance we have on record for MongoDB and the first QoQ sales decline ever,” White wrote in a note to clients. “Moreover, we believe MongoDB will catapult over the Street’s profit forecast. Despite a clear pattern of ultra-conservative guidance for many quarters now, the Street continues to parrot management’s guidance.”
Delving deeper, White believes that Atlas is likely to keep growing in importance for MongoDB (MDB), as it accounted for 63% of revenue in the second-quarter, has more than 43,500 customers and saw 38% revenue growth last quarter.
White also noted that there has been “less disruption” in the cloud computing market in recent memory, as the slowdown for the three largest public cloud vendors – Amazon (AMZN) Microsoft (MSFT) and Google (GOOG) (GOOGL) slowed to 21% in the third-quarter, down from 22% in the second-quarter. Datadog (DDOG) also had strong third-quarter results and issued solid guidance, which may bode well for MongoDB (MDB), White explained.
Looking to the fourth-quarter, White is expecting MongoDB (MDB) to guide to $504.2M in revenue, up 40% year-over-year, well above the $413.9M that Wall Street is expecting. He expects $1.21 per share in earnings, well above the 37 cent consensus estimate.
For fiscal 2025, he is estimating sales of $2.55B and earnings of $7.38 per share.
More on MongoDB
Mirae Asset Global Investments Co. Ltd. Acquires Shares of 16312 MongoDB, Inc. (NASDAQ:MDB)

MMS • RSS
 Mirae Asset Global Investments Co. Ltd. acquired a new stake in MongoDB, Inc. (NASDAQ:MDB – Free Report) in the second quarter, according to the company in its most recent Form 13F filing with the SEC. The fund acquired 16,312 shares of the company’s stock, valued at approximately $6,704,000.
Mirae Asset Global Investments Co. Ltd. acquired a new stake in MongoDB, Inc. (NASDAQ:MDB – Free Report) in the second quarter, according to the company in its most recent Form 13F filing with the SEC. The fund acquired 16,312 shares of the company’s stock, valued at approximately $6,704,000.
A number of other institutional investors and hedge funds also recently made changes to their positions in MDB. Jennison Associates LLC lifted its stake in MongoDB by 101,056.3% in the 2nd quarter. Jennison Associates LLC now owns 1,988,733 shares of the company’s stock valued at $817,350,000 after purchasing an additional 1,986,767 shares during the last quarter. 1832 Asset Management L.P. increased its position in shares of MongoDB by 3,283,771.0% during the fourth quarter. 1832 Asset Management L.P. now owns 1,018,000 shares of the company’s stock worth $200,383,000 after buying an additional 1,017,969 shares during the period. Price T Rowe Associates Inc. MD increased its position in shares of MongoDB by 13.4% during the first quarter. Price T Rowe Associates Inc. MD now owns 7,593,996 shares of the company’s stock worth $1,770,313,000 after buying an additional 897,911 shares during the period. Norges Bank acquired a new stake in MongoDB in the fourth quarter worth $147,735,000. Finally, Champlain Investment Partners LLC acquired a new stake in MongoDB in the first quarter worth $89,157,000. Institutional investors own 88.89% of the company’s stock.
Insider Activity at MongoDB
In other MongoDB news, CAO Thomas Bull sold 518 shares of MongoDB stock in a transaction that occurred on Monday, October 2nd. The shares were sold at an average price of $342.41, for a total transaction of $177,368.38. Following the completion of the sale, the chief accounting officer now directly owns 16,672 shares in the company, valued at $5,708,659.52. The sale was disclosed in a document filed with the SEC, which is available at the SEC website. In other MongoDB news, CAO Thomas Bull sold 518 shares of MongoDB stock in a transaction that occurred on Monday, October 2nd. The shares were sold at an average price of $342.41, for a total transaction of $177,368.38. Following the completion of the sale, the chief accounting officer now directly owns 16,672 shares in the company, valued at $5,708,659.52. The sale was disclosed in a document filed with the SEC, which is available at the SEC website. Also, CRO Cedric Pech sold 308 shares of the business’s stock in a transaction that occurred on Wednesday, September 27th. The stock was sold at an average price of $326.27, for a total transaction of $100,491.16. Following the completion of the sale, the executive now owns 34,110 shares of the company’s stock, valued at $11,129,069.70. The disclosure for this sale can be found here. Over the last 90 days, insiders sold 321,077 shares of company stock valued at $114,507,479. Corporate insiders own 4.80% of the company’s stock.
MongoDB Trading Up 0.6 %
MDB opened at $407.70 on Monday. The company has a current ratio of 4.48, a quick ratio of 4.48 and a debt-to-equity ratio of 1.29. The firm has a 50-day moving average price of $357.65 and a 200-day moving average price of $364.46. MongoDB, Inc. has a twelve month low of $137.70 and a twelve month high of $439.00.
MongoDB (NASDAQ:MDB – Get Free Report) last issued its quarterly earnings data on Thursday, August 31st. The company reported ($0.63) EPS for the quarter, beating the consensus estimate of ($0.70) by $0.07. The company had revenue of $423.79 million during the quarter, compared to analysts’ expectations of $389.93 million. MongoDB had a negative net margin of 16.21% and a negative return on equity of 29.69%. As a group, analysts predict that MongoDB, Inc. will post -2.17 EPS for the current year.
Analyst Ratings Changes
MDB has been the topic of a number of recent research reports. Macquarie raised their price objective on shares of MongoDB from $434.00 to $456.00 in a research note on Friday, September 1st. UBS Group raised their price objective on shares of MongoDB from $425.00 to $465.00 and gave the company a “buy” rating in a research note on Friday, September 1st. Tigress Financial raised their price objective on shares of MongoDB from $490.00 to $495.00 and gave the company a “buy” rating in a research note on Friday, October 6th. Stifel Nicolaus raised their price objective on shares of MongoDB from $420.00 to $450.00 and gave the company a “buy” rating in a research note on Friday, September 1st. Finally, Royal Bank of Canada reissued an “outperform” rating and set a $445.00 price target on shares of MongoDB in a research report on Friday, September 1st. One research analyst has rated the stock with a sell rating, two have assigned a hold rating and twenty-four have assigned a buy rating to the company’s stock. Based on data from MarketBeat, the stock has an average rating of “Moderate Buy” and an average target price of $419.74.
Check Out Our Latest Analysis on MDB
MongoDB Company Profile
MongoDB, Inc provides general purpose database platform worldwide. The company offers MongoDB Atlas, a hosted multi-cloud database-as-a-service solution; MongoDB Enterprise Advanced, a commercial database server for enterprise customers to run in the cloud, on-premise, or in a hybrid environment; and Community Server, a free-to-download version of its database, which includes the functionality that developers need to get started with MongoDB.
Read More
Want to see what other hedge funds are holding MDB? Visit HoldingsChannel.com to get the latest 13F filings and insider trades for MongoDB, Inc. (NASDAQ:MDB – Free Report).
This instant news alert was generated by narrative science technology and financial data from MarketBeat in order to provide readers with the fastest and most accurate reporting. This story was reviewed by MarketBeat’s editorial team prior to publication. Please send any questions or comments about this story to contact@marketbeat.com.
Before you consider MongoDB, you’ll want to hear this.
MarketBeat keeps track of Wall Street’s top-rated and best performing research analysts and the stocks they recommend to their clients on a daily basis. MarketBeat has identified the five stocks that top analysts are quietly whispering to their clients to buy now before the broader market catches on… and MongoDB wasn’t on the list.
While MongoDB currently has a “Moderate Buy” rating among analysts, top-rated analysts believe these five stocks are better buys.

Wondering when you’ll finally be able to invest in SpaceX, StarLink or The Boring Company? Click the link below to learn when Elon Musk will let these companies finally IPO.

MMS • Sergio De Simone

Besides extending the language through macros and borrow-stile memory management, Swift 5.9 also introduces some helpful features for program debugging, including an out-of-process crash handler, just-in-time debugging support, and backtracking to makes it easier to interpret control flow when using structured concurrency.
Out-of-process crash handling is a powerful new feature that will prevent a program from crashing normally and gives you the possibility to inspect it or attach a debugger to it.
When this new feature is enabled and your program crashes, you will be presented with a prompt allowing you to change the backtracer settings, generate a new backtrace, list loaded images, display register and memory contents, and get a listing of all of the threads in the process. Alternatively, you can attach a debugger to the crashed process and inspect its state interactively. If you do not choose any option, the program will crash after 30 seconds or a configurable amount of time.
The out-of-process crash handler is specifically relevant for Linux developers, who were used to getting just a succinct error message on the console for a program crash without any additional facilities. For this reason, the crash handler is on by default on Linux, while it must be manually enabled on macOS. On Windows, the new feature is not supported yet, but developers can access the OS built-in crash report to get additional information about what caused the crash.
Another welcome improvement is that the backtracer is now concurrency-aware, meaning it will be able to step back through asynchronous frames, such as when an async function is executed through an await statement. In such cases, the await/async call will appear like a normal call in the backtrace and will not show intermediate frames belonging to the runtime await/async mechanics. This new feature requires the backtracer to be able to look up program symbols to tell if a frame is asynchronous, though.
As a final note, the new backtracer is Swift 5.9 also improves readability by letting you configure the maximum number of frames that the backtracer will generate as well as the number of frames at the top of the stack you want to be displayed. Additionally, it will by default skip over system frames and Swift thunks, which are seldom of any interest to app developers.
Microsoft Brings AI to Logic Apps (Standard) with Workflow Assistant in Public Preview

MMS • Steef-Jan Wiggers
Microsoft recently announced a workflow assistant for Logic Apps (standard), the company’s integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) offering in public preview. With the assistant, developers have a chat interface that provides access to Azure Logic Apps documentation and best practices without requiring them to navigate documentation or search online forums.
The workflow assistant is another enhancement the Logic App product team made for Logic Apps next to the general availability of .NET custom code support, application insights support, and the data mapper. These enhancements are all for the standard version of Logic Apps, the tier that allows developers to run workflows anywhere.
The workflow assistant uses Azure Open AI and ChatGPT to query diverse knowledge sources related to Azure Logic Apps, delivering curated information to the workflow a developer builds. The results of the queries are processed into a vectorized format and are then accessible through a backend system built on top of Azure App Service.
Divya Swarnkar, a program manager on the Logic Apps team at Microsoft, writes:
When you provide an input prompt, the Azure Logic Apps backend performs pre-processing and forwards the prompt to an Azure Open AI large language model. This model generates responses based on the given context (in the form of workflow JSON) and your prompt.
The company recommends using the workflow assistant when choosing a connector or action, given the 1000+ available connectors, describing the workflow when collaborating with other developers or looking for the best way to build a workflow.
Swarnkar told InfoQ:
At the core of our mission is boosting developer productivity, and AI is our key ally in achieving this. Our latest release, Workflow Assistant, is designed to empower users to integrate AI into their workflows seamlessly. It offers innovation and a bridge to discover product help, best practices, standard patterns, and the creation of optimal applications.
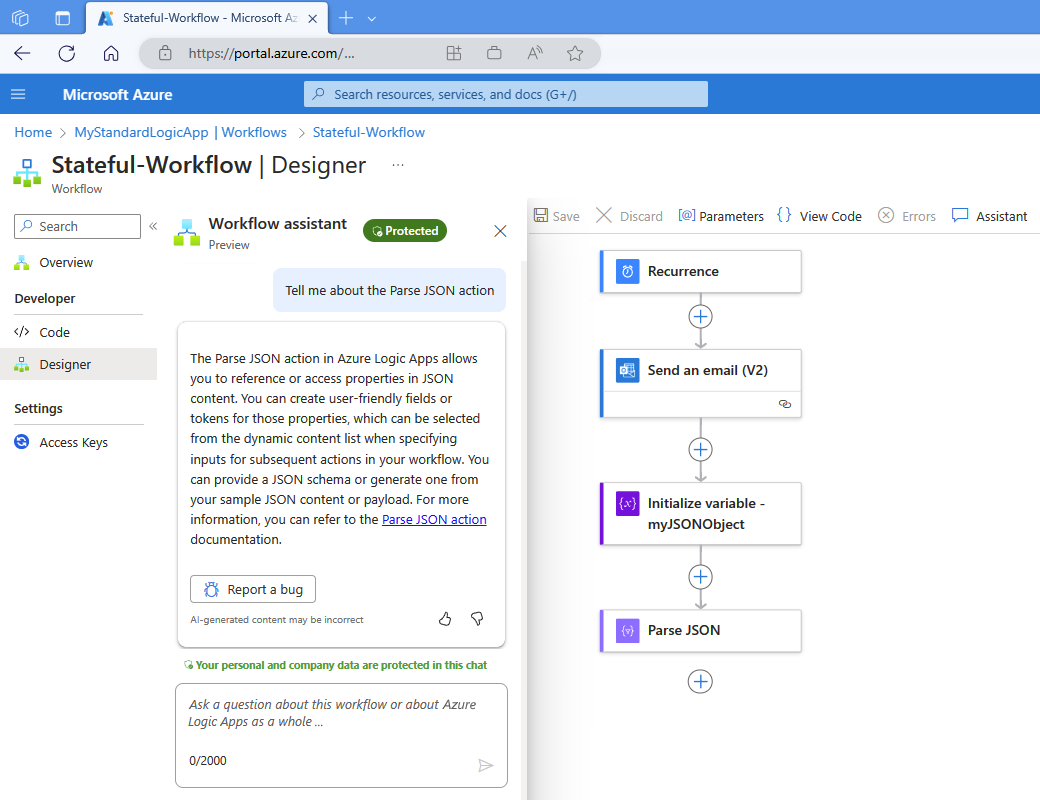
Workflow Assistant (Source: Microsoft Learn)
One of Microsoft’s competitors in the iPaaS space is Google, which recently launched the Application Integration Service, which was later integrated with Duet AI. The Duet AI in Application Integration can create integration flows from requirements described in the natural language provided in the service through an interface. In addition, Duet AI can create a default data mapping within the integration flow that connects the two applications based on the variables created in the integration flow and the integrated applications.
When asked by InfoQ what Microsoft sees going forward with workflow assistant, Swarnkar said:
The vast possibilities AI opens are fueled by customer feedback and real-world problem-solving. In the pipeline is the introduction of workflow documentation through our workflow assistant. AI’s potential to add value across all stages of application development—from creation and deployment to testing and monitoring—is immense, and customer feedback will guide our investments.
Lastly, more details on the workflow assistant in Logic Apps (standard) are available on the documentation pages.

MMS • Agazi Mekonnen

Transformers.js, the JavaScript counterpart to the Python Transformers library, is designed for running Transformers models directly within web browsers, eliminating the necessity for external server processing. In the recent update to version 2.7, Transformers.js introduced enhancements, including notable text-to-speech (TTS) support. This upgrade, responding to user demand, increased the library’s versatility for additional use cases.
Text-to-speech (TTS) involves creating natural-sounding speech from text, supporting multiple spoken languages and speakers. Currently, Transformers.js only supports TTS with Xenova/speecht5_tts, which is based on Microsoft’s SpeechT5 with ONNX weights. There are plans for future updates, including adding support for bark and MMS.
Developers can use the text-to-speech functionality by employing the pipeline function from @xenova/transformers. This involves specifying the ‘text-to-speech’ task and the model (‘Xenova/speecht5_tts’) to be used, with the option { quantized: false }. Additionally, a link to a file containing speaker embeddings is provided.
Once the TTS model is applied to a given text, the output includes an audio array and the sampling rate. This array represents the synthesized speech, which can be further processed or played directly in the browser.
Transformers.js caters to various use cases, including style transfer, image inpainting, image colorization, and super-resolution. Its versatility and regular updates position it as a valuable asset for developers exploring the intersection of machine learning and web development, making it a reliable tool in the realm of web-based machine learning.
Transformers.js is designed to be functionally equivalent to Hugging Face’s transformers python library, meaning you can run the same pre-trained models using a very similar API.
Supporting a vast array of tasks and models, Transformers.js spans natural language processing, vision, audio, tabular data, multimodal applications, and reinforcement learning. The library covers tasks from text classification and summarization to image segmentation and object detection, making it a versatile tool for various machine learning applications.
The extensive list of supported models includes architectures such as BERT, GPT-2, T5, and Vision Transformer (ViT), among many others, ensuring users can choose the right model for their specific task.
The community has been positive about the release of Transformers.js. In a Reddit thread initiated earlier this year, user Intrepid-Air6525 stated:
I decided to use it to replace openai’s embeddings model. Works pretty fast. I am using webLLM for the actual LLM since I don’t want to use up too much CPU processing.
User 1EvilSexyGenius commented about Hugging Face’s positioning in the market and the related focus on the discussion of practical implementations:
[…]Between transformers.js and their optimum libraries I think it’s clear that [Hugging Face] are truly trying to democratize language models and bring them to the people.
This community could benefit from posts like these vs all of the daily model releases.
Interested readers can learn more from the Hugging Face Transformers.js website and associated GitHub repo.
Java News Roundup: Spring Boot 3.2, Spring Pulsar 1.0, Hibernate 6.4, JEP 447 Targeted to JDK 22

MMS • Michael Redlich

This week’s Java roundup for November 20th, 2023 features news from OpenJDK, JDK 22, JCON World 2023, and point, milestone and GA releases for: Spring Boot, Spring Framework, Spring Security, Spring Authorization Server, Spring GraphQL, Spring Integration, Spring Session, Spring Vault, Quarkus, Hibernate ORM, Hibernate Search, Infinispan, JHipster, JBang, OpenXava, Testcontainers and Gradle.
OpenJDK
After its review has concluded, JEP 447, Statements before super(…) (Preview), has been promoted from Proposed to Target to Targeted for JDK 22. This JEP, under the auspices of Project Amber, proposes to: allow statements that do not reference an instance being created to appear before the this() or super() calls in a constructor; and preserve existing safety and initialization guarantees for constructors. Gavin Bierman, consulting member of technical staff at Oracle, has provided an initial specification of this JEP for the Java community to review and provide feedback.
JEP 461, Stream Gatherers (Preview), has been promoted from Candidate to Proposed to Target for JDK 22. This JEP proposes to enhance the Stream API to support custom intermediate operations. “This will allow stream pipelines to transform data in ways that are not easily achievable with the existing built-in intermediate operations.” More details on this JEP may be found in the original design document written by Viktor Klang, Software Architect, Java Platform Group at Oracle. The review is expected to conclude on November 29, 2023.
JEP 462, Structured Concurrency (Second Preview), has been promoted from Candidate to Proposed to Target for JDK 22. This JEP will propose to re-preview the API in JDK 22, without change, in order to gain more feedback from the previous round of preview: JEP 453, Structured Concurrency (Preview), delivered in JDK 21. This feature simplifies concurrent programming by introducing structured concurrency to “treat groups of related tasks running in different threads as a single unit of work, thereby streamlining error handling and cancellation, improving reliability, and enhancing observability.” The review is expected to conclude on December 1, 2023.
JEP 458, Launch Multi-File Source-Code Programs, has been promoted from Candidate to Proposed to Target for JDK 22. This JEP proposes to enhance the Java Launcher to execute an application supplied as one or more files of Java source code. This allows a more gradual transition from small applications to larger ones by postponing a full-blown project setup. The review is expected to conclude on December 1, 2023.
JDK 22
Build 25 of the JDK 22 early-access builds was made available this past week featuring updates from Build 24 that include fixes to various issues. Further details on this build may be found in the release notes.
For JDK 22, developers are encouraged to report bugs via the Java Bug Database.
Spring Framework
The release of Spring Boot 3.2.0 delivers bug fixes, improvements in documentation, dependency upgrades and new features such as: support for Oracle Free, the replacement for Oracle XE, that comes with Testcontainers and Docker Compose; a change in parameter name discovery that replaces deducing parameter names by parsing bytecode; support for Jetty 12; and support for the new RestClient interface that was introduced in Spring Framework 6.1. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Similarly, versions 3.1.6, 3.0.13 and 2.7.18 of Spring Boot provides bug fixes, improvements in documentation, dependency upgrades and a new feature in which the default Cloud Native Buildpacks (CNBs) have been upgraded to Paketo Jammy due to the Paketo Bionic Builder having been declared as unsafe. More details on these releases may be found in the version 3.1.6, version 3.0.13 and version 2.7.18.
The release of Spring Framework 6.1.1 ships with bug fixes, improvements in documentation and new features such as: skip unnecessary buffer allocation in the copy(String) method defined in the StreamUtils class; and a fix for concurrency leaks large amounts of non-heap memory in JDK 17 from the isReadable() method defined in the Resource interface. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
The release of Spring Security 6.2.0 delivers bug fixes, dependency upgrades and new features: support for Kotlin coroutines in the AuthorizationManagerBeforeReactiveMethodInterceptor and AuthorizationManagerAfterReactiveMethodInterceptor classes; and a simplification on configuring the OAuth2 Client component model. More details on this release may be found in the release notes and What’s New page.
The release of Spring Authorization Server 1.2.0 provides improvements in documentation, dependency upgrades and new features such as: allow a configurable refresh token strategy for AUTHORIZATION_CODE and REFRESH_TOKEN grant types defined in the Spring Security AuthorizationGrantType class; and introduce Ahead-of-Time (AOT) optimizations, or AOT hints, for types and resources used across the codebase to resolve failure in generating native images with GraalVM. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
The release of Spring for GraphQL 1.2.4 ships with bug fixes, improvements in documentation, dependency upgrades and new features such as: improved parsing of the line and column attributes from the GraphQL SourceLocation class within the ResponseMapGraphQlResponse class; and use of the isOmitted() method rather than the isPresent() method from the ArgumentValue class within ArgumentValueValueExtractor class to allow validation of null arguments. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
The release of Spring Integration 6.2.0 delivers notable changes such as: a fix for a race condition within the HazelcastMetadataStoreTests class; a more robust readRaw() and finalizeRaw() methods defined in the FtpSession class to eliminate exceptions thrown due to 550 FTP Response errors; and an increase in the timeout for the FTP RotatingServersTests class due to unknown delays on MacOS that cause the tests to fail. More details on this release may be found in the release notes and What’s New page.
The release of Spring Session 3.2.0 provides many dependency upgrades and a new feature in which improvements in documentation and logging have been made if a rememberMeRequestAttribute attribute has not been set within a custom implementation of the CookieSerializer interface. More details on this release may be found in the release notes and What’s New page.
The release of Spring Vault 3.1 ships with improvements in documentation, dependency upgrades and new features such as: support for HashiCorp Vault role_name and entity_alias parameters in the VaultTokenRequest class; and a new AuthenticationEventMulticaster interface to manage a number of AuthenticationEvent and AuthenticationErrorEvent objects and publish events to them. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
The release of Spring for Apache Pulsar 1.0.0 delivers notable changes such as: the PulsarAdministration class now accepts multiple instances of the PulsarAdminBuilderCustomizer interface; and a dependency break with Spring Boot to avoid a “chicken-and-egg” problem for times when Spring Boot has a dependency on Spring for Apache Pulsar. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Version 3.1.0 of Spring for Apache Kafka and Spring for RabbitMQ have been released to provide bug fixes, improvements in documentation and dependency upgrades. New features in Spring for Apache Kafka include: removal of setting the brokerListProperty property within the EmbeddedKafkaKraftBroker class that could lead to an exception if the property is null; and provide a way to define a ContainerCustomizer bean name to associate with the @KafkaListener annotation. More details on this release may be found in the release notes for Apache Kafka and for RabbitMQ.
Versions 1.1.0 and 1.0.3 of Spring Modulith have been released that ship with bug fixes, dependency upgrades and new features such as: use the Spring Framework BeanFactoryInitializationAotProcessor interface to initialize actuator endpoints on native images rather than the ApplicationModules class; and a warning to alert developers that the updateFirst() method defined in the Spring Data MongoTemplate class does not support sort operations. Developers should instead use the findAndModify() method. More details on this release may be found in the release notes for version 1.1.0 and version 1.0.3.
Eclipse Store
The Eclipse Foundation has released version 1.0.0 of EclipseStore, a Java native-persistence library. Formerly known as MicroStream, this new version is the initial release under the Eclipse Foundation and a migration from MicroStream Storage 8.1.1. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Quarkus
Red Hat has released version 3.5.3 of Quarkus 3.5.3 featuring notable changes such as: a switch from HashMap to LinkedHashMap in the MultipartFormDataOutput class to maintain the users’ input order; and ensure that authentication and authorization occur before the WebSocket injector for GraphQL is injected. More details on this release may be found in the changelog.
Similarly, Quarkus 3.2.9.Final has also been released with notable changes such as: a resolution to the @ServerResponseFilter annotation with a Throwable parameter not being called when a REST resource is throwing an exception; and handle duplicate contexts that get mixed when caching the response of a REST call via the CacheResultInterceptor class. More details on this release may be found in the changelog.
Hibernate
The release of Hibernate ORM 6.4.0.Final delivers: a new @SoftDelete annotation to support soft deletes, values as deleted/non-deleted versus active/inactive (reversed); implementation of the remaining functions for handling arrays in HQL and Criteria queries; and support for writing Hibernate-specific events in the JDK Flight Recorder.
The second release candidate of Hibernate Search 7.0.0 features: bug fixes; compatibility with Jakarta EE, the Hibernate ORM discriminator-based multi-tenancy, Elasticsearch 8.11 and OpenSearch 2.10 and 2.11; and dependency upgrades to Hibernate ORM 6.4.0.Final and Apache Lucene 9.8. Hibernate Search 7.0.0.CR2 requires a minimal version of JDK 11.
Infinispan
Version 15.0.0.Dev05 of Infinispan has been released with notable changes such as: the use of the Spring Framework @DirtiesContext annotation on Spring tests to force the cache manager to stop; an improved WriteSkewConsistencyTest class to resolve random failures; and update the Jakarta JSON Processing dependency from the javax.* namespace to the jakarta.* namespace as required by WildFly Elytron 2.x. More details on this release may be found in the list of issues.
Similarly, version 14.0.21.Final of Infinispan has also been released with notable changes such as: default methods in the Java ConcurrentMap interface should ensure that their iterators are closed upon encountering an error; improvements in implementing virtual threads; and the creation of metrics to measure latency between nodes. More details on this release may be found in the list of issues.
JHipster
Version 0.49.0 of JHipster Lite has been released featuring bug fixes, dependency upgrades and enhancements: GraalVM automated builds; and a package-info.java file in their Dummy feature. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
JBang
Versions 0.113.0 and 0.112.4 of JBang deliver notable changes such as: a new magic %{deps:..} expansion on the command line that will resolve dependencies within that expression and replace it with a classpath (see example below); a fix for when a custom port is provided via the --debug command line parameter, the default of 4004 is still used; and an updated docker-compose file for testing proxies that require authentication. More details on these releases may be found in the release notes for version 0.113.0 and version 0.112.4.
The new command line expansion allows developers to write something like:
$ jbang sqlline@maxandersen -cp %{deps:org.hsqldb:hsqldb:RELEASE} other args
OpenXava
The release of OpenXava 7.2.0 features bug fixes, dependency upgrades and new features such as: support for JDK 21; improvements to the calendar to show the week or the day; and numerous web security enhancements. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Testcontainers for Java
Testcontainers for Java 1.19.3 has been released with notable bug fixes such as: register missing default network aliases using the ContainerDef class; a regression due to a breaking change upon using the setImage() method defined in the GenericContainer class; and bugs within the SQLScriptScanner with large String literals and PostgreSQL identifiers.
Gradle
The fourth release candidate of Gradle 8.5.0 delivers continuous improvements on new features such as: full support for compiling, testing and running on JDK 21; improvements in the Kotlin DSL that include faster first use and version catalog support in precompiled Kotlin script plugins; and improved reporting of errors and warnings. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
JCON World
The JCON World 2023 conference, the international online Java community conference organized by the Java User Group Oberpfalz, was held this past week, featuring over 100 speakers from the Java community who presented keynote addresses, one-hour sessions and workshops over a three-day timeframe.

MMS • RSS
David Iben put it well when he said, ‘Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.’ It’s only natural to consider a company’s balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. As with many other companies MongoDB, Inc. (NASDAQ:MDB) makes use of debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can’t fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
View our latest analysis for MongoDB
What Is MongoDB’s Debt?
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that MongoDB had US$1.14b in debt in July 2023; about the same as the year before. But it also has US$1.90b in cash to offset that, meaning it has US$759.5m net cash.
A Look At MongoDB’s Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, MongoDB had liabilities of US$512.3m due within 12 months, and liabilities of US$1.25b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$1.90b as well as receivables valued at US$272.4m due within 12 months. So it actually has US$410.3m more liquid assets than total liabilities.
This state of affairs indicates that MongoDB’s balance sheet looks quite solid, as its total liabilities are just about equal to its liquid assets. So it’s very unlikely that the US$29.1b company is short on cash, but still worth keeping an eye on the balance sheet. Simply put, the fact that MongoDB has more cash than debt is arguably a good indication that it can manage its debt safely. There’s no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine MongoDB’s ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you’re focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Over 12 months, MongoDB reported revenue of US$1.5b, which is a gain of 37%, although it did not report any earnings before interest and tax. With any luck the company will be able to grow its way to profitability.
So How Risky Is MongoDB?
While MongoDB lost money on an earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) level, it actually generated positive free cash flow US$45m. So although it is loss-making, it doesn’t seem to have too much near-term balance sheet risk, keeping in mind the net cash. We think its revenue growth of 37% is a good sign. There’s no doubt fast top line growth can cure all manner of ills, for a stock. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet – far from it. To that end, you should be aware of the 3 warning signs we’ve spotted with MongoDB .
If, after all that, you’re more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
Valuation is complex, but we’re helping make it simple.
Find out whether MongoDB is potentially over or undervalued by checking out our comprehensive analysis, which includes fair value estimates, risks and warnings, dividends, insider transactions and financial health.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.