Month: June 2023
ASP.NET Core in .NET 8 Preview 5: Improved Debugging, Blazor Updates, SignalR Reconnects, and More

MMS • Almir Vuk
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

The latest release of .NET 8 Preview 5 brings significant additions to ASP.NET Core. Notable enhancements include an improved debugging experience for ASP.NET Core, changes regarding the servers and middleware, the introduction of new features and improvements in Blazor, enhanced API authoring capabilities, seamless reconnect functionality in SignalR, and improvements and changes in authentication and authorization.
Regarding productivity notable advancements have been made to enhance the debugging experience in ASP.NET Core. Specifically, developers will benefit from the introduction of debug customization attributes that facilitate the retrieval of crucial information related to types such as HttpContext, HttpRequest, HttpResponse, and ClaimsPrincipal within the Visual Studio debugger.
In the latest .NET 8 preview 5, developers can experience early support for “seamless reconnects” in SignalR. This new feature aims to minimize downtime for clients facing temporary network disruptions, such as network switches or tunnel passages. By temporarily buffering data on both the server and client sides and acknowledging messages, it ensures a smoother user experience. Currently, this support is limited to .NET clients using WebSockets, and configuration options are not yet available. Developers have the freedom to opt-in to this feature and tweak around options.UseAcks, at HubConnectionBuilder. Upcoming previews are expected to introduce server-side configuration, customizable buffering settings, timeout limits, and expanded support for other transports and clients.
Blazor has also received a significant number of updates in the latest release of .NET 8 Preview 5. Updates like the new Blazor Web App template available through the command line and within the Visual Studio, webcil is now the default packaging format when publishing a Blazor WebAssembly app is being done, and regarding the Blazor WebAssembly, there is no longer requirement for unsafe-eval to be enabled, while specifying a Content Security Policy (CSP).
Also, the Blazor Router component now integrates with endpoint routing to handle both server-side and client-side routing. This integration allows for consistent routing to components regardless of whether server-side or client-side rendering is employed. The new Blazor Web App template includes sample pages, such as Index.razor and ShowData.razor, which utilize endpoint routing and streaming rendering for displaying weather forecast data, with enhanced navigation support expected in future .NET 8 previews.
Blazor Server introduces the ability to enable interactivity for individual components. With the new [RenderModeServer] attribute, developers can activate interactivity for specific components by utilizing the AddServerComponents extension method. This enhancement offers greater flexibility and control when building interactive applications with Blazor Server rendering mode.
The comment section of the original release blog post has generated significant activity, with users engaging in numerous questions and discussions with the development team. Developers are encouraged to explore the comment section for further information and insights.
Generic attributes were introduced in C# 11 and now regarding updates for API authoring, there is support added for generic attributes, providing cleaner alternatives to attributes that previously relied on a System.Type parameter. Generic variants are now available for the following attributes: ProducesResponseType, Produces, MiddlewareFilter, ModelBinder, ModelMetadataType, ServiceFilter, and TypeFilter.
Authentication and authorization, have also seen some changes, ASP.NET Core React and Angular project templates have removed the dependency on Duende IdentityServer. Instead, these templates now utilize the default ASP.NET Core Identity UI and cookie authentication to handle authentication for individual user accounts. Also, a new Roslyn analyzer is introduced in this preview to facilitate the adoption of a more “terser” syntax using the AddAuthorizationBuilder API, where applicable.
Other notable changes include the servers & middleware area, the introduction of the IHttpSysRequestTimingFeature interface allows for the detailed info of timestamp data during request processing when utilizing the HTTP.sys server. Additionally, the ITlsHandshakeFeature interface now exposes the Server Name Indication (SNI) hostname information. The addition of IExceptionHandler interface, enables services to be resolved and invoked by the exception handler middleware in order to provide developers with a callback mechanism to handle known exceptions in a centralized location.
Furthermore, regarding Native AOT, the latest preview incorporates enhancements to minimal APIs generated at compile-time. These improvements include support for parameters adorned with the AsParameters attribute and the automatic inference of metadata for request and response types.
Lastly, developers are welcome to leave feedback and follow the progress of the ASP.NET Core in .NET 8 by visiting the official GitHub project repository.
Canonical Sunbeam Aims to Simplify Migrating from Small-Scale Legacy IT Solutions to OpenStack

MMS • Sergio De Simone
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

Canonical has announced a new open-source project to enable organizations to transition their small-scale proprietary IT solutions to OpenStack. Named Sunbeam, the project is free of charge and does not require an expensive professional services engagement, says Canonical.
Sunbeam’s goal is to enable the deployment of OpenStack in hybrid contexts where both Kubernetes and native nodes coexist. Thanks to its ability to run OpenStack inside containers, Sunbeam can be seen as a sort of OpenStack on Kubernetes on steroids. Sunbeam leverages Canonical Juju to orchestrate and manage nodes in multiclouds or hybrid clouds using charms operators.
Charms are the basic encapsulation unit for business logic, providing a wrapper around an application containing all the instructions for deploying, configuring, and scaling it. Sunbeam adopts native Kubernetes concepts such as StatefulSets and operators, thus making it possible to deploy and operate OpenStack in a way similar to other Kubernetes deployments.
Another basic tenet of Sunbeam are relation handlers that mediate between charms and interfaces to create an intermediate abstraction which allows the charm to interact in a consistent way with a diverse range of interfaces. Relation handlers provide, for example, a ready property which tells the charms whether all data has been received at the interface. On the opposite end, container handlers mediate between charms and pebble containers to enable configuring the container, restarting it, inspecting its running status, and so on.
While Sunbeam is actually able to support OpenStack operation and management at any scale, from single nodes and small deployments on the edge to large clouds including thousands of hypervisors, Canonical is specifically targeting it to the initial phase in adopting OpenStack, such as when transitioning a small-scale legacy IT solution, as Canonical product manager Tytus Kurek confirms:
Sunbeam emerged to remove numerous barriers around the initial adoption of OpenStack and is just the first step towards an autonomous private cloud.
As a direct consequence of this vision, Sunbeams strives to provide a simple interface aiming to be friendly for non-OpenStack savvy customers, who can bootstrap and OpenStack cloud in minutes, claims Canonical.
At the moment, Sunbeam ships with the latest OpenStack version, 2023.1 but it only includes core OpenStack services, although Canonical says it will evolve quickly.

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts

Amazon DynamoDB is a popular NoSQL database service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It provides low-latency and high-performance access to data without requiring the user to manage the underlying hardware and software infrastructure. This database service is highly scalable, and it can handle multiple terabytes of data with ease. In this article, we will explore the features, benefits, use cases, and performance advantages of Amazon DynamoDB.
Features of Amazon DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB has several key features that set it apart from other NoSQL databases:
- Scalability: DynamoDB automatically scales horizontally to handle more traffic and data without manual intervention. It can handle tables with hundreds of terabytes of data and billions of items.
- Availability: DynamoDB offers automatic failover and multi-region replication, making it a highly available database service. It can survive the failure of a data center or a server with minimal disruption to the system.
- Performance: DynamoDB is designed to provide low latency access to data, with predictable and consistent performance at any scale. It can handle millions of read and write requests per second without any degradation in performance.
- Security: DynamoDB provides several security features such as encryption at rest, encryption in transit, fine-grained access control using IAM and VPC, and auditing through CloudTrail.
- Flexibility: DynamoDB supports a wide range of data models, including document data, key-value pairs, and graph data. It also allows users to create secondary indexes and to define their own data access patterns.
Benefits of Amazon DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB offers several benefits to users who are looking for a highly scalable and available NoSQL database service:
- Seamless scalability: DynamoDB scales automatically to handle more traffic and data without the need for manual intervention. It can handle massive data sets and unpredictable traffic patterns without any downtime or degradation.
- High availability: DynamoDB offers automatic failover and multi-region replication, making it a highly available database service. It can survive the failure of a data center or a server with minimal disruption to the system.
- Low latency: DynamoDB is designed to provide fast and consistent access to data, with predictable performance at any scale. It can handle millions of read and write requests per second without any degradation in performance or throughput.
- Cost-effective: DynamoDB has a pay-per-use pricing model, which means that users only pay for the resources they consume. This makes it a cost-effective NoSQL database service compared to other options in the market.
- Developer-friendly: DynamoDB provides a simple and intuitive API that allows developers to access data using a variety of programming languages and tools. It also provides real-time metrics and tools for debugging and monitoring.
Use Cases for Amazon DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB is a versatile and powerful NoSQL database service that can be used for a wide range of use cases, including:
Web and mobile applications
DynamoDB is ideal for web and mobile applications that require low latency and high throughput. It can handle millions of concurrent users and high volumes of data with ease. Applications that require real-time updating of user-generated content, such as social networks, gaming platforms, and chat applications, are a good fit for DynamoDB.
Internet of Things (IoT) applications
DynamoDB can be used for IoT applications that generate massive amounts of data streams. It can handle real-time data ingestion and processing, as well as historical data storage and analytics. Applications such as smart homes, connected cars, and industrial equipment monitoring can benefit from the scalability and availability of DynamoDB.
eCommerce applications
DynamoDB is well-suited for eCommerce applications that require high availability and low latency. It can handle high volumes of transactions and real-time inventory management. Online marketplaces, retail websites, and booking platforms are examples of eCommerce applications that can benefit from the simplicity and scalability of DynamoDB.
Gaming applications
DynamoDB is an excellent choice for gaming applications that require real-time user interactions, high performance, and low latency. It can handle massive player profiles, real-time game states, and transactional updates. Multiplayer games, mobile games, and online gaming platforms are examples of gaming applications that can benefit from the performance and scalability of DynamoDB.
Adtech applications
DynamoDB can be used for adtech applications that require real-time bidding, campaign management, and user targeting. It can handle billions of ad impressions and clicks per day, as well as extensive user profiling and segmentation. Advertising networks, demand-side and supply-side platforms, and digital agencies are examples of adtech applications that can benefit from the scalability and performance of DynamoDB.
Performance Advantages of Amazon DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB provides several performance advantages over other NoSQL database services:
Consistent and predictable performance
DynamoDB is designed to provide consistent and predictable performance, regardless of the scale or type of workload. It can handle up to 20 million reads and 10 million writes per second per table, with an average latency of less than 10 milliseconds. This makes it an ideal choice for applications that require low-latency and high-throughput access to data.
Automatic scaling
DynamoDB scales automatically to handle changes in traffic and data volume. It can scale up or down in response to changes in demand, without any manual intervention. This makes it a highly scalable and efficient database service that can handle unpredictable workloads without any downtime or performance degradation.
Highly available and durable
DynamoDB offers automatic failover and multi-region replication, making it a highly available and durable database service. It can survive the failure of a data center or a server with minimal disruption to the system. It also provides backup and restore capabilities, enabling users to recover data in case of accidental deletion or corruption.
Flexible data modeling
DynamoDB supports multiple data models, including document data, key-value pairs, and graph data. It also allows users to create secondary indexes and to define their own data access patterns. This makes it a flexible and versatile database service that can handle a wide range of data structures and use cases.
Amazon DynamoDB is a highly scalable, available, and performant NoSQL database service provided by Amazon Web Services. It offers several key features, benefits, and performance advantages that make it an ideal choice for web and mobile applications, IoT applications, eCommerce applications, gaming applications, and adtech applications. With its automatic scaling, consistent and predictable performance, and flexible data modeling, DynamoDB provides a reliable and cost-effective alternative to traditional relational databases and other NoSQL database services.

MMS • Matt Campbell
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

GitHub has moved push protection into general availability and made it free for all public repositories. Push protection helps detect secrets in code as changes are pushed. As part of the GA release, push protection is also available to all private repositories with a GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) license.
If code is pushed that contains a secret, push protection will trigger a prompt indicating the secret type, location, and steps to remediate. These prompts occur inline with the developer experience, either in the IDE or CLI. According to Zain Malik, Senior Product Marketing Manager at GitHub, and Mariam Sulakian, Product Manager at GitHub, “push protection only blocks secrets with low false positive rates.” A full list of secrets supported by push protection is available within the GitHub docs.
Push protection can be bypassed if needed by providing a reason. The options presented include marking the secret as needed for a test, marking it as a false positive, and marking it to be fixed later. Bypassing push protection will automatically trigger an email alert to repository and organization administrators as well as defined security managers. All bypasses can be reviewed via audit logs, the alert view UI, the REST API, or via webhook events. If marked as “fix later”, an open security alert is created. In all other cases, a closed and resolved security alert is created.
Push protection can be enabled via the Code security and analysis settings. It is possible to have push protection enabled automatically for all new public and GHAS-enabled private repositories. A custom resource link can also be specified that will appear in the CLI and web UI when push protection blocks a commit.
Custom patterns can be defined for push protection to scan for and block. It is recommended to first test custom patterns using the built-in dry-run feature before publishing and enabling the pattern. The pattern is specified as a regular expression.
User greysteil noted on Hacker News that they worked on this feature while at GitHub. They shared that:
This release is a repo-level setting, which is nice, but it will be even more useful when the team releases a user-level setting in June/July. That will allow you to configure GitHub to (softly) prevent you from pushing any easily identifiable secrets to any public repo. The plan is for it to be on by default.
They continued by sharing that approximately 200 new GitHub personal access tokens (PAT) are exposed in public repositories daily. User darthbanane raised a concern that if the scanner detects a secret then that implies that the secret has already left the user’s machine and has traversed the internet. User awesome_dude replied that:
The scanner has seen the credentials, yes, and it’s then up to the individual to decide if that credential should be considered “compromised” or not (seeing as the GitHub scanner has seen that credential).
In response to a query about how GitHub is performing the scan, greysteil noted that “it’s a bespoke scanning setup designed to deal with GitHub’s scale, minimise false positives, and scan fast enough to be in the `git push` request/response cycle.” They continued by sharing that it is leveraging Intel’s Hyperscan as the regex engine.
GitHub push protection is available free of charge to all public repositories. It is available for use in private repositories as part of GitHub Advanced Security.

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts

As businesses are increasingly relying on data to drive their decision-making process, there has been a surge in data-intensive applications. This necessitates robust and scalable databases that can efficiently manage large quantities of data, support highly-available and performant applications and provide real-time analysis and insights. AWS provides a suite of cloud-based database solutions that offer organizations of all sizes, the flexibility, scalability and reliability required to manage their data effectively.
AWS Database Options
AWS offers a variety of database solutions which can be classified into two categories, Relational Database Services (RDS) and NoSQL Databases.
Relational Database Services (RDS)
RDS is a cloud-based relational database service that makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale a relational database. RDS automates time-consuming administrative tasks whether they are typical maintenance, backups or patching. RDS supports multiple relational database engines such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, and Aurora. RDS provides the following benefits:
Ease of Use and Management: RDS simplifies the setup of a relational database by automating the deployment, scaling and maintenance of the infrastructure. RDS takes care of all administrative tasks such as patching, backing up, and monitoring.
Scalability: With RDS, you can gracefully scale vertically or horizontally, depending on your needs. Vertical scaling allows you to add more compute and memory resources, whereas horizontal scaling enables you to add more nodes to the cluster.
High Availability: RDS provides multiple features, including automated backups, snapshots, and replicas. These enable you to recover data easily in the event of a disaster.
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases provide a flexible and scalable database solution that can handle a huge amount of structured and unstructured data. NoSQL databases are often a preferred choice for applications such as e-commerce, content management systems, social media sites, and IoT. AWS provides two databases that fit under this category; Amazon DynamoDB and Amazon DocumentDB.
Amazon DynamoDB: Amazon DynamoDB is a fully-managed, highly scalable, and secure NoSQL database that supports both document and key-value data models. DynamoDB is designed to deliver fast, predictable performance for applications that need to handle large amounts of data and requests throughput. DynamoDB provides the following benefits:
• Security – DynamoDB is secure by default, providing automatic data encryption at rest and in transit.
• Scalability – DynamoDB is highly scalable and can handle requests up to millions per second.
• Performance – DynamoDB offers predictable sub-millisecond latency for reads and writes.
• Integration – DynamoDB has built-in integrations with some of the most popular AWS services, such as AWS Lambda.
Amazon DocumentDB: Amazon DocumentDB is a fully-managed, highly available, and scalable document database. DocumentDB is compatible with MongoDB, which makes it an ideal choice for migrating an existing MongoDB application to the cloud. DocumentDB provides the following benefits:
• Highly Scalable – DocumentDB can horizontally scale up to petabytes of data and millions of reads and writes per second.
• Fully Managed – AWS manages the operational aspects of DocumentDB such as patching, backups, and failover.
• Compatibility with MongoDB – DocumentDB is fully compatible with MongoDB, including the query language, indexes, and drivers. This makes the migration of MongoDB-based applications to DocumentDB a seamless process.
Use Cases for AWS Databases
Organizations choose different databases depending on their specific needs and applications. Below are some common use cases of AWS databases:
Content Management Systems and eCommerce: The ultimate goal of content management systems and eCommerce sites is to provide a personalized experience to the user. For that reason, they require databases that can scale to meet the demands of a growing user base. A good database solution for these applications is Amazon Aurora, which is specifically designed for high availability and performance.
Online Gaming: Online gaming applications require databases that are highly available, fast, and scalable. These requirements can be achieved by using Elasticache and DynamoDB, which are designed for high throughput and low latency.
Analytics and Big Data: Applications that require big data processing capabilities, such as data warehousing and business intelligence, need databases that can scale easily to handle massive amounts of data. Amazon Redshift provides extremely fast data ingestion and querying for large data sets, hence it’s a popular choice for big data processing use cases.
In conclusion, AWS has plenty of database services that are ideal for various use cases. AWS offers fully-managed, flexible and reliable database solutions that enable organizations to manage their data effectively. With AWS, you can easily deploy relational and non-relational databases that deliver the performance, security, scalability, and availability you need. With the variety of database solutions offered by AWS, organizations of all sizes and tech know-how, can choose the best database service for their specific needs and requirements.

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts
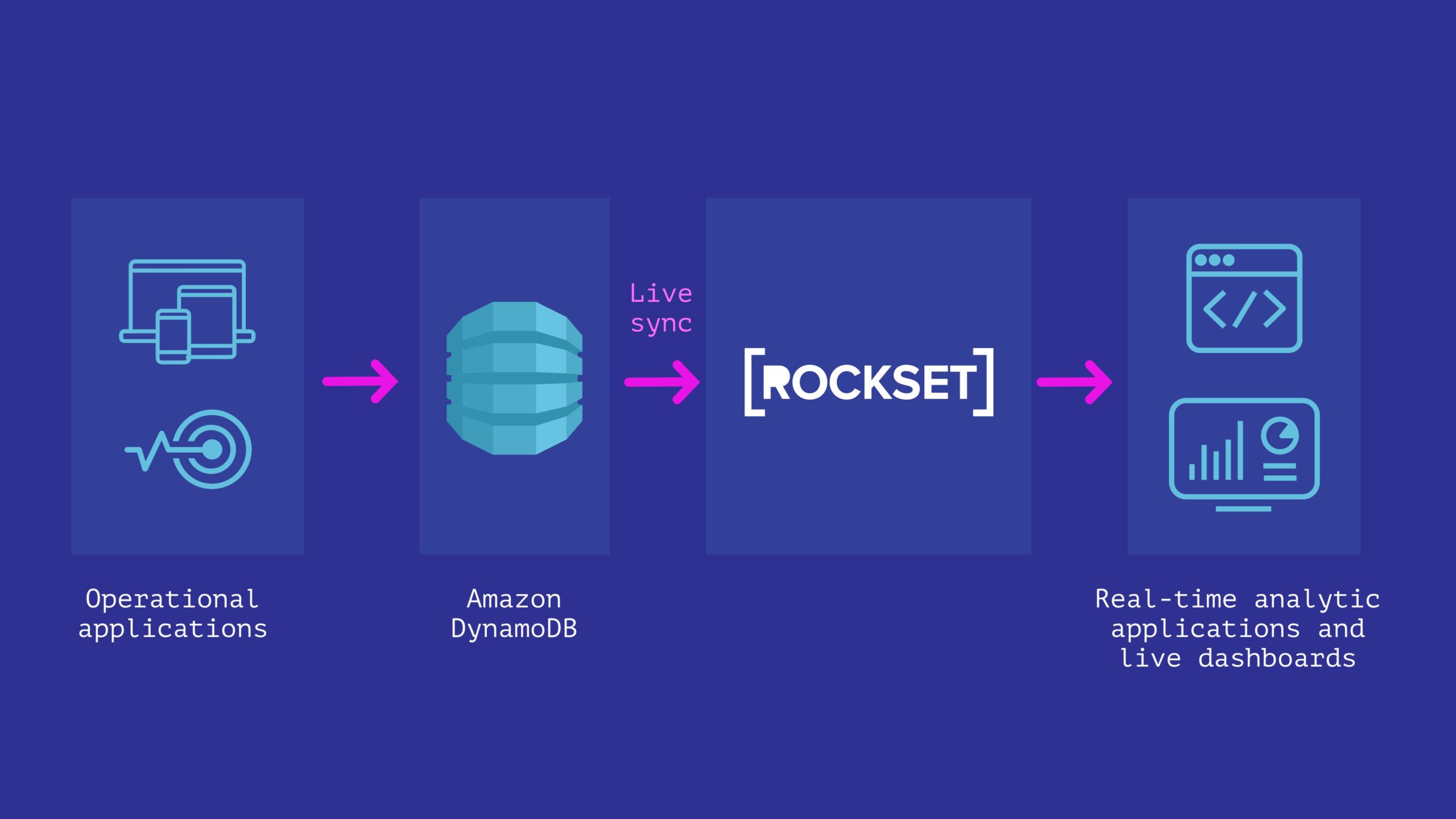
AWS DynamoDB is a NoSQL database service by AWS that offers scalability and high performance for applications that require low-latency data access. The service was launched in 2012 to compete with other managed NoSQL databases such as MongoDB and Cassandra. DynamoDB is designed to handle large volumes of data and can scale horizontally without any downtime. It is used by many popular companies such as Netflix, Airbnb, and Lyft, to name a few.
Features and Benefits
DynamoDB offers several features that make it a powerful tool when it comes to managing large volumes of data. These features include:
- Scalability: DynamoDB can handle millions of requests per second and can scale horizontally without any downtime. This means that as your application grows, you can easily add more capacity to handle the increased load.
- Availability: DynamoDB offers high availability with automatic failover and multi-region replication. This means that even if a region goes down, your application can continue to operate without any downtime.
- Performance: DynamoDB offers low-latency data access, which makes it an excellent fit for applications that require high performance.
- Security: DynamoDB integrates with other AWS services such as IAM and KMS to provide advanced security features such as encryption at rest and in transit.
- Flexibility: DynamoDB offers a flexible data model that allows you to store structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Data Model
DynamoDB has a flexible data model that allows you to store structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. In DynamoDB, data is organized into tables, which consist of items and attributes. An item is a set of attributes that represent a single record, while an attribute is a key-value pair that represents a specific data element.
Each table in DynamoDB must have a primary key, which can either be a partition key or a composite key (partition key and sort key). Partition keys are used to partition the data across multiple nodes in the DynamoDB cluster, while sort keys are used to sort the items within a partition.
Querying Data
DynamoDB offers two ways of querying data: Query and Scan.
- Query: Query allows you to retrieve data by specifying a partition key and an optional sort key. Query returns a subset of items that matches the specified key condition expression. Query is a more efficient way of retrieving data compared to Scan, as it retrieves only the items that match the specified key condition expression.
- Scan: Scan allows you to retrieve all the items in a table or a subset of items by specifying a filter expression. Scan reads all the items in a table or a subset and applies the filter expression to return only the items that match the expression. Scan can be inefficient when dealing with large amounts of data since it reads the entire table or a subset of items.
DynamoDB Streams
DynamoDB Streams is a feature that allows you to capture a real-time stream of updates to a table and store them in a separate stream. Each stream consists of a sequence of events that have taken place on the table. Streams can be used to trigger events such as sending notifications or updating other tables in real-time.
Streams can also be used to replicate data across multiple tables or regions. By consuming the stream and writing the updates to other tables, you can ensure that data is replicated across multiple regions or tables in real-time.
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) is a caching service that sits between your application and DynamoDB to improve the performance of read-intensive applications. DAX caches frequently accessed data in memory, which reduces the number of requests that need to be sent to DynamoDB. This results in lower latency and better application performance.
AWS DynamoDB is a powerful and flexible NoSQL database service that provides scalability, high availability, and low-latency data access. Its ability to store structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, combined with its scalability, enables you to build applications that can handle large volumes of data with ease. With features such as DynamoDB Streams and DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX), DynamoDB is well-suited for real-time, read-intensive applications. If you’re looking for a NoSQL database that can handle large volumes of data and provides high performance, then AWS DynamoDB is definitely worth considering.
NoSQL Database Market: A Systematic Review of Modern Threats, Trends and Emerging Challenges

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts
What analysis has been conducted in the NoSQL Database market report to assess the implications of the COVID-19 impact, ongoing Russia-Ukraine war?
This report studies the NoSQL Database market, covering market size for segment by type (Key-Value Based Database, Document Based Database, etc.), by application (BFSI, Healthcare, etc.), by sales channel (Direct Channel, Distribution Channel), by player (Aerospike, Amazon Web Services, Apache Cassandra, Basho Technologies, Cisco Systems, etc.) and by region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America and Middle East & Africa).
The NoSQL Database Market report thoroughly studies and analyzes the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the geopolitical tensions on the world economy and trade. Additionally, it assesses the implications of the Russia-Ukraine war on market dynamics. The report offers a comprehensive outlook on the NoSQL Database market industry, encompassing overview, challenges, opportunities, restraints, and future trends. It also includes a forecast for future trends and growth prospects in the industry for the year 2023. The report further analyzes key metrics such as CAGR, market share, market revenue, demand and supply, consumption patterns, manufacturing capabilities of industry leaders, regional analysis, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes. These insights enable businesses to identify market potentials and facilitate informed decision-making.
Prominent players in the industry:
- Aerospike
- Amazon Web Services
- Apache Cassandra
- Basho Technologies
- Cisco Systems
- CloudDB
- Couchbase Server
- DynamoDB
- Hypertable
- IBM
- MarkLogic
- Microsoft
- MongoDB
- MySQL
- Neo Technology
- Objectivity
- Oracle
- PostgreSQL
Get a Sample of the Report @ https://www.regalintelligence.com/request-sample/242675
NoSQL Database market research report provides in-depth information and insights into the market for the forecast period of 2023-2031. Major players in the NoSQL Database market and their competitive landscapes are analyzed, as the players drive the market and get affected on the frontline. The report addresses key challenges faced by the market and provides effective solutions for its growth. Additionally, it examines the supply chain channels encompassing raw materials, distribution, and production operations of major market players.
How the market segmentation analysis benefits in terms of understanding market growth over the forecasted time frame?
The report contemplates different regions of the global NoSQL Database market based on end consumer type, item type, application and geographical analysis. The analysts altogether study these fragments of the market to give clear bits of information on various segments of the market. Various touchpoints like overall market share, revenue, regional development, cost of production, and income and cost evaluation, are considered while assessing the market segments. This segmentation analysis encourages users to comprehend the market development over the forecasted time frame in the context of segments and make the best knowledgeable decisions as needs be.
NoSQL Database Market Major Applications:
- BFSI
- Healthcare
- Telecom
- Government
- Retail
NoSQL Database Market Segment by Product Types:
- Key-Value Based Database
- Document Based Database
- Column Based Database
- Graph Based Database
For Any Query, Contact Us: https://www.regalintelligence.com/enquiry/242675
What are the secondary sources utilized and how were industry experts, such as CEOs, VPs, directors, and executives, involved in the research methodology?
The research methodology used to estimate and forecast this market begins by capturing the revenues of the key players and their shares in the market. Various secondary sources such as press releases, annual reports, non-profit organizations, industry associations, governmental agencies and customs data, have been used to identify and collect information useful for this extensive commercial study of the market. Calculations based on this led to the overall market size. After arriving at the overall market size, the total market has been split into several segments and subsegments, which have then been verified through primary research by conducting extensive interviews with industry experts such as CEOs, VPs, directors, and executives. The data triangulation and market breakdown procedures have been employed to complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics for all segments and subsegments.
Primary Objectives of NoSQL Database Market Report:
- To conduct a comprehensive analysis of the market landscape, including current trends, growth prospects, and future forecasts.
- To identify potential opportunities and assess the associated challenges, obstacles, and threats in the market.
- To develop strategic business plans that are aligned with industry and economic shifts, ensuring adaptability and long-term success.
- To evaluate the competitive landscape and devise strategies to gain maximum advantage over rivals.
- To provide actionable insights and data-driven recommendations for making informed business decisions.
What are the major areas that the report focuses upon?
- What will be the NoSQL Database market size in 2030 and growth rate?
- What are the key factors driving the market at global, regional and country level?
- Who are the key vendors in the NoSQL Database market and their market strategies?
- What are the restraints and challenges to NoSQL Database market growth?
- What are the NoSQL Database market opportunities and threats faced by the vendors in the global NoSQL Database market?
- What are some of the competing products in this NoSQL Database and how big of a threat do they pose for loss of market share by product substitution?
- What M&A activity has taken place in the past 5 years?
Get Full Report: https://www.regalintelligence.com/buyNow/242675
To summarize, the NoSQL Database market research report includes market analysis, strategic planning, and providing valuable insights for decision-making. Moreover, the report additionally considers a lot of critical factors like production and utilization patterns, supply and demand gap checks, market development factors, future patterns, trends, industry outlook, Cost and revenue study, and so on. This report likewise gives investigative bits of information by using tools like, SWOT, PESTEL and Porter’s Five Forces, investment return report is additionally included helping the readers and financial specialists to get appropriate assessment in regards to potential market development, growth factors and rate of profitability analysis.
For More Related Reports Click Here :
Human Machine Interface (HMI) Software Market
3-Phase Vacuum Circuit Breaker Market
1-Ethynyl-3,5-Dimethoxybenzene Market
About Us:
Regal Intelligence aims to change the dynamics of market research backed by quality data. Our analysts validate data with exclusive qualitative and analytics driven intelligence. We meticulously plan our research process and execute in order to explore the potential market for getting insightful details. Our prime focus is to provide reliable data based on public surveys using data analytics techniques. If you have come here, you might be interested in highly reliable data driven market insights for your product/service, reach us here 24/7.
Mention your Queries here to Get a Call from Our Industry Expert @ sales@regalintelligence.com
Contact Us:
Regal Intelligence: www.regalintelligence.com
Phone no: +1 231 930 2779 (U.S.)
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/regal-intelligence
Twitter: https://twitter.com/regalinsights
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/regalintelligence/

MMS • Michael Redlich
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

Day Two of the 9th annual QCon New York conference was held on June 14th, 2023 at the New York Marriott at the Brooklyn Bridge in Brooklyn, New York. This three-day event is organized by C4Media, a software media company focused on unbiased content and information in the enterprise development community and creators of InfoQ and QCon. It included a keynote address by Alicia Dwyer Cianciolo and presentations from these four tracks:
- Designing Modern Reliable Architectures
- Hosted by Silvia Esparrachiari, Software Engineer at Google.
- Provides a diverse collection of reliability strategies covering finance applications, gaming platforms and other real world segments of the tech industry.
- MLOps – Production & Delivery for ML Platforms
- Hosted by Bozhao (Bo) Yu, Founder at BentoML.ai.
- Explores the latest trends, best practices, and case studies in MLOps, and discusses how they can be applied to improve the reliability, scalability, and efficiency of machine learning systems.
- Next Gen Fintech: Performance, Complexity & Privacy
- Hosted by Neha Sardana, Vice President and Senior Developer at Morgan Stanley.
- Provides solutions to the challenges of data breaches, privacy, security, and performance, and stays on top of the latest trends and best practices in Fintech.
- Optimizing Teams for Fast Flow – Surviving in the Post-Agile Aftermath
- Hosted by Katharine Chajka, Senior Product Manager at Planview Flow Methodology.
- Focuses on understanding how to identify the specific issues slowing down flow and finding changes that resolve those impediments to make the most of the time and money spent on change.
There was also one sponsored solutions track.
Danny Latimer, Content Product Manager at C4Media, kicked off the day two activities by welcoming the attendees and introduced Daniel Bryant, InfoQ News Manager, who discussed InfoQ news activities and the InfoQ core values: information robin hoods; best, not (necessarily) first; facilitators, not leaders; and content that can trusted. Pia von Beren, Project Manager & Diversity Lead at C4Media, discussed the QCon Alumni Program and the benefits of having attended multiple QCon conferences. The aforementioned track leads for Day Two introduced themselves and described the presentations in their respective tracks.
Keynote Address
Alicia Dwyer Cianciolo, senior technical lead for Advanced Entry, Descent and Landing Vehicle Technology Development at the NASA Langley Research Center, presented a keynote entitled, NASA’S Return to the Moon: Managing Complexity in the Artemis Program. Cianciolo started her presentation with the famous quote from John F. Kennedy’s speech at Rice University in 1962: “We choose to go to the moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard.” With than in mind, she introduced the Artemis program, considered the “sister” to the Apollo program, as a collection of projects, namely:
Artemis = Space Launch System + Orion Spacecraft + Human Landing System (HLS) + Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program (EHP) + Gateway
Cianciolo currently works on the Human Landing System. Artemis and its component projects were designed as a collaboration for space missions. After introducing each of these projects, she provided background and orbit information on previous and upcoming Artemis launches. Artemis I, launched on November 16, 2022 and splashed down on December 11, 2022 featured the Space Launch System and Orion projects. Artemis II, scheduled to launch at the end of 2024, will feature the Space Launch System and Orion projects and include a flight crew: Reid Wiseman (commander), Victor Glover (pilot), Christina Hammock Koch (Mission Specialist) and Jeremy Hansen (Mission Specialist). The plan for Artemis III is to land on the moon and will feature the Space Launch System, Orion, HLS and EHP projects and include another flight crew that is still to be determined. She described the complex of operations related to the HLS that includes mission segments, contracts, landing requirements and gateway orbit. Apollo 11 through Apollo 17 landed on or near the moon’s equator. The landing plan for Artemis III is to land within 6° latitude and less than 10° surface slopes on the moon’s south pole due to the rough terrain. Another challenge is the amount of daylight that often changes. The crew will need a six-day window of daylight and to be in constant communication with Earth. “What could go wrong?” Cianciolo asked. The hardest part of going to the moon is talking to people, Cianciolo said, as she recalled her experience in which it took six months to resolve this seemingly simple issue related to sharing a bathroom space. The plan for Artemis IV is to land on the International Habitation Module and will feature the Space Launch System, Orion, HLS, EHP and Gateway projects and include a flight crew to be determined.
Highlighted Presentations
Maximizing Performance and Efficiency in Financial Trading Systems through Vertical Scalability and Effective Testing by Peter Lawrey, CEO at Chronical Software. Lawrey kicked off his presentation by discussing how allocating objects may have an overhead of 80x than that of collecting them. He maintained that the loss of objects can be allocated, but recommends against this strategy that has been a practice. As the legendary Grace Hopper once said: “The most dangerous phrase in the English language is: “‘We’ve always done it that way.'” He provided various analyses and benchmarks on why allocations don’t scale well. Allocations can spend approximately 0.3% of the time in the garbage collector. The concept of accidental complexity is complexity that is not inherent in a problem, but rather in a solution that can be removed or reduced with a better design or technology choice. Lawrey provided many examples and analyses of accidental complexity that included memory usage analysis from Chronical Queue where most of the allocation activity was from the JDK Flight Recorder. In many applications, especially in the financial industry, selecting a “source of truth” can significantly impact the latency and complexity of the application. The concept of durability guarantees identifies critical paths for performance, but are often considered the largest bottlenecks. Examples include: a database; durable messaging that is guaranteed to be on disk; redundant messaging; and persisted messaging that will eventually be on disk. Lawrey introduced Little’s Law, a founding principle in queueing theory, as L = λ, such that:
- L = average number of items in a system
- λ = average arrival rate = exit rate = throughput
- W = average wait time in a system for an item (duration inside)
Little’s Law is applied in many aspects of system design and performance enhancement. The higher the latency, the higher the inherent parallelism required to achieve a desired throughput. On the opposite end of that spectrum, the lower the latency, the inherent required parallelism is minimized. Traditional object allocation in Java can impede performance, especially in high throughput scenarios, creating a bottleneck that hinders vertical scalability. By minimizing accidental complexity and using an event-driven architecture, vertical scalability can be achieved.
Performance and Scale – Domain-Oriented Objects vs Tabular Data Structures by Donald Raab, Managing Director and Distinguished Engineer at BNY Mellon, and Rustam Mehmandarov, Chief Engineer at Computas AS. Raab and Mehmandarov started their presentation with a retrospective into the problems with in-memory Java architectures using both 32-bit and 64-bit memory circa 2004. In the 32-bit world, it was challenging for developers to place, say, 6GB of data, into 4GB of memory. The solution was to build their own “small size” Java collections. The emergence of 64-bit provided some relief, but total heap size became an issue. Compressed Ordinary Object Pointers (OOPS), available with the release of Java 6 in late 2006, allowed developers to create 32-bit references (4 bytes) in 64-bit heaps. Solutions in this case include; building their own memory-efficient mutable Set, Map and List data structures; and building primitive collections for the List, Set, Stack, Bag and Map data structures. Raab and Mehmandarov then described the challenges developers face today where, for instance, large CSV data needs to be processed in-memory. They asked the questions: “How can that efficiently be accomplished in Java?,” “How can memory efficiency of data structures be measured?,” “What decisions affect memory efficiency?,” and “Which approach is better: row vs. columns?” To measure the cost of memory in Java, Raab and Mehmandarov introduced the Java Object Layout (JOL), a small toolbox to analyze object layout schemes in JVMs, and how to use it within an application. Using a large CSV data set as an example, Raab and Mehmandarov provided a comprehensive look into the various memory considerations: boxed vs. primitive types; mutable vs. immutable data; data pooling; and row-based vs. column-based structures. They also explored three libraries: Java Streams, introduced in Java 8; Eclipse Collections, invented by Raab; and DataFrame-EC, a tabular data structure based on the Eclipse Collections framework. Three Java projects: Amber, Valhalla and Lilliput, are working to improve productivity, value objects and user-defined primitives, and reduce the object header to 64 bits, respectively.
A Bicycle for the (AI) Mind: GPT-4 + Tools by Sherwin Wu, Member of the Technical Staff at OpenAI, and Atty Eleti, Software Engineer at OpenAI. In 1973, efficiencies in cycling started to emerge which were compared to a condor bird. Wu and Eleti coined the phrase “A bicycle for the mind” and used this as a metaphor for Steve Jobs and the creation of Apple. In 2023, the emergence of ChatGPT has evolved the phrase to “A bicycle for the AI mind.” They discussed large language models (LLMs) and their limitations followed by an introduction to new function calling capability that improves their gpt-4 and gpt-3.5-turbo applications. Wu and Eleti provided numerous demos for: converting natural language into queries; calling external APIs and multiple functions; and combining advanced reasoning with daily tasks. They maintained that technology is still in its infancy and they are excited to see how this technology will evolve in the future.
Implementing OSSF Scorecards Across an Organization by Chris Swan, Engineer at atsign.
Swan introduced the Open Source Security Foundation (OSSF or OpenSSF), a “cross-industry organization that brings together the industry’s most important open source security initiatives and the individuals and companies that support them.” The OpenSSF Scorecard project, just one of the projects under OpenSSF, helps open source maintainers improve their security best practices and to help open source consumers judge whether their dependencies are safe. A number of important software security heuristics are measured against an open source software project and assign each heuristic with a score of 0-10. A badge is generated containing the heuristic and score that may be placed on the GitHub repository. This provides a visual representation that the maintainers of the open source repository care about security, and a feeling of safety and security. Swan explored the five holistic security practices: code vulnerabilities, maintenance, continuous testing, source risk assessment and build risk assessment. He encouraged developers who are new to OpenSSF to use Allstar, another OpenSSF project, as a starting point for assessing security for their own open source projects. Swan provided a comprehensive introduction on how to get started by exploring tools such as: GitHub Insights, a tool that can guide developers to create a good quality open source repository; and Terraform, an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) resource that provides scripts to improve a GitHub repository. The process also includes a very long questionnaire in which developers should budget at least one hour. The 80:20 rule in OpenSSF states that 20% of effort is required to obtain 80% of the Scorecard score. However, Swan commented that it gets more difficult from there and that it is really hard to achieve high scores.
Summary
In summary, day two featured a total of 27 presentations with topics such as: reliable architectures, machine learning, financial technology (fintech) and optimizing engineering teams.

MMS • Renato Losio
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

Microsoft recently announced the general availability of Azure Linux container host for AKS. Available on GitHub under the CBL-Mariner project codename, the lightweight Linux distribution includes only the packages needed to run workloads on a cloud environment.
The Azure Linux container host for AKS is an open-source Linux distribution available as a container host on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). The new distribution is designed to provide reliability and consistency across the AKS, AKS-HCI, and Arc products. Azure Linux node pools can be deployed in a new cluster or added to existing Ubuntu clusters. It is also possible to migrate existing Ubuntu nodes to Azure Linux nodes.
The distribution is designed to be lightweight, both for performance and security, with a 400MB core image and around 300 packages. Jim Perrin, principal program manager lead at Microsoft, writes:
Azure Linux is designed with a minimalist view and a cloud focus. Window managers and other graphical interfaces are removed, resulting in a lower attack surface, reduced dependencies, and a generally smaller footprint. This ultimately helps reduce update interruptions and improves reboot speeds.
The general availability follows last year’s preview announcement and Azure Linux is the same distribution as CBL-Mariner. The distribution has the primary purpose of serving as the container host for AKS (AKS), running as a VM on Hyper-V but bare metal installations on x64 or ARM64 are also possible. Perrin adds:
Getting started with the Azure Linux container host is as easy as changing the OSSku parameter in your ARM template or other deployment tooling.
User cpressland on Reddit writes:
We’ve been running Mariner Linux in Production for just over a month and it’s been absolutely rock solid. Nice to see this get an official name (…) and for our non-AKS workloads I hope this becomes an option there too.
While the general availability is recent, Microsoft claims to be running Mariner as the internal Linux OS since last year, with products such as Xbox, Playfab, Minecraft, and many Azure services deployed on Mariner.
The famous Linux is a cancer quote from Steve Ballmer has been mentioned by many since the announcement. Peter Zaitsev, founder at Percona and open source advocate, tweets:
A couple of decades ago you could hardly imagine there would be such a thing as Microsoft Linux.
Microsoft is not the only cloud provider developing a lightweight distribution for cloud deployments, with Amazon Linux 2023, an option with long-term support on AWS, and Container-Optimized OS from Google, based on the Chromium OS project, other popular choices.
The CBL-Mariner documentation is available on GitHub.

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts

DynamoDB is a managed NoSQL database service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It has gained immense popularity as a highly available, scalable, and reliable data solution among cloud computing infrastructures. DynamoDB is a fully managed service that eliminates the need for AWS customers to manage their own database servers and provides extraordinary flexibility in terms of data access, storage, and management.
What is DynamoDB?
DynamoDB is a popular NoSQL database offering from AWS that provides high availability and scalability. It eliminates the need for manual scaling, managing, and monitoring of data infrastructure. It provides an efficient and reliable data storage service in a managed environment. DynamoDB can handle big data, and it helps users to store and retrieve any amount of data with automated and optimal performance allocation and dynamic provisioning capacity.
The platform is designed to serve adaptable workloads, and its flexibility to handle varying data demands makes it ideal for real-time applications. DynamoDB supports JSON-based document storage and semi-structured data models. It enables users to access and manage their data across multiple regions globally and provides secure and fast access to data with advanced features like encryption, backup, and restore capabilities.
DynamoDB Architectural Overview
The DynamoDB architecture allows for partitioned scaling, load balancing, and multi-region support. Every item in the table is automatically distributed across multiple partitions, and the partitions are distributed uniformly to maximize storage operations and cache utilization. The platform operates on a master-slave data replication configuration, with writes directed to a master node that forwards the data to its corresponding slaves.
The write propagation is performed for both local and global scenario, where writes are attempted entirely on local nodes before being distributed globally to all affected nodes. This design helps to reduce response time latency for local and regional reads and actions. DynamoDB offers high-performance querying via its well-designed indexing system. The platform employs Local Secondary Index (LSI) and Global Secondary Indexes (GSI) to support fast querying operations.
Features of DynamoDB
Scalability and High Availability
DynamoDB is a highly available, scalable, and distributed data storage service, making it an ideal solution for enterprises with fluctuating workloads. It was designed for scale from its inception and can be scaled up or down based on business demands automatically. Scaling is performed through partitioning; a technique that divides data into smaller units and allocates storage and processing resources to each partition. The platform provides multiple built-in features, such as auto scaling, capacity on-demand, read/write provisioning, and more, all aimed at providing scale and elasticity.
Flexible Data Models
DynamoDB supports a flexible data model that allows users to store unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data in its service. Its data models can be categorized as key-value, document, and more. The platform supports data types such as numbers, strings, binary data, sets, and document data format, including list and maps. Users can choose from any of these data models and formats based on their data needs and access or modify their data in real-time to suit their use cases.
Security and Availability
DynamoDB provides an enhanced level of security and availability for users and their data. It provides automated backups, point-in-time recovery, multi-copying, and encryption of data-at-rest and in-transit. These features provide data protection and privacy, making it ideal for businesses that require compliance and regulatory compliance. AWS also provides users with tools to manage and monitor access to their data and network traffic in real-time, including encryption for access keys, data encryption, and data access control management.
Low Latency and High Performance
DynamoDB provides a low read and write latency data access process through its global and multi-region availability, partitioning, and load balancing features. It ensures that all read and write actions are performed quickly and efficiently, irrespective of the volume or changing patterns of traffic. DynamoDB also supports caching and indexing, which enables the application to easily store and retrieve frequently used data records. Its caching feature helps reduce the overall response time for frequently accessed data records, leading to optimized performance and lower costs.
Use Cases for DynamoDB
Internet of Things Sensors and Devices
DynamoDB can handle IoT data as sensor data, device telemetry data, and more. IoT devices generate massive amounts of data generated in real-time, which may require immediate processing, querying, and analysis to identify anomalies, optimize performance, and reduce downtime. It is a perfect solution for data storage with high availability, capacity, and fast access speeds to support IoT device data management and analytics.
Gaming
DynamoDB provides gamers with a scalable, efficient, and high-performance solution for managing their data, including user profiles, game data, and game metadata. The platform is designed to handle high traffic and sudden spikes in usage demands, providing low latency and high throughput read and write actions, with automatic scaling and capacity provisioning.
High-Speed and Scalable Web Applications
DynamoDB is perfect for high-traffic web applications, chat applications, and social media networks. It is designed to deliver fast response times and high throughput, providing low latency, read and write actions with high scalability. Its support for multiple data models, flexible schema, and rich querying options makes it an ideal solution for web applications with various data requirements.
Real-Time Analytics
DynamoDB is a perfect solution for real-time analytics in the cloud. It can store and process large datasets and provide developers with a flexible, cost-effective, and highly available solution for running large-scale data analytics and machine learning models. Its stateless architecture, support for various data models, and built-in indexing make it a good platform for real-time data processing and querying operations.
DynamoDB is a powerful managed NoSQL database service that is designed to handle any size workload and data model with high scalability, availability, and performance. It eliminates the need for manual database management, provisioning, scaling, and monitoring and allows the users to focus on their business logic and application development. It provides a robust solution for multiple use cases, including IoT, gaming, web applications, and analytics, and has advanced security and data protection features.