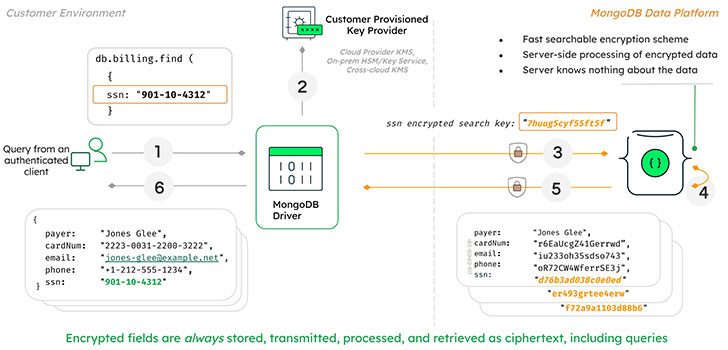
The pursuit of massively distributed databases that can scale horizontally into infinity has led to an explosion of specialized databases, with literally dozens of differing data models and entire products released for hyper-specific use cases.
Aug 16th, 2023 7:15am by

This is the second of a two-part series. Read Part 1.
We left off in 1979, with the release of INGRES and Oracle v2. At that point in history, databases were almost exclusively a tool built for and used by enterprises, developed according to their needs. But then the 1980s arrived (in our opinions, the most fashionable decade) and with them came the desktop computing era and some historically significant hacker movies to go with them.
Computers were no longer something that took up an entire room and required a specialized skill set to operate; they fit on your desk, they were affordable and a lot of the difficulties of interacting with one had been abstracted away.
Initially, a handful of different lightweight databases jockeyed for dominance in the desktop market. When IBM was developing its DOS-based PCs, it commissioned a DOS port of dBase. The IBM PCs were released in 1981 with dBase as one of the first pieces of software available, and it rocketed into popularity.
Interestingly, there is no dBase I — it was originally released as Vulcan and renamed when it was re-released. The name “dBase II” was chosen solely because the “two” implies a second, and thus less-buggy, release. The marketing stunt worked, and dBase II was destined for dominance.

dBase logo
dBase abstracted away a lot of the required but boring and technically complex aspects of interacting with a database, like opening and closing files and managing the allocation of storage space. This ease of use, relative to its predecessors, secured its place in history. Entire businesses sprung up around it, with multiple databases built on top of it and the associated programming language, but none was initially able to unseat it.
dBase remained one of the top-selling pieces of software throughout the ’80s and most of the ’90s, until a single bad release very nearly killed it.
In the 1990s, changes in the way we think about software development pushed databases in a slightly different direction. Object-oriented programming became the dominant design paradigm, and this necessitated a change in the way databases handle data.
Since we began thinking of both our code and our data as reusable objects with associated attributes, we needed to interact with the data in a slightly different way than a lot of databases at the time allowed out of the box. Additional abstraction layers become necessary so that we can think about what we’re doing rather than the specific implementation. This is how we got object-relational mapping tools (ORMs).

Visual FoxPro logo
To answer the needs of object-oriented programming, Microsoft acquired FoxPro and subsequently built Visual FoxPro based on it with support for some object-oriented design features. That acquisition gave them something even more important, though — FoxPro’s query optimization routines, which were built into Microsoft Access, almost immediately making it the most widely-used database in Windows environments.
In 1995, Access began shipping as part of the standard Microsoft Office suite rather than a standalone product, increasing its spread further and solidifying its dominance in the Windows market.
In the 2000s, the widespread popularity of the internet and an ever-present need to scale wider than ever before forced another innovation in databases and NoSQL entered the ring, but let’s go into the name first.
Carlo Strozzi originally used the name “NoSQL” in 1998 for a lightweight database he was developing, but it bears no resemblance to the NoSQL of today. Strozzi was still building a relational database; it just didn’t use SQL. Instead, it used shell scripts. According to Strozzi, today’s NoSQL should more accurately be called NoRel.
The term made a comeback in 2009 thanks to Johan Oskarsson at an event he held in response to the emergence and growth of some new technologies in databases: Google’s BigTable and Amazon’s DynamoDB, as well as their open source clones.
“Open source distributed, non-relational databases” was a bit too wordy and not pithy enough for a Twitter hashtag, though, so Eric Evans of Rackspace suggested an alternative: NoSQL. It took off, and the rest is history.
Back to the technology itself: While relational databases focus on ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability), non-relational databases focus on CAP (consistency, availability, partition tolerance) theorem. The idea is that no distributed system is immune to network failures by its very nature, so you may only have two of the three. When a failure occurs, a choice has to be made to ensure consistency by canceling the operation, which sacrifices availability, or ensure availability by continuing with the operation, sacrificing consistency.
Most distributed databases address this shortfall by offering “eventual consistency,” wherein changes aren’t necessarily propagated to all nodes at the same time, but within a few milliseconds of one another.

NoSQL
Usually, when people think about a NoSQL database, they’re thinking about something using a document model, similar to MongoDB. The playing field is much wider than that, though — we have several different flavors of key-value databases like Redis, wide column stores like DynamoDB, graph databases like Neo4j, hybrid databases that implement all these models like CosmosDB and more. These all have different strengths, weaknesses and use cases, but they all store denormalized data and generally do not support joint operations.
The pursuit of massively distributed databases that can scale horizontally into infinity has led to an explosion of specialized databases, with literally dozens of differing data models and entire products released for hyper-specific use cases. Technically, the world wide web itself is a large, distributed hypertext database.
Between the variety of relational and non-relational databases available today, the modern era is the database era. Nearly every action we take to interact with the world today is a database action made possible in large part by technology that originated before most of the people building the tools of the future were even born, with decades of iterative growth in between, and we’re moving faster than ever before. What will speed and scale mean to us in another 60 years?
Created with Sketch.










 Global Retirement Partners LLC increased its position in MongoDB, Inc. (
Global Retirement Partners LLC increased its position in MongoDB, Inc. (