Month: June 2023

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts

(Benny Marty/Shutterstock)
PayPal last month released the source code for JunoDB, a distributed key-value store it developed internally and which today powers a variety of backend services at the payment site, including 350 billion transaction requests per day, the company says.
JunoDB was originally developed over a decade ago in C++ to address the specific needs of the company, according to a May 17 blog post by Yaping Shi, principal MTS, architect at PayPal. The company was moving to a microservices architecture that would require supporting a large number of persistent inbound connections to data stores, but the company’s IT architects couldn’t find a suitable product to support that approach.
“Since no commercial or open-source solutions were available to handle the required scale out-of-the-box, we developed our own solution to adopt a horizontal scaling strategy for key-value stores,” Shi writes.
The new database would addresses two primary scaling needs in distributed key-value stores, according to Shi: handling the a large number of client connections, and handling growth in read and write throughput.
PayPal database developers created JunoDB with a proxy-based architecture to enable horizontal scaling. The JunoDB client library, which resides in the application, was developed to enable simple data actions through the JunoDB proxy, which manage requests from the clients, coordinates with the data stored on the JunoDB storage server, and provides load balancing. All data is encrypted, either at the client or the proxy layer using TLS; all stored data is also encrypted using TLS.
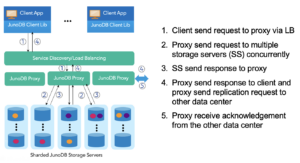
JunoDB architecture (Source: JunoDB GitHub page)
JunoDB utilizes consistent hashing to partition data and minimize data movement. To support horizontal scale, it shards data among a number of database partitions located on server nodes. It also uses shards within shards, or “micro shards,” which serve as building blocks for data redistribution, Shi writes.
“Our efficient data redistribution process enables quick incremental scaling of a JunoDB cluster to accommodate traffic growth,” Shi writes. “Currently, a large JunoDB cluster could comprise over 200 storage nodes, processing over 100 billion requests daily.”
JunoDB has since been rewritten in Golang to provide multi-threading and multi-core capabilities. With JunoDB’s data replication methods, including within-data center and cross-data center replication, the key-value store delivers six 9’s of system availability for PayPal.
JunoDB has become a critical part of PayPal’s infrastructure, and powers almost all of the company’s applications today. That includes use as a temporary cache for data, to reduce loads on relational databases, as a “latency bridge” for Oracle applications, and to provide “idempotency,” or a reduction in duplicate processing.
“While other NoSQL solutions may perform well in certain use-cases, JunoDB is unmatched when it comes to meeting PayPal’s extreme scale, security, and availability needs,” Shi writes.
The database is named after Juno, who was the queen of heaven in Greek mythology.
PayPal has released JunoDB under a permissive Apache 2.0 license. You can download JunoDB from GitHub at github.com/paypal/junodb.
Related Items:
PayPal Feeds the DL Beast with Huge Vault of Fraud Data
There’s a NoSQL Database for That
Vendors Compete to Make Serverless NoSQL in the Cloud Drop-Dead Simple
Database as a Service Market Type | Research 2023-2029, With 111 Pages – Digital Journal

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts
PRESS RELEASE
Published June 11, 2023
Global “Database as a Service Market Size is projected to Reach Multimillion USD by 2029, In comparison to 2022, at unexpected CAGR during the forecast Period 2023-2029.”
Top research study on“Database as a Service Market”with 111 + pages of analysis on industry tactic taken up byemerging business players, topographical opportunity, market sectors, product landscape and price, and cost structure. It also assists in market breakdown according to the industry’s newest and future movements to the bottom-most level, geographical markets, and key progress from both market and technology-aligned standpoints. Each section of the Database as a Service Market business research report is specifically prepared to examine key aspects of the market. Get Sample PDF Report.
Latest 2023 Top Manufactures in Database as a Service Market are:
- Amazon Web Service
- Rackspace
- Oracle
- Accenture
- Redcentric
- EMC
- HP
- HOSTING
- Salesforce.com
- IBM
- Microsoft
- SAP
- CSC
- CenturyLink
- Tesora
Get a Sample Copy of the Database as a Service Market Report
Short Summary About Database as a Service Market: –
Database as a Service Market size, segment (mainly covering Major Type (SQL, NoSQL, ,), End Users (Small-Sized Enterprises, Medium-Sized Enterprise, Large Enterprises,), and regions), recent status, development trendsa and competitor landscape. Furthermore, the 111 pages report provides detailed cost analysis, supply chain.
Technological innovation and advancement will further optimize the performance of the product, making it more widely used in downstream end users. Also, Consumer behaviour analysis and market dynamics (drivers, restraints, opportunities) provides crucial information for knowing the Database as a Service market.
“The Readers in the section will understand how the Database as a Service market scenario changed across the globe during the pandemic, post-pandemic and Russia-Ukraine War.”
To Understand How Covid-19 Impact Is Covered in This Report @https://www.industryresearch.biz/enquiry/request-covid19/19835256
The Database as a Service market is segmented by Types 2023:
The Database as a Service market is segmented by Applications 2023:
- Small-Sized Enterprises
- Medium-Sized Enterprise
- Large Enterprises
Get a Sample PDF of the Report @https://www.industryresearch.biz/enquiry/request-sample/19835256
Global Database as a Service Market: Drivers and Restrains
The research report has incorporated the analysis of different factors that augment the market’s growth. It constitutes trends, restraints, and drivers that transform the market in either a positive or negative manner. This section also provides the scope of different segments and applications that can potentially influence the market in the future. The detailed information is based on current trends and historic milestones. This section also provides an analysis of the volume of production about the global market and about each type from 2017 to 2028. This section mentions the volume of production by region from 2017 to 2028. Pricing analysis is included in the report according to each type from the year 2017 to 2028, manufacturer from 2017 to 2022, region from 2017 to 2022, and global price from 2017 to 2028.
Global Database as a Service Market: Segment Analysis
The research report includes specific segments by region (country), by manufacturers, by Type and by Application. Each type provides information about the production during the forecast period of 2017 to 2028. By Application segment also provides consumption during the forecast period of 2017 to 2028. Understanding the segments helps in identifying the importance of different factors that aid the market growth.
A thorough evaluation of the restrains included in the report portrays the contrast to drivers and gives room for strategic planning. Factors that overshadow the market growth are pivotal as they can be understood to devise different bends for getting hold of the lucrative opportunities that are present in the ever-growing market. Additionally, insights into market expert’s opinions have been taken to understand the market better.
Inquire or Share Your Questions If Any Before the Purchasing This Report @https://www.industryresearch.biz/enquiry/pre-order-enquiry/19835256
Reasons to Procure this Report: –
- This report helps stakeholders to identify some of the crucial players in the request and understand their precious donation.
- This report helps stakeholders to understand the COVID- 19 and Russia- Ukraine War Influence on the Database as a Service assiduity.
- This report will help the compendiums to understand the competition within the diligence and strategies for the competitive terrain to enhance the implicit profit.
- This report will help stakeholders to understand the global assiduity status and trends of Database as a Service and provides them with information on crucial request motorists, conditions, challenges, and openings.
- This report will help stakeholders to understand challengers better and gain further perceptivity to strengthen their position in their businesses.
- The competitive geography section includes the request share and rank (in volume and value), contender ecosystem, new product development, expansion, and accession.
- This report stays streamlined with new technology integration, features, and the rearmost developments in the request
- This report helps stakeholders to gain perceptivity into which regions to target encyclopedically
- This report helps stakeholders to gain perceptivity into the end- stoner perception concerning the relinquishment of Database as a Service.
Detailed TOC of Global Database as a Service Market Research Report 2023
1 Database as a Service Market Overview
1.1 Product Overview and Scope of Database as a Service
1.2 Database as a Service Segment by Type
1.2.1 Global Database as a Service Market Size Growth Rate Analysis by Type 2022 VS 2028
1.3 Database as a Service Segment by Application
1.3.1 Global Database as a Service Consumption Comparison by Application: 2017 VS 2022 VS 2028
1.4 Global Market Growth Prospects
1.4.1 Global Database as a Service Revenue Estimates and Forecasts (2017-2028)
1.4.2 Global Database as a Service Production Capacity Estimates and Forecasts (2017-2028)
1.4.3 Global Database as a Service Production Estimates and Forecasts (2017-2028)
1.5 Global Database as a Service Market by Region
1.5.1 Global Database as a Service Market Size Estimates and Forecasts by Region: 2017 VS 2022 VS 2028
1.5.2 North America Estimates and Forecasts (2017-2028)
1.5.3 Europe Estimates and Forecasts (2017-2028)
1.5.5 China Estimates and Forecasts (2017-2028)
1.5.5 Japan Estimates and Forecasts (2017-2028)
Get a Sample Copy of the Database as a Service Market Report
2 Market Competition by Manufacturers
2.1 Global Database as a Service Production Capacity Market Share by Manufacturers (2017-2022)
2.2 Global Database as a Service Revenue Market Share by Manufacturers (2017-2022)
2.3 Database as a Service Market Share by Company Type (Tier 1, Tier 2 and Tier 3)
2.4 Global Database as a Service Average Price by Manufacturers (2017-2022)
2.5 Manufacturers Database as a Service Production Sites, Area Served, Product Types
2.6 Market Competitive Situation and Trends
2.6.1 Market Concentration Rate
2.6.2 Global 5 and 10 Largest Database as a Service Players Market Share by Revenue
2.6.3 Mergers and Acquisitions, Expansion
3 Production and Capacity by Region
3.1 Global Production Capacity of Market Share by Region (2017-2022)
3.2 Global Revenue Market Share by Region (2017-2022)
3.3 Global Production, Revenue, Price and Gross Margin (2017-2022)
3.4 North America Database as a Service Production
3.4.1 North America Database as a Service Production Growth Rate (2017-2022)
3.4.2 North America Database as a Service Production Capacity, Revenue, Price and Gross Margin (2017-2022)
3.5 Europe Database as a Service Production
3.5.1 Europe Production Growth Rate (2017-2022)
3.5.2 Europe Production Capacity, Revenue, Price and Gross Margin (2017-2022)
3.6 China Production
3.6.1 China Production Growth Rate (2017-2022)
3.6.2 China Production Capacity, Revenue, Price and Gross Margin (2017-2022)
3.7 Japan Production
3.7.1 Japan Production Growth Rate (2017-2022)
3.7.2 Japan Production, Revenue, Price and Gross Margin (2017-2022)
4 Global Database as a Service Consumption by Region
4.1 Global Database as a Service Consumption by Region
4.1.1 Global Consumption by Region
4.1.2 Global Consumption Market Share by Region
4.2 North America
4.2.1 North America Consumption by Country
4.2.2 U.S.
4.2.3 Canada
4.3 Europe
4.3.1 Europe Consumption by Country
4.3.2 Germany
4.3.3 France
4.3.4 U.K.
4.3.5 Italy
4.3.6 Russia
4.4 Asia Pacific
4.4.1 Asia Pacific Consumption by Region
4.4.2 China
4.4.3 Japan
4.4.4 South Korea
4.4.5 Taiwan
4.4.6 Southeast Asia
4.4.7 India
4.4.8 Australia
4.5 Latin America
4.5.1 Latin America Consumption by Country
4.5.2 Mexico
4.5.3 Brazil
5 Production, Revenue, Price Trend by Type
5.1 Global Database as a Service Production Market Share by Type (2017-2022)
5.2 Global Database as a Service Revenue Market Share by Type (2017-2022)
5.3 Global Database as a Service Price by Type (2017-2022)
6 Consumption Analysis by Application
6.1 Global Database as a Service Consumption Market Share by Application (2017-2022)
6.2 Global Database as a Service Consumption Growth Rate by Application (2017-2022)
Continued…
Purchase this Report (Price 2980 USD for a Single-User License) @https://www.industryresearch.biz/purchase/19835256
About Us:
Market is changing rapidly with the ongoing expansion of the industry. Advancement in technology has provided today’s businesses with multifaceted advantages resulting in daily economic shifts. Thus, it is very important for a company to comprehend the patterns of market movements in order to strategize better. An efficient strategy offers the companies a head start in planning and an edge over the competitors. Industry Research is a credible source for gaining market reports that will provide you with the lead your business needs.
Contact Us:
Industry Research Biz
Phone: US +1 424 253 0807
UK +44 203 239 8187
Email:[email protected]
Web:https://www.industryresearch.biz
Latest Reports:
Global “Solid State Drive (SSD) Market” Analysis | Research 2023
Global “Mobile AB Testing Market” Trend | Research 2023
Global “Road Milling Machine Market” Key-players | Research 2023
Carbon Offset or Carbon Credit Trading Service Market Share | Research 2023
Global “Soccer Cleats Market” Insight | Research 2023
2023 Research On “Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Market” Insight | 2029
2023 Research On “Aluminum Chlorohydrate Market” Growth | 2029
2023 Research On “Needle Pet Coke Market” Report | 2029
2023 Research On “Water-Based Polyurethane Dispersions Market” Report | 2029
2023 Research On “Blood Glucose Test Strip Market” Survey | 2029
2023 Research On “Super Absorbent Polymer (SAP) Market” Type | 2029
2023 Research On “Feed Carbohydrase Market” Trend | 2029
Global “Deception Technology Market” Overview | Research 2023-2029
Global “Log Management Market” Size | Research 2023-2029
Press Release Distributed by The Express Wire
To view the original version on The Express Wire visit Latest Research on- Database as a Service Market Type | Research 2023-2029, With 111 Pages
TheExpressWire
Global NoSQL Database Market Size and Forecast | Objectivity Inc, Neo Technology Inc …

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts

New Jersey, United States – Verified Market Research recently published a research report titled, “Global NoSQL Database Market Insight, Forecast 2030“. The Global NoSQL Database market is elaborately discussed in the report so as to help readers to gain a sound understanding of key trends, top strategies, and potential growth opportunities. The Global NoSQL Database report offers Porter’s Five Forces analysis, PESTEL analysis, and qualitative and quantitative analysis to give a complete and accurate picture of the current and future market situations. The analysts have carefully forecast the market size, CAGR, market share, revenue, production, and other vital factors with the help of industry-best primary and secondary research tools and methodologies. Players can use the Global NoSQL Database report to build effective strategies for concentrating on key segments and regions and boosting their business in the Global NoSQL Database market.
Our report includes ongoing and latest market trends, company market shares, market forecasts, competitive benchmarking, competitive mapping, and in-depth analysis of key sustainability tactics and their impact on market growth and competition. In order to estimate quantitative aspects and segment the Global NoSQL Database market, we used a recommended combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches. We studied the Global NoSQL Database market from three key perspectives through data triangulation. Our iterative and comprehensive research methodology helps us to provide the most accurate market forecasts and estimates with no to minimum errors.
Get Full PDF Sample Copy of Report: (Including Full TOC, List of Tables & Figures, Chart) @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/download-sample/?rid=129411
Key Players Mentioned in the Global NoSQL Database Market Research Report:
In this section of the report, the Global NoSQL Database Market focuses on the major players that are operating in the market and their competitive landscape present in the market. The Global NoSQL Database report includes a list of initiatives taken by the companies in the past years along with the ones, which are likely to happen in the coming years. Analysts have also made a note of their expansion plans for the near future, financial analysis of these companies, and their research and development activities. This research report includes a complete dashboard view of the Global NoSQL Database market, which helps the readers to view an in-depth knowledge about the report.
Objectivity Inc, Neo Technology Inc, MongoDB Inc, MarkLogic Corporation, Google LLC, Couchbase Inc, Microsoft Corporation, DataStax Inc, Amazon Web Services Inc & Aerospike Inc.
Global NoSQL Database Market Segmentation:
NoSQL Database Market, By Type
• Graph Database
• Column Based Store
• Document Database
• Key-Value Store
NoSQL Database Market, By Application
• Web Apps
• Data Analytics
• Mobile Apps
• Metadata Store
• Cache Memory
• Others
NoSQL Database Market, By Industry Vertical
• Retail
• Gaming
• IT
• Others
For a better understanding of the market, analysts have segmented the Global NoSQL Database market based on application, type, and regions. Each segment provides a clear picture of the aspects that are likely to drive it and the ones expected to restrain it. The segment-wise explanation allows the reader to get access to particular updates about the Global NoSQL Database market. Evolving environmental concerns, changing political scenarios, and differing approaches by the government towards regulatory reforms have also been mentioned in the Global NoSQL Database research report.
In this chapter of the Global NoSQL Database Market report, the researchers have explored the various regions that are expected to witness fruitful developments and make serious contributions to the market’s burgeoning growth. Along with general statistical information, the Global NoSQL Database Market report has provided data of each region with respect to its revenue, productions, and presence of major manufacturers. The major regions which are covered in the Global NoSQL Database Market report includes North America, Europe, Central and South America, Asia Pacific, South Asia, the Middle East and Africa, GCC countries, and others.
Inquire for a Discount on this Premium Report @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ask-for-discount/?rid=129411
What to Expect in Our Report?
(1) A complete section of the Global NoSQL Database market report is dedicated for market dynamics, which include influence factors, market drivers, challenges, opportunities, and trends.
(2) Another broad section of the research study is reserved for regional analysis of the Global NoSQL Database market where important regions and countries are assessed for their growth potential, consumption, market share, and other vital factors indicating their market growth.
(3) Players can use the competitive analysis provided in the report to build new strategies or fine-tune their existing ones to rise above market challenges and increase their share of the Global NoSQL Database market.
(4) The report also discusses competitive situation and trends and sheds light on company expansions and merger and acquisition taking place in the Global NoSQL Database market. Moreover, it brings to light the market concentration rate and market shares of top three and five players.
(5) Readers are provided with findings and conclusion of the research study provided in the Global NoSQL Database Market report.
Key Questions Answered in the Report:
(1) What are the growth opportunities for the new entrants in the Global NoSQL Database industry?
(2) Who are the leading players functioning in the Global NoSQL Database marketplace?
(3) What are the key strategies participants are likely to adopt to increase their share in the Global NoSQL Database industry?
(4) What is the competitive situation in the Global NoSQL Database market?
(5) What are the emerging trends that may influence the Global NoSQL Database market growth?
(6) Which product type segment will exhibit high CAGR in future?
(7) Which application segment will grab a handsome share in the Global NoSQL Database industry?
(8) Which region is lucrative for the manufacturers?
For More Information or Query or Customization Before Buying, Visit @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/product/nosql-database-market/
About Us: Verified Market Research®
Verified Market Research® is a leading Global Research and Consulting firm that has been providing advanced analytical research solutions, custom consulting and in-depth data analysis for 10+ years to individuals and companies alike that are looking for accurate, reliable and up to date research data and technical consulting. We offer insights into strategic and growth analyses, Data necessary to achieve corporate goals and help make critical revenue decisions.
Our research studies help our clients make superior data-driven decisions, understand market forecast, capitalize on future opportunities and optimize efficiency by working as their partner to deliver accurate and valuable information. The industries we cover span over a large spectrum including Technology, Chemicals, Manufacturing, Energy, Food and Beverages, Automotive, Robotics, Packaging, Construction, Mining & Gas. Etc.
We, at Verified Market Research, assist in understanding holistic market indicating factors and most current and future market trends. Our analysts, with their high expertise in data gathering and governance, utilize industry techniques to collate and examine data at all stages. They are trained to combine modern data collection techniques, superior research methodology, subject expertise and years of collective experience to produce informative and accurate research.
Having serviced over 5000+ clients, we have provided reliable market research services to more than 100 Global Fortune 500 companies such as Amazon, Dell, IBM, Shell, Exxon Mobil, General Electric, Siemens, Microsoft, Sony and Hitachi. We have co-consulted with some of the world’s leading consulting firms like McKinsey & Company, Boston Consulting Group, Bain and Company for custom research and consulting projects for businesses worldwide.
Contact us:
Mr. Edwyne Fernandes
Verified Market Research®
US: +1 (650)-781-4080
UK: +44 (753)-715-0008
APAC: +61 (488)-85-9400
US Toll-Free: +1 (800)-782-1768
Email: sales@verifiedmarketresearch.com
Website:- https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/
NoSQL Market is booming Globally with Top key players-IBM Corporation, Aerospike Inc …

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts

A market study Global examines the performance of the NoSQL 2023. It encloses an in-depth analysis of the NoSQL state and the competitive landscape globally. The Global NoSQL can be obtained through the market details such as growth drivers, latest developments, NoSQL business strategies, regional study, and future market status. The report also covers information including NoSQL industry latest opportunities and challenges along with the historical and NoSQL future trends. It focuses on the NoSQL dynamics that is constantly changing due to the technological advancements and socio-economic status.
Pivotal players studied in the NoSQL report:
IBM Corporation, Aerospike Inc, MarkLogic Corporation, Hibernate, MariaDB, Oracle Database, Neo technology, MongoDB, Basho Technologies, Couchbase, PostgreSQL
Get free copy of the NoSQL report 2023: https://www.mraccuracyreports.com/report-sample/478158
Recent market study NoSQL analyses the crucial factors of the NoSQL based on present industry situations, market demands, business strategies adopted by NoSQL players and their growth scenario. This report isolates the NoSQL based on the key players, Type, Application and Regions. First of all, NoSQL report will offer deep knowledge of company profile, its basic products and specification, generated revenue, production cost, whom to contact. The report covers forecast and analysis of NoSQL on global and regional level.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis:
In this report, the pre- and post-COVID impact on the market growth and development is well depicted for better understanding of the NoSQL based on the financial and industrial analysis. The COVID epidemic has affected a number of NoSQL is no challenge. However, the dominating players of the Global NoSQL are adamant to adopt new strategies and look for new funding resources to overcome the rising obstacles in the market growth.
Access full Report Description, TOC, Table of Figure, Chart, etc. @ https://www.mraccuracyreports.com/reportdetails/reportview/478158
Product types uploaded in the NoSQL are:
Key-Value Store, Document Databases, Column Based Stores, Graph Database
Key applications of this report are:
Retail, Online Game Development, IT, Social Network Development, Web Applications Management, Others
Geographic region of the NoSQL includes:
North America NoSQL(United States, North American country and Mexico),
Europe Market(Germany, NoSQL France Market, UK, Russia and Italy),
Asia-Pacific market (China, NoSQL Japan and Korea market, Asian nation and Southeast Asia),
South America NoSQL Regions inludes(Brazil, Argentina, Republic of Colombia etc.),
NoSQL Africa (Saudi Arabian Peninsula, UAE, Egypt, Nigeria and South Africa)
The NoSQL report provides the past, present and future NoSQL industry Size, trends and the forecast information related to the expected NoSQL sales revenue, growth, NoSQL demand and supply scenario. Furthermore, the opportunities and the threats to the development of NoSQL forecast period from 2023 to 2029.
Please click here today to buy full report @ https://www.mraccuracyreports.com/checkout/478158
Further, the NoSQL report gives information on the company profile, market share and contact details along with value chain analysis of NoSQL industry, NoSQL industry rules and methodologies, circumstances driving the growth of the NoSQL and compulsion blocking the growth. NoSQL development scope and various business strategies are also mentioned in this report.

MMS • Sergio De Simone
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

At WWDC 2023, Apple introduced SwiftData, a new framework that provides a declarative, Swift-first API enabling to work with data persistence in iOS apps. SwiftData can easily make a Swift class into a persistent model and is especially suited to be used with SwiftUI.
After radically changing the way UIs can be defined on its platforms a few years ago with SwiftUI, Apple is now moving its first steps to move beyond Core Data, an ORM-based persistency framework strictly tied to Objective-C dynamic capabilities.
While it provides an API that enabled the definition of persistent models, albeit in a rather cumbersome way, Core Data is usually used through the Schema Model Editor integrated in Xcode. The resulting .xcdatamodeld file is therefore the source of truth, which is then used to automatically generate stubs. The stubs provide base classes used as base classes for the actual model classes.
SwiftData takes the opposite approach, where the code is the source of truth about the persistent data model. This is how you can define a simple model:
@Model
class Recipe {
@Attribute(.unique) var name: String
var summary: String?
var ingredients: [Ingredient]
}
Note how SwiftData relies on a new macro feature introduced in Swift 5.9. Under the hood, the @Model macro will apply the @PersistedProperty to each property in Recipe, as well as add initialization code and other required properties to the class implementation.
Thanks to this additional logic, completely transparent to the developer, SwiftData is able to map all properties to the underlying storage. According to Apple, persistent objects are fetched from and updated to the persistent storage when required.
While simple types, including Bool, Int, and String, are supported out-of-the-box, more complex types must conform to the Codable protocol in order to be used in a persistent class.
As mentioned, SwiftData is particularly suited for use with SwiftUI. Indeed, the @Model macro will also make a class conform to the ObservableObject protocol, as well as have each persisted property behave as a @Published property. In addition to this, to connect a SwiftUI View to the persistent model, you only need to use a new @Query attribute, similarly to how you use @State and @Binding. @Query will ensure the view will be automatically re-rendered each time the underlying data change.
SwiftData also provides support for the definition of predicates that can be used to filter data. Predicates are checked at compile-time and will raise compilation errors in case of type mismatch. Additionally, a SwiftData model can be synchronized across devices using CloudKit or as documents stored in iCloud Drive.
To make it easier for developers to migrate to SwiftData, the framework supports incremental adoption in an existing Core Data app. Apple is providing a sample project showing how you can use SwiftData only for a portion of a Core Data app.
As a final note, it is worth noting that SwiftData is not a wrapper around Core Data. As Apple showed at WWDC indeed, SwiftData leverages the same persistent engine that Core Data uses, but is a completely independent stack.

MMS • Robert Krzaczynski
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

The Microsoft Build 2023 event showcased the latest updates and additions to the Azure App Service. The event, held in person in Seattle, included some group sessions, demonstrations and Q&A sessions on Azure App Service with such topics as changes within PremiumV3, Automatic Scaling or memory optimisation for ASEv3.
The first addition was related to PremiumV3. The Azure App Service has expanded its PremiumV3 offering, introducing a 1 virtual processor/4GB option and memory-optimised options ranging from 2 virtual processors/16GB to 32 virtual processors/256GB. PremiumV3 provides a wide range of computing options for different workloads. It offers better pricing with Azure Dev/Test, Azure Savings Plans and Reserved Instances services. Deployment is available in most Azure service delivery regions.
The topic of WordPress also appeared. The Azure App Service continues to invest in optimising the WordPress environment on the Linux App Service. A comprehensive update was released, offering an optimised WordPress configuration with performance improvements. The Quickstart experience was enhanced, providing simplified price/performance options and reducing costs by 20% to 35%.
In general, WordPress on Azure App Service is getting positive feedback from the community. Among others, Santasu Das commented below one of the videos about the service, that it’s enjoyable to see the fantastic way to set up WordPress in Azure in just some clicks.
Another recently updated feature is Automatic Scaling, integrating it into the Azure Portal with an improved user experience. This feature allows developers to easily scale web applications based on the current frequency of HTTP requests. By setting minimum and maximum parameters for scaling the number of instances, the platform automatically adjusts the number of workers in response to incoming requests and real-time load. The core technology, inspired by serverless scaling in Azure Functions, is now available for any web application. Future updates will include support for memory-optimised Pmv3 SKUs. Demonstrations of the auto-scaling feature can be seen as part of the Azure App Service Community Standup and in the “Auto Scaling for Azure App Service Web Apps” demo session at Build 2023.
There was mention of programming language updates too. The Azure App Service is preparing for the launch of the .NET 8.0 platform, making it available on both Windows and Linux versions. Minor version updates have been made for existing versions of Node, Java, Python and PHP. Future plans include support for Node 20, Python 3.12, PHP 8.3 and general availability of .NET 8.0. In addition, the App Service will soon introduce JBoss clustering to ensure the high availability of JBoss EAP applications, which will be automatically enabled when virtual network integration is configured.
A new feature is coming soon to the multi-tenant App Service, allowing multiple App Service plans to be attached to a single subnet. This eliminates the need for separate subnets for each plan, reducing subnet sprawl. In addition, the App Service plans to introduce support for incoming HTTP traffic over IPv6, enabling Web applications to accept traffic on both IPv6 and IPv4 addresses.
The App Service also introduced a new feature that allows developers to customise the TLS cipher suites used in their web applications. This gives them the ability to enforce more modern cipher suites while supporting legacy clients. This feature is currently in public preview and is fully supported for production workloads. Moreover, the App Service implements end-to-end TLS encryption, securing intra-cluster traffic within the App Service to enhance application security.
The last thing is supporting custom error pages in the App Service. This new feature allows developers to provide custom site content, including branding and app layout, instead of the generic error pages returned by the App Service for HTTP error codes such as 403, 502 and 503. The custom error page feature is now available in the familiarisation version, giving developers more flexibility and control.
Java News Roundup: JDK 21 in Rampdown, JEP 404, JDK 22 Expert Group, Jakarta EE 11 Updates

MMS • Michael Redlich
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

This week’s Java roundup for June 5th, 2023 features news from OpenJDK, JDK 21 in Rampdown, JDK 22 expert group, Jakarta EE 11 update, Spring Security Kerberos 2.0.0, Quarkus 3.1.1, Micronaut 3.9.3, Eclipse Vert.x 4.4.3, Apache Commons IO 2.13, Apache Tomcat 11.0.0-M7 and 9.0.76, Infinispan 14.0.10 and 13.0.17, JHipster Lite 0.34, OpenXava 7.1.1, Yupiik Fusion 1.0.3, Gradle 8.2-RC2 and JNation.
OpenJDK
JEP 453, Structured Concurrency (Preview), has been promoted from Proposed to Target to Targeted for JDK 21. Formerly a incubating API, this initial preview incorporates enhancements in response to feedback from the previous two rounds of incubation: JEP 428, Structured Concurrency (Incubator), delivered in JDK 19; and JEP 437, Structured Concurrency (Second Incubator), delivered in JDK 20. The only significant change features the fork() method, defined in the StructuredTaskScope class, returns an instance of TaskHandle rather than a Future since the get() method in the TaskHandle interface was restructured to behave the same as the resultNow() method in the Future interface. More details on this JEP may be found in this detailed InfoQ news story.
JEP 446, Scoped Values (Preview), has been promoted from Proposed to Target to Targeted for JDK 21. Formerly known as Extent-Local Variables (Incubator), this JEP is now a preview feature following JEP 429, Scoped Values (Incubator), delivered in JDK 20. This JEP proposes to enable sharing of immutable data within and across threads. This is preferred to thread-local variables, especially when using large numbers of virtual threads. InfoQ will follow-up with a more detailed news story.
Roman Kennke, principal engineer at AWS and owner of JEP 404, Generational Shenandoah (Experimental), has proposed to drop this JEP from JDK 21 due to the “risks identified during the review process and the lack of time available to perform the thorough review that such a large contribution of code requires.” The Shenandoah team has decided to “deliver the best Generational Shenandoah that they can” and will seek to target JDK 22. The review is expected to conclude on June 14, 2023.
JDK 21
Build 26 of the JDK 21 early-access builds was also made available this past week featuring updates from Build 25 that include fixes to various issues. Further details on this build may be found in the release notes.
As per the JDK 20 release schedule, Mark Reinhold, chief architect, Java Platform Group at Oracle, formally declared that JDK 21 has entered Rampdown Phase One. This means that the main-line source repository has been forked to the JDK stabilization repository and no additional JEPs will be added for JDK 21. Therefore, the final set of 15 features for the GA release in September 2023 will include:
This feature set assumes that the proposal to remove the aforementioned JEP 404, Generational Shenandoah (Experimental), originally targeted for JDK 21, will be approved.
For JDK 21, developers are encouraged to report bugs via the Java Bug Database.
JDK 22
JSR 397, Java SE 22, was submitted this past week to formally announce the six-member expert group for JDK 22, namely Simon Ritter (Azul Systems), Manoj Palat (Eclipse Foundation), Andrew Haley (Red Hat), Christoph Langer (SAP SE), Iris Clark (Oracle) and Brian Goetz (Oracle). Clark and Goetz will serve as the specification leads. Other notable dates at this time include a public review from January 2024 through February 2024 and the GA release in March 2024.
Build 0 and Build 1 of the JDK 22 early-access builds were also made available this past week featuring the initial set of release updates.
Jakarta EE
Ivar Grimstad, Jakarta EE developer advocate at the Eclipse Foundation, announced in his Hashtag Jakarta EE weekly blog that the requests for plan review for Jakarta EE 11 have been submitted ahead of the May 30, 2023 deadline. Developers can expect updates to the Jakarta Authentication 3.1, Jakarta Authorization 3.0, Jakarta Concurrency 3.1, Jakarta Contexts and Dependency Injection 4.1, Jakarta Expression Language 6.0, Jakarta Faces 5.0, Jakarta RESTful Web Services 4.0, Jakarta Server Pages 4.0, Jakarta Persistence 3.2, Jakarta Security 4.0, Jakarta Servlet 6.1 and Jakarta WebSocket 2.2 specifications with the release of Jakarta EE 11, scheduled for the first quarter of 2024.
It is also important to note that the Jakarta Data 1.0, Jakarta NoSQL 1.0 and Jakarta MVC 3.0 specifications with approved release plans, are currently considered as standalone, i.e., they haven’t yet been incorporated into the Platform, Web or Core profiles of Jakarta EE.
Spring Framework
The release of Spring Security Kerberos 2.0.0 delivers notable changes such as: backwards compatible support for JDK 8; wrap the execution of the UserDetailsService interface in a PrivilegedAction interface so that it can reuse Kerberos authentication; and a fix for a NotSerializableException with the JaasSubjectHolder class. More details on this release may be found in the list of issues.
Quarkus
Red Hat has released Quarkus 3.1.1.Final featuring dependency upgrades and notable changes such as: properly catch non-unique result exceptions with Security Jakarta Persistence Reactive; prevent a NullPointerException in preparation of Jacoco reports when a workspace module has no sources; a fix for the @NamedNativeQuery annotation not working in Hibernate Reactive when converting to native image; and a fix for Quarkus 3.1 throwing an IllegalStateException exception if the @Produces annotation is not defined on a stream response. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Micronaut
The Micronaut Foundation has released Micronaut Framework 3.9.3 featuring bug fixes and updates to modules: Micronaut Servlet and Micronaut AWS. There was also a dependency upgrade to Netty 4.1.92. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
The third release candidate of Micronaut 4.0 delivers bug fixes and improvements such as: add a default method to the overloaded set of writeValueAsString() methods in the JsonMapper interface; improved exception handling on scheduled jobs; and a new parameter, missingBeans=EndpointSensitivityHandler.class, for the @Requires annotation on the EndpointsFilter class to convey that endpoint sensitivity is handled externally and the filter will not be loaded. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Eclipse Vert.x
Eclipse Vert.x 4.4.3 has been released with dependency upgrades and notable fixes such as: a broken tracing integration with the JDBC SQL client; an IndexOutOfBoundsException from the serviceName() method in the GrpcMethodCall class; and a NullPointerException from the updateSSLOptions() method in the HttpServer interface due to a null instance of the SSLHelper class. More details on this release may be found in the release notes and deprecations and breaking changes.
Version 4.4.3.1 of the Vert.x JDBC Client has also been released to fix an IP address parsing regression introduced in Vert.x 4.4.3. Developers who use the vertx-jdbc-client module should upgrade to this dependency until an upgrade to the next full stack release is provided.
Apache Software Foundation
The release of Apache Commons IO 2.13.0 delivers notable changes such as: a fix for the FileAlreadyExistsException from the createParentDirectories() method in the PathUtils class; reset the setCharset(null) and setCharsetEncoder(null) methods in the ReaderInputStream.Builder class to return a default object instead of throwing a NullPointerException; and add missing conversions to the subclasses of the AbstractOrigin class. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Versions 11.0.0-M7 and 9.0.76 of Apache Tomcat both ship with: support for JDK 21 and virtual threads; a new RateLimitFilter class to help mitigate Denial of Service and Brute Force attacks by limiting the number of a requests that are allowed from a single IP address within a given time window; and a dependency upgrade to Tomcat Native to 2.0.4 which includes binaries for Windows built with OpenSSL 3.0.9. More details may be found in the changelogs for version 11.0.0-M7 and version 9.0.76.
Infinispan
Infinispan 14.0.10.Final provides notable changes such as: Spring Framework 6.x and Spring Boot 3.x dependency upgrades; a fix to the IPv6 wildcard address when detecting multihoming; and an implementation of the the conditional methods, computeIfAbsent() and computeIfPresent(), in the RemoteCache interface. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Similarly, Infinispan 13.0.17.Final features notable changes such as: eliminate the corruption of binary files by not filtering binary resources; an issue where a JNDI data source is not available when deploying to Tomcat by lazily initiating the data source from the getConnection() method in the ManagedConnectionFactory class; and correct the documented port number in the property file examples in the Spring Boot starter documentation. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
JHipster
The JHipster team has released version 0.34.0 of JHipster Lite with many dependency upgrades and notable enhancements such as: the removal of unused local variables; the replacement of concatenating strings with text blocks; and improvements in the React application. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.
OpenXava
Version 7.1.1 of OpenXava has been released featuring dependency upgrades and the ability to visit a website resource that is annotated with @HtmlText. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Yupik
Version 1.0.3 of Yupiik Fusion has been released with notable changes such as: support for kubeconfig files in Kubernetes Client libraries; improved reuse of the CliAwaiter class; and expose the prepare() method in the KubenetesClient class by changing the access specifier from private to public. Further details on this release may be found in the release notes.
Gradle
The second release candidate of Gradle 8.2 features improvements such as: continued improvements to the Kotlin DSL reference documentation, clean and actionable error reporting for the console output, and dependency verification that mitigates security risks with compromised dependencies; and the simple property assignment operator (=) operator, introduced in the Kotlin DSL with the last release, is enabled by default. More details on this release may be found in the release notes.
JNation Conference
The JNation conference was held at the Convento São Francisco in Coimbra, Portugal, this past week featuring many speakers from the Java community who presented sessions and workshops on topics such as Project Loom, JavaScript, Java on ARM, WebAssembly, Kubernetes and GraalVM.

MMS • Matt Campbell
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

AWS has open-sourced Cedar, their language for defining access permissions using policies. Cedar is integrated within both Amazon Verified Permissions and AWS Verified Access. Cedar can also be integrated directly into an application via the provided SDK and language specification.
Cedar allows for expressing policies separate from the application code. This decoupling enables them to be independently authored, analyzed, and audited. Cedar supports role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC) approaches.
The SDK can be used for authoring and validating policies as well as authorizing access requests. Cedar is written in Rust but also has both a Rust crate and a Java package to allow for using Cedar from Java.
Validating that a request is authorized can be done by invoking the Cedar authorization engine. The request information is translated into a Cedar request and passed into the Cedar authorization engine. The following example demonstrates this in Rust:
pub fn is_authorized(
&self,
principal: impl AsRef,
action: impl AsRef,
resource: impl AsRef,
) -> Result {
let es = self.entities.as_entities();
let q = Request::new(
Some(principal.as_ref().clone().into()),
Some(action.as_ref().clone().into()),
Some(resource.as_ref().clone().into()),
Context::empty(),
);
info!(
"is_authorized request: principal: {}, action: {}, resource: {}",
principal.as_ref(),
action.as_ref(),
resource.as_ref()
);
let response = self.authorizer.is_authorized(&q, &self.policies, &es);
info!("Auth response: {:?}", response);
match response.decision() {
Decision::Allow => Ok(()),
Decision::Deny => Err(Error::AuthDenied(response.diagnostics().clone())),
}
}
The Cedar authorization engine is invoked via the call self.authorizer.is_authorized(&q, &self.policies, &es). The arguments to the call include the access request, Cedar policies, and the entity set. The access request contains the principal, action, and resource information needed to confirm if the request is permitted. Based on the analysis, the call will return either Decision::Allow or Decision::Deny.
Policies can be created via the SDK as well. The following Java example creates a policy that permits the principal Alice to perform the action View_Photo on any resource that is a child of the Vacation resource:
private Set buildPolicySlice() {
Set ps = new HashSet();
String fullPolicy = "permit(principal == User::"Alice", action == Action::"View_Photo", resource in Album::"Vacation");";
ps.add(new Policy(fullPolicy, "p1"));
return ps;
}
In Java, a query can be performed using the isAuthorized method:
public boolean sampleMethod() throws AuthException {
AuthorizationEngine ae = new WrapperAuthorizationEngine();
AuthorizationQuery q = new AuthorizationQuery("User::"Alice"", "Action::"View_Photo"", "Photo::"pic01"");
return ae.isAuthorized(q, buildSlice()).isAllowed();
}
Permit.io followed the AWS announcement with the release of Cedar-Agent, an HTTP server that acts as a policy store and data store for Cedar-based policies. The store allows for creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting policies. The data store allows for in-memory storage of the application’s data. It integrates with Cedar-Agent to allow for authorization checks to be performed on the stored data. Authorization checks are performed on incoming HTTP requests.
User dadadad100, on a HackerNews post, commented that they saw Cedar potentially filling a gap in the application authorization space:
Cedar falls somewhere between OPA with its datalog (prolog) based search approach and a Zanzibar based approach. It’s not clear which direction will win out, but it is time that this problem got some attention.
Other users, such as Oxbadcafebee, expressed frustration that AWS didn’t lend their support to Open Policy Agent instead.
Cedar is open-source under Apache License 2.0 and is available via GitHub. More details can be found in the recent AWS blog and by joining the Cedar Policy Slack workspace.

MMS • A N M Bazlur Rahman
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

JEP 443, Unnamed Patterns and Variables (Preview), has been Completed from Targeted status for JDK 21. This preview JEP proposes to “enhance the language with unnamed patterns, which match a record component without stating the component’s name or type, and unnamed variables, which can be initialized but not used.” Both of these are denoted by the underscore character, as in r instanceof _(int x, int y) and r instanceof _. This is a preview language feature.
Unnamed patterns are designed to streamline data processing, particularly when working with record classes. They allow developers to elide the type and name of a record component in pattern matching, which can significantly improve code readability. For example, consider the following code snippet:
if (r instanceof ColoredPoint(Point p, Color c)) {
// ...
}
In this instance, if the Color c component is not needed in the if block, it can be laborious and unclear to include it in the pattern. With JEP 443, developers can simply omit unnecessary components, resulting in cleaner, more readable code:
if (r instanceof ColoredPoint(Point p, _)) {
// ...
}
Unnamed variables are useful in scenarios where a variable must be declared, but its value is not used. This is common in loops, try-with-resources statements, catch blocks, and lambda expressions. For instance, consider the following loop:
for (Order order : orders) {
if (total < limit) total++;
}
In this case, the order variable is not used within the loop. With JEP 443, developers can replace the unused variable with an underscore, making the code more concise and clear:
for (_ : orders) {
if (total < limit) total++;
}
Unnamed patterns and variables are a preview feature, disabled by default. To use it, developers must enable the preview feature to compile this code, as shown in the following command:
javac --release 21 --enable-preview Main.java
The same flag is also required to run the program:
java --enable-preview Main
However, one can directly run this using the source code launcher. In that case, the command line would be:
java --source 21 --enable-preview Main.java
The jshell option is also available but requires enabling the preview feature as well:
jshell --enable-preview
Let’s look at a few more advanced use cases of unnamed patterns and variables introduced in JEP 443:
Unnamed patterns can be particularly useful in nested pattern-matching scenarios where only some components of a record class are required. For example, consider a record class ColoredPoint that contains a Point and a Color. If you only need the x coordinate of the Point, you can use an unnamed pattern to omit the y and Color components:
if (r instanceof ColoredPoint(Point(int x, _), _)) {
// ...
}
Unnamed pattern variables can be beneficial in switch statements where the same action is executed for multiple cases, and the variables are not used. For example:
switch (b) {
case Box(RedBall _), Box(BlueBall _) -> processBox(b);
case Box(GreenBall _) -> stopProcessing();
case Box(_) -> pickAnotherBox();
}
In this example, the first two cases use unnamed pattern variables because their right-hand sides do not use the box’s component. The third case uses the unnamed pattern to match a box with a null component.
Unnamed variables can be used in lambda expressions where the parameter is irrelevant. For example, in the following code, the lambda parameter v is not used, so its name is irrelevant:
stream.collect(Collectors.toMap(String::toUpperCase, _ -> "No Data"));
In try-with-resources statements, a resource represents the context in which the code of the try block executes. If the code does not use the context directly, the name of the resource variable is irrelevant. For example:
try (var _ = ScopedContext.acquire()) {
// No use of acquired resource
}
Unnamed variables can be used in catch blocks where the name of the exception parameter is irrelevant. For example:
try {
int i = Integer.parseInt(s);
} catch (NumberFormatException _) {
System.out.println("Bad number: " + s);
}
Notably, the underscore character was previously valid as an identifier in Java 10. However, since Java 8, the use of underscore as an identifier has been discouraged, and it was turned into a compile-time error in Java 9. Therefore, it is assumed that a minimal amount of existing and actively maintained code uses underscore as a variable name. In instances where such code does exist, it will need to be modified to avoid using an underscore as a variable name.
Given this, JEP 443 is a significant step towards making Java code more readable and maintainable. This is particularly beneficial in complex data structures where the shape of the structure is just as important as the individual data items within it. By allowing developers to omit unnecessary components and variables, it reduces code clutter and makes the code easier to understand. As developers gain more experience with this feature, it is expected to become an integral part of Java programming.

MMS • Sergio De Simone
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

GitHub has launched code scanning support for Swift in beta and announced it will include Swift security advisories in its Advisory Database to extend the capabilities of its Dependabot vulnerability monitor.
GitHub code scanning enables receiving actionable security alerts in pull requests, which are shown as a review on the PR Conversation tab. Swift support extends the set of programming languages that GitHub can scan for weaknesses, which already included C/C++, Java/Kotlin, JS/TS, Python, Ruby, C#, and Go.
Having both Kotlin and Swift support is crucial for CodeQL, the engine that powers GitHub code scanning, due to the growing popularity and adoption of these programming languages. Kotlin and Swift are widely used in mobile app development, particularly for Android and iOS platforms.
Currently, code scanning for Swift covers path injection, unsafe web view fetches, cryptographic misuses, processing of unsanitized data, and more. GitHub says they will increase the number of weaknesses Swift code scanning is able to detect as the beta progresses. For the rest of supported languages, code scanning includes nearly 400 checks and strives to keep false positive rate low and precision high, says GitHub.
Code scanning for Swift uses macOS runners, which are more expensive than Linux and Windows runners. Due to this, GitHub recommends building only the code you want to analyze and targeting only one architecture. Currently, Swift versions from 5.4 to 5.7 can be analyzed on macOS, while Swift 5.7.3 can be also analyzed using Linux.
On the supply chain security front, GitHub also announced they will add curated Swift advisories to the Advisory Database and Swift dependencies analysis to dependency graphs. This will enable Dependabot to send alerts about vulnerable dependencies included in Swift projects.
The GitHub Advisory Database contains known security vulnerabilities and malware (still in beta). Advisories can be curated or not curated. The dependency graph includes all the dependencies of a repository, including direct and indirect dependencies, and is generated automatically for all public repositories. According to GitHub, Swift support will come later in June.
On a related note, GitHub has launched a Bug Bounty program for Kotlin and Swift security researchers to submit new CodeQL queries that can uncover new vulnerabilities in Swift and Kotlin programs.