Month: March 2022

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts
New Jersey, United States – This NoSQL Databases Software Market report provides a comprehensive overview of important aspects that will drive market growth such as Market drivers, restraints, prospects, opportunities, restraints, current trends, and technical and industrial advancements. The detailed industry study, industry sector development and improvement, and new product launches presented in this NoSQL Databases Software market report are of tremendous help to the significant new commercial entrants entering the market. This NoSQL Databases Software market report carries out an attentive market assessment and offers an expert analysis of the market considering the market development the current market situation and future projections. This NoSQL Databases Software market report study further highlights the market driving factors, market overview, industry volume, and market share. Since this NoSQL Databases Software market report offers an effective market strategy, key players can reap huge profits by making the right investments in the market. As this NoSQL Databases Software Market report depicts the ever-changing needs of consumers, sellers, and buyers across different regions, it becomes easy to target specific products and attain significant revenue in the global market.
Get Full PDF Sample Copy of Report: (Including Full TOC, List of Tables & Figures, Chart) @ https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com/download-sample/?rid=87212
The report includes company profiles of almost all the major players operating in the NoSQL Databases Software market. The Company Profiles section provides valuable analysis of key market players’ strengths and weaknesses, business developments, recent advances, mergers and acquisitions, expansion plans, global footprint, market presence, and product portfolios. This information can be used by players and other market participants to maximize their profitability and streamline their business strategies. Our competitive analysis also includes key insights to help new entrants identify barriers to entry and assess the level of competitiveness in the NoSQL Databases Software market.
Key Players Mentioned in the NoSQL Databases Software Market Research Report:
MongoDB, Amazon, ArangoDB, Azure Cosmos DB, Couchbase, MarkLogic, RethinkDB, CouchDB, SQL-RD, OrientDB, RavenDB, Redis
NoSQL Databases Software Market Segmentation:
By the product type, the market is primarily split into:
• Cloud Based
• Web Based
By the application, this report covers the following segments:
• Large Enterprises
• SMEs
The study included in this report will help organizations in understanding the top threats and opportunities faced by retailers in the global market. In addition, the study provides an overview of the competitive landscape as well as a SWOT analysis. This report provides detailed information about product or technological developments in the NoSQL Databases Software market and an overview of the impact of these developments on the potential growth of the market.
In order to maintain their supremacy in the NoSQL Databases Software industry, the majority of companies are currently implementing new technologies, strategies, product innovations, expansions, and long-term contracts. After reviewing key companies, the report focuses on startups driving business growth. The report’s authors identify possible mergers and acquisitions between the startups and key organizations in the study. Big players are working hard to adopt the latest technologies to gain a strategic advantage over the competition as new technologies are introduced regularly.
Get Discount On The Purchase Of This Report @ https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com/ask-for-discount/?rid=87212
NoSQL Databases Software Market Report Scope
| ATTRIBUTES | DETAILS |
|---|---|
| ESTIMATED YEAR | 2022 |
| BASE YEAR | 2021 |
| FORECAST YEAR | 2029 |
| HISTORICAL YEAR | 2020 |
| UNIT | Value (USD Million/Billion) |
| SEGMENTS COVERED | Types, Applications, End-Users, and more. |
| REPORT COVERAGE | Revenue Forecast, Company Ranking, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
| BY REGION | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| CUSTOMIZATION SCOPE | Free report customization (equivalent up to 4 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
Geographic Segment Covered in the Report:
The NoSQL Databases Software report provides information about the market area, which is further subdivided into sub-regions and countries/regions. In addition to the market share in each country and sub-region, this chapter of this report also contains information on profit opportunities. This chapter of the report mentions the market share and growth rate of each region, country, and sub-region during the estimated period.
• North America (USA and Canada)
• Europe (UK, Germany, France and the rest of Europe)
• Asia Pacific (China, Japan, India, and the rest of the Asia Pacific region)
• Latin America (Brazil, Mexico, and the rest of Latin America)
• Middle East and Africa (GCC and rest of the Middle East and Africa)
Key questions answered in the report:
1. Which are the five top players in the NoSQL Databases Software market?
2. How will the NoSQL Databases Software market change in the next five years?
3. Which product and application will take a lion’s share of the NoSQL Databases Software market?
4. What are the drivers and restraints of the NoSQL Databases Software market?
5. Which regional market will show the highest growth?
6. What will be the CAGR and size of the NoSQL Databases Software market throughout the forecast period?
For More Information or Query or Customization Before Buying, Visit @ https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com/product/global-nosql-databases-software-market-growth-status-and-outlook-2019-2024/
Visualize NoSQL Databases Software Market using Verified Market Intelligence:-
Verified Market Intelligence is our BI-enabled platform for narrative storytelling of this market. VMI offers in-depth forecasted trends and accurate Insights on over 20,000+ emerging & niche markets, helping you make critical revenue-impacting decisions for a brilliant future.
VMI provides a holistic overview and global competitive landscape with respect to Region, Country, and Segment, and Key players of your market. Present your Market Report & findings with an inbuilt presentation feature saving over 70% of your time and resources for Investor, Sales & Marketing, R&D, and Product Development pitches. VMI enables data delivery In Excel and Interactive PDF formats with over 15+ Key Market Indicators for your market.
Visualize NoSQL Databases Software Market using VMI @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/vmintelligence/
Top Trending Reports
Global Cryptocurrency Software Market Size And Forecast
Global Cryptocurrency Exchanges Market Size And Forecast
Global Big Data Analytics Software Market Size And Forecast
Global Key-Value Stores Market Size And Forecast
Global Document Databases Software Market Size And Forecast
Global NoSQL Databases Software Market Size And Forecast
Global Learning Management System (LMS) Software Market Size And Forecast
Global Student Information Systems SIS Software Market Size And Forecast
Global Higher Education Student Information Systems Software Market Size And Forecast
Global Language Learning Software Market Size And Forecast
About Us: Verified Market Reports
Verified Market Reports is a leading Global Research and Consulting firm servicing over 5000+ global clients. We provide advanced analytical research solutions while offering information-enriched research studies.
We also offer insights into strategic and growth analyses and data necessary to achieve corporate goals and critical revenue decisions.
Our 250 Analysts and SME’s offer a high level of expertise in data collection and governance using industrial techniques to collect and analyze data on more than 25,000 high-impact and niche markets. Our analysts are trained to combine modern data collection techniques, superior research methodology, expertise, and years of collective experience to produce informative and accurate research.
Our research spans over a multitude of industries including Energy, Technology, Manufacturing and Construction, Chemicals and Materials, Food and Beverages etc. Having serviced many Fortune 2000 organizations, we bring a rich and reliable experience that covers all kinds of research needs.
Contact us:
Mr. Edwyne Fernandes
US: +1 (650)-781-4080
UK: +44 (753)-715-0008
APAC: +61 (488)-85-9400
US Toll-Free: +1 (800)-782-1768
Email: sales@verifiedmarketreports.com
Website: – https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com/
NoSQL Software market to showcase an annual healthy growth rate over 2021-2026 – Running Africa

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts

The Global NoSQL Software Market report provides information about the Global industry, including valuable facts and figures. This research study explores the Global Market in detail such as industry chain structures, raw material suppliers, with manufacturing the NoSQL Software Sales market examines the primary segments of the scale of the market. This intelligent study provides historical data forecast from 2020 to 2025.
The recent study of NoSQL Software market assists companies in gaining a competitive advantage in the industry vertical by scrutinizing the factors that have been crucial for the market expansion. It expounds on major global developments, prevalent tactics, and prospects in order to draft effectual business plans.
The document contains a holistic analysis of this business sphere, with regards to primary growth catalysts, constraints, and opportunities shaping the market dynamics during the analysis timeframe.
Request Sample Copy of this Report @ https://www.runningafrica.com/request-sample/5837
Furthermore, it provides insights of the market share alongside estimates pertaining to the growth rate over the forecast period. In hindsight of the COVID-19 pandemic, the report suggests prevalent strategies for stakeholders to make well-informed decisions in order to adapt to the industry uncertainties.
Key pointers from the TOC of the NoSQL Software market report:
Product terrain
- Product gamut: Cloud Based and Web Based
- Estimates reflecting the growth rate of each product segment during the analysis timeframe.
- Market share and total revenue amassed by each product segment.
Application scope
- Application spectrum: E-Commerce , Social Networking , Data Analytics , Data Storage and Others
- Market share held by each application segment.
- Expected growth rate of each application segment over the forecast period.
Regional analysis
- Regional bifurcation: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa
- Details encircling sales & revenue netted by each regional contributor.
- Deep-dive investigation of each regional market, inclusive of their projected CAGR.
Competitive landscape
- Key participants:
- MongoDB
- Amazon
- ArangoDB
- Azure Cosmos DB
- Couchbase
- MarkLogic
- RethinkDB
- CouchDB
- SQL-RD
- OrientDB
- RavenDB
- Redis and Microsoft
- In-depth profile of the listed players alongside their product portfolio, key applications, production patterns, and market remuneration.
- A summary of revenue share, sales graph, pricing models, and manufacturing costs of each partaker.
- Latest developments including strategic alliances, acquisitions, mergers, and expansion proposals.
To summarize, the NoSQL Software market report thoroughly analyzes the industry through various segments and offers an in-depth scrutiny of the sales channel and supply chain in terms of upstream traders, distributors, and downstream consumers in this business domain.
Strategic Analysis Covered in TOC: – Key Topics Covered
- Introduction
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Global NoSQL Software Competitor Landscape by Players
- Market Size by Type (2015-2025)
- Market Size by Application (2015-2025)
- NoSQL Software Market, By Region
- Competitive Landscape
- Company Profile
Request Customization on This Report @ https://www.runningafrica.com/request-for-customization/5837

MMS • Steef-Jan Wiggers
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ
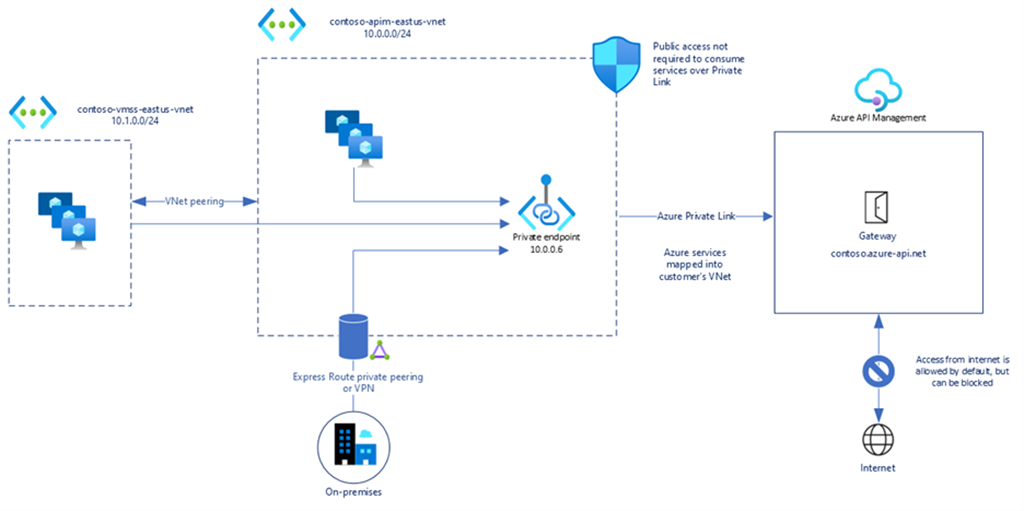
Recently, Microsoft announced the preview of Azure Private Link support for Azure API Management service, a fully managed service that enables customers to publish, secure, transform, maintain, and monitor APIs.
With the Private Link support, customers can now configure a private endpoint for their API Management instance to allow clients in their private network to securely access the instance over Azure Private Link. Moreover, communications between the customers’ virtual network and the Azure API Management gateway travel over the Microsoft backbone network privately and securely, eliminating the need to expose the service to the public internet. Earlier, only the Developer and Premium tiers of API Management supported VNET integration. However, with the Private Link support, customers can privately integrate with clients in a virtual network, using the API Management tiers- Developer, Basic, Standard, and Premium.
Customers can use Azure Private Link to create a private endpoint for the gateway component, which will be accessible via a private IP address within their virtual network. This endpoint allows inbound traffic to the private IP address to reach the Azure API Management gateway.
Jeff Hollan, Director of Product for Azure Apps at Microsoft, tweeted:
Often with PaaS services, the hardware itself isn’t running in your private network. So you don’t have like a dedicated IP or VM. Private Link lets you secure traffic through a VNet, even in those cases. More a different approach/way of trying to provide similar functionality. So, in this case – now the “basic” tier of APIM can have secured VNet inbound requests.
In addition, Fernando Mejia, a Senior Program Manager, Azure API Management, stated in an Azure blog post on the Private Link support for API Management:
With the preview of Azure Private Link for Azure API Management, you are now empowered to bring your Azure API Management instances to a virtual network using the same consistent experience of other Azure PaaS services. You can create and manage private endpoints for the gateway of your Azure API Management instance. We will be sharing more updates and content in the future, so stay tuned for new updates towards the general availability of this feature.
Currently, Microsoft will only support inbound traffic coming to the gateway, instances using the STV2 compute platform, all pricing tiers except consumption, and Azure Private Link is limited to instances not using virtual network injection (internal or external).

MMS • RSS
Posted on mongodb google news. Visit mongodb google news

It’s been a wild ride over the past six years as ZDNet gave us the opportunity to chronicle how, in the data world, bleeding edge has become the norm. In 2016, Big Data was still considered the thing of early adopters. Machine learning was confined to a relative handful of Global 2000 organizations, because they were the only ones who could afford to recruit teams from the limited pool of data scientists. The notion that combing through hundreds of terabytes or more of structured and variably structured data would become routine was a pipedream. When we began our part of Big on Data, Snowflake, which cracked open the door to the elastic cloud data warehouse that could also handle JSON, was barely a couple years post stealth.
In a short piece, it’s going to be impossible to compress all the highlights of the last few years, but we’ll make a valiant try.
The Industry Landscape: A Tale of Two Cities
When we began our stint at ZDNet, we’d already been tracking the data landscape for over 20 years. So at that point, it was all too fitting that our very first ZDNet post on July 6, 2016, looked at the journey of what became one of the decade’s biggest success stories. We posed the question, “What should MongoDB be when it grows up?” Yes, we spoke of the trials and tribulations of MongoDB, pursuing what cofounder and then-CTO Elliot Horowitz prophesized, that the document form of data was not only a more natural form of representing data, but would become the default go-to for enterprise systems.
MongoDB got past early performance hurdles with an extensible 2.0 storage engine that overcame a lot of the platform’s show-stoppers. Mongo also began grudging coexistence with features like the BI Connector that allowed it to work with the Tableaus of the world. Yet today, even with relational database veteran Mark Porter taking the tech lead helm, they are still drinking the same Kool Aid that document is becoming the ultimate end state for core enterprise databases.
We might not agree with Porter, but Mongo’s journey revealed a couple core themes that drove the most successful growth companies. First, don’t be afraid to ditch the 1.0 technology before your installed base gets entrenched, but try keeping API compatibility to ease the transition. Secondly, build a great cloud experience. Today, MongoDB is a public company that is on track to exceed $1 billion in revenues (not valuation), with more than half of its business coming from the cloud.
We’ve also seen other hot startups not handle the 2.0 transition as smoothly. InfluxDB, a time series database, was a developer favorite, just like Mongo. But Influx Data, the company, frittered away early momentum because it got to a point where its engineers couldn’t say “No.” Like Mongo, they also embraced a second generation architecture. Actually, they embraced several of them. Are you starting to see a disconnect here? Unlike MongoDB, InfluxDB’s NextGen storage engine and development environments were not compatible with the 1.0 installed base, and surprise, surprise, a lot of customers didn’t bother with the transition. While MongoDB is now a billion dollar public company, Influx Data has barely drawn $120 million in funding to date, and for a company of its modest size, is saddled with a product portfolio that grew far too complex.
It’s no longer Big Data
It shouldn’t be surprising that the early days of this column were driven by Big Data, a term that we used to capitalize because it required unique skills and platforms that weren’t terribly easy to set up and use. The emphasis has shifted to “data” thanks, not only to the equivalent of Moore’s Law for networking and storage, but more importantly, because of the operational simplicity and elasticity of the cloud. Start with volume: You can analyze pretty large multi-terabyte data sets on Snowflake. And in the cloud, there are now many paths to analyzing the rest of The Three V’s of big data; Hadoop is no longer the sole path and is now considered a legacy platform. Today, Spark, data lakehouses, federated query, and ad hoc query to data lakes (a.k.a., cloud storage) can readily handle all the V’s. But as we stated last year, Hadoop’s legacy is not that of historical footnote, but instead a spark (pun intended) that accelerated a virtuous wave of innovation that got enterprises over their fear of data, and lots of it.
Over the past few years, the headlines have pivoted to cloud, AI, and of course, the continuing saga of open source. But peer under the covers, and this shift in spotlight was not away from data, but because of it. Cloud provided economical storage in many forms; AI requires good data and lots of it, and a large chunk of open source activity has been in databases, integration, and processing frameworks. It’s still there, but we can hardly take it for granted.
Hybrid cloud is the next frontier for enterprise data
The operational simplicity and the scale of the cloud control plane rendered the idea of marshalling your own clusters and taming the zoo animals obsolete. Five years ago, we forecast that the majority of new big data workloads would be in the cloud by 2019; in retrospect, our prediction proved too conservative. A couple years ago, we forecast the emergence of what we termed The Hybrid Default, pointing to legacy enterprise applications as the last frontier for cloud deployment, and that the vast majority of it would stay on-premises.
That’s prompted a wave of hybrid cloud platform introductions, and newer options from AWS, Oracle and others to accommodate the needs of legacy workloads that otherwise don’t translate easily to the cloud. For many of those hybrid platforms, data was often the very first service to get bundled in. And we’re also now seeing cloud database as a service (DBaaS) providers introduce new custom options to capture many of those same legacy workloads where customers require more access and control over operating system, database configurations, and update cycles compared to existing vanilla DBaaS options. Those legacy applications, with all their customization and data gravity, are the last frontier for cloud adoption, and most of it will be hybrid.
The cloud has to become easier
The data cloud may be a victim of its own success if we don’t make using it any easier. It was a core point in our parting shot in this year’s outlook. Organizations that are adopting cloud database services are likely also consuming related analytic and AI services, and in many cases, may be utilizing multiple cloud database platforms. In a managed DBaaS or SaaS service, the cloud provider may handle the housekeeping, but for the most part, the burden is on the customer’s shoulders to integrate use of the different services. More than a debate between specialized vs. multimodel or converged databases, it’s also the need to either bundle related data, integration, analytics, and ML tools end-to-end, or to at least make these services more plug and play. In our Data 2022 outlook, we called on cloud providers to start “making the cloud easier” by relieving the customer of some of this integration work.
One place to start? Unify operational analytics and streaming. We’re starting to see it Azure Synapse bundling in data pipelines and Spark processing; SAP Data Warehouse Cloud incorporating data visualization; while AWS, Google, and Teradata bring in machine learning (ML) inference workloads inside the database. But folks, this is all just a start.
And what about AI?
While our prime focus in this space has been on data, it is virtually impossible to separate the consumption and management of data from AI, and more specifically, machine learning (ML). It’s several things: using ML to help run databases; using data as the oxygen for training and running ML models; and increasingly, being able to process those models inside the database.
And in many ways, the growing accessibility of ML, especially through AutoML tools that automate or simplify putting the pieces of a model together or the embedding of ML into analytics is reminiscent of the disruption that Tableau brought to the analytics space, making self-service visualization table stakes. But ML will only be as strong as its weakest data link, a point that was emphasized to us when we in-depth surveyed a baker’s dozen of chief data and analytics officers a few years back. No matter how much self-service technology you have, it turns out that in many organizations, data engineers will remain a more precious resource than data scientists.
Open source remains the lifeblood of databases
Just as AI/ML has been a key tentpole in the data landscape, open source has enabled this Cambrian explosion of data platforms that, depending on your perspective, is blessing or curse. We’ve seen a lot of cool modest open source projects that could, from Kafka to Flink, Arrow, Grafana, and GraphQL take off from practically nowhere.
We’ve also seen petty family squabbles. When we began this column, the Hadoop open source community saw lots of competing overlapping projects. The Presto folks didn’t learn Hadoop’s lesson. The folks at Facebook who threw hissy fits when the lead developers of Presto, which originated there, left to form their own company. The result was stupid branding wars that resulted in Pyric victory: the Facebook folks who had little to do with Presto kept the trademark, but not the key contributors. The result fractured the community, knee-capping their own spinoff. Meanwhile, the top five contributors joined Starburst, the company that was exiled from the community, whose valuation has grown to 3.35 billion.
One of our earliest columns back in 2016 posed the question on whether open source software has become the default enterprise software business model. Those were innocent days; in the next few years, shots started firing over licensing. The trigger was concern that cloud providers were, as MariaDB CEO Michael Howard put it, strip mining open source (Howard was referring to AWS). We subsequently ventured the question of whether open core could be the salve for open source’s growing pains. In spite of all the catcalls, open core is very much alive in what players like Redis and Apollo GraphQL are doing.
MongoDB fired the first shot with SSPL, followed by Confluent, CockroachDB, Elastic, MariaDB, Redis and others. Our take is that these players had valid points, but we grew concerned about the sheer variation of quasi open source licenses du jour that kept popping up.
Open source to this day remains a topic that gets many folks, on both sides of the argument, very defensive. The piece that drew the most flame tweets was our 2018 post on DataStax attempting to reconcile with the Apache Cassandra community, and it’s notable today that the company is bending over backwards not to throw its weight around in the community.
So it’s not surprising that over the past six years, one of our most popular posts posed the question, Are Open Source Databases Dead? Our conclusion from the whole experience is that open source has been an incredible incubator of innovation – just ask anybody in the PostgreSQL community. It’s also one where no single open source strategy will ever be able to satisfy all of the people all of the time. But maybe this is all academic. Regardless of whether the database provider has a permissive or restrictive open source license, in this era where DBaaS is becoming the preferred mode for new database deployments, it’s the cloud experience that counts. And that experience is not something you can license.
Don’t forget data management
As we’ve noted, looking ahead is the great reckoning on how to deal with all of the data that is landing in our data lakes, or being generated by all sorts of polyglot sources, inside and outside the firewall. The connectivity promised by 5G promises to bring the edge closer than ever. It’s in large part fueled the emerging debate over data meshes, data lakehouses, and data fabrics. It’s a discussion that will consume much of the oxygen this year.
It’s been a great run at ZDNet but it’s time to move on. Big on Data is moving. Big on Data bro Andrew Brust and myself are moving our coverage under a new banner, The Data Pipeline, and we hope you’ll join us for the next chapter of the journey.
Stay connected with us on social media platform for instant update click here to join our Twitter, & Facebook
Article originally posted on mongodb google news. Visit mongodb google news
Zacks: Brokerages Anticipate MongoDB, Inc. (NASDAQ:MDB) to Post -$0.13 Earnings Per Share

MMS • RSS
Posted on mongodb google news. Visit mongodb google news
 Equities analysts expect that MongoDB, Inc. (NASDAQ:MDB – Get Rating) will announce earnings per share of ($0.13) for the current fiscal quarter, Zacks Investment Research reports. Five analysts have issued estimates for MongoDB’s earnings, with the highest EPS estimate coming in at ($0.08) and the lowest estimate coming in at ($0.30). MongoDB posted earnings per share of ($0.15) in the same quarter last year, which suggests a positive year-over-year growth rate of 13.3%. The company is scheduled to issue its next quarterly earnings report on Monday, January 1st.
Equities analysts expect that MongoDB, Inc. (NASDAQ:MDB – Get Rating) will announce earnings per share of ($0.13) for the current fiscal quarter, Zacks Investment Research reports. Five analysts have issued estimates for MongoDB’s earnings, with the highest EPS estimate coming in at ($0.08) and the lowest estimate coming in at ($0.30). MongoDB posted earnings per share of ($0.15) in the same quarter last year, which suggests a positive year-over-year growth rate of 13.3%. The company is scheduled to issue its next quarterly earnings report on Monday, January 1st.
On average, analysts expect that MongoDB will report full year earnings of ($0.46) per share for the current year, with EPS estimates ranging from ($0.74) to ($0.33). For the next year, analysts anticipate that the business will post earnings of $0.03 per share, with EPS estimates ranging from ($0.11) to $0.19. Zacks’ earnings per share calculations are a mean average based on a survey of research analysts that follow MongoDB.
MongoDB (NASDAQ:MDB – Get Rating) last posted its quarterly earnings data on Tuesday, March 8th. The company reported ($0.09) EPS for the quarter, topping analysts’ consensus estimates of ($1.26) by $1.17. The company had revenue of $266.50 million for the quarter, compared to analyst estimates of $243.42 million. MongoDB had a negative return on equity of 66.70% and a negative net margin of 35.12%. The business’s revenue was up 55.8% on a year-over-year basis. During the same quarter in the previous year, the firm earned ($1.01) earnings per share.
Looking to invest into DeFi? Kevin O’Leary’s stock pick could be the way to go.
A number of research firms have commented on MDB. Stifel Nicolaus lowered their price objective on MongoDB from $550.00 to $425.00 in a research note on Wednesday, March 9th. Barclays cut their price objective on MongoDB from $556.00 to $410.00 and set an “overweight” rating on the stock in a report on Wednesday, March 9th. Piper Sandler lifted their target price on MongoDB from $525.00 to $585.00 and gave the stock an “overweight” rating in a report on Tuesday, December 7th. Canaccord Genuity Group lowered their price objective on MongoDB from $560.00 to $400.00 in a research report on Wednesday, March 9th. Finally, Credit Suisse Group decreased their target price on MongoDB from $700.00 to $650.00 and set an “outperform” rating for the company in a research report on Wednesday, March 9th. One investment analyst has rated the stock with a sell rating, one has given a hold rating and fifteen have assigned a buy rating to the company’s stock. According to MarketBeat, the stock has a consensus rating of “Buy” and an average price target of $496.72.
In related news, CEO Dev Ittycheria sold 35,000 shares of the firm’s stock in a transaction that occurred on Friday, March 4th. The shares were sold at an average price of $309.78, for a total transaction of $10,842,300.00. The sale was disclosed in a filing with the Securities & Exchange Commission, which is accessible through the SEC website. Also, CRO Cedric Pech sold 290 shares of the firm’s stock in a transaction that occurred on Monday, January 3rd. The shares were sold at an average price of $515.05, for a total transaction of $149,364.50. The disclosure for this sale can be found here. Insiders sold 180,362 shares of company stock valued at $75,246,152 over the last 90 days. 7.40% of the stock is currently owned by company insiders.
A number of large investors have recently bought and sold shares of MDB. Confluence Wealth Services Inc. purchased a new position in shares of MongoDB during the 4th quarter worth $25,000. Quent Capital LLC bought a new stake in MongoDB in the 4th quarter valued at $26,000. Arlington Partners LLC bought a new stake in MongoDB in the 4th quarter valued at $30,000. Winch Advisory Services LLC increased its holdings in shares of MongoDB by 54.2% in the 3rd quarter. Winch Advisory Services LLC now owns 74 shares of the company’s stock worth $35,000 after buying an additional 26 shares during the last quarter. Finally, HBC Financial Services PLLC increased its holdings in shares of MongoDB by 3,233.3% in the 4th quarter. HBC Financial Services PLLC now owns 400 shares of the company’s stock worth $39,000 after buying an additional 388 shares during the last quarter. 89.57% of the stock is owned by institutional investors and hedge funds.
Shares of MDB stock traded up $7.62 on Tuesday, hitting $428.54. 4,478 shares of the stock were exchanged, compared to its average volume of 1,722,669. The business has a 50-day moving average of $379.86 and a 200 day moving average of $456.87. MongoDB has a fifty-two week low of $238.01 and a fifty-two week high of $590.00. The company has a current ratio of 4.02, a quick ratio of 4.02 and a debt-to-equity ratio of 1.70. The firm has a market capitalization of $28.96 billion, a P/E ratio of -90.41 and a beta of 0.83.
MongoDB Company Profile (Get Rating)
MongoDB, Inc engages in the development and provision of a general-purpose database platform. The firm’s products include MongoDB Enterprise Advanced, MongoDB Atlas and Community Server. It also offers professional services including consulting and training. The company was founded by Eliot Horowitz, Dwight A.
Read More
Get a free copy of the Zacks research report on MongoDB (MDB)
For more information about research offerings from Zacks Investment Research, visit Zacks.com
This instant news alert was generated by narrative science technology and financial data from MarketBeat in order to provide readers with the fastest and most accurate reporting. This story was reviewed by MarketBeat’s editorial team prior to publication. Please send any questions or comments about this story to [email protected]
Should you invest $1,000 in MongoDB right now?
Before you consider MongoDB, you’ll want to hear this.
MarketBeat keeps track of Wall Street’s top-rated and best performing research analysts and the stocks they recommend to their clients on a daily basis. MarketBeat has identified the five stocks that top analysts are quietly whispering to their clients to buy now before the broader market catches on… and MongoDB wasn’t on the list.
While MongoDB currently has a “Buy” rating among analysts, top-rated analysts believe these five stocks are better buys.
Article originally posted on mongodb google news. Visit mongodb google news

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts
Cisco’s HyperFlex hyperconverged system is embracing disaggregated storage. A HyperFlex iSCSI feature can provide storage outside of the HyperFlex cluster. This makes it equivalent to HPE Nimble’s DHCI design. It’s said to be suitable for Windows failover clustering, Oracle database and Oracle RAC, and Microsoft Exchange. The HyperFlex iSCSI feature is available from Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform Release 4.5 and higher.
…
The Aerospike Real-time Data Platform is now certified with Red Hat OpenShift for Aerospike Kubernetes Operator 2.0 and enables OpenShift customers to deploy Aerospike in a familiar and standardized environment. Google Cloud Platform customers will have access to the Aerospike Cloud Managed Service to manage and maintain their Aerospike Real-time Data Platform.
…
MLOps provider Iguazio says Latin America airlines group LATAM has selected its MLOps platform for a large scale, cross-company AI project. The use cases include optimizing and safeguarding the company’s frequent flyer program from fraud, improving pilot training through better understanding of the factors that create un-stabilized approaches to landing, and intelligent route planning to reduce CO2 emissions. LATAM works extensively with GCP, utilizing tools like Google Big Query, Google Cloud Storage and Google Workload Identity. Iguazio is fully compatible with GCP and has a strong partnership with Google. LATAM is planning to deploy its AI products on GCP using Iguazio.
…
Hyperscale data analytics storage provider Ocient has announced a partnership with Basis Technologies for its next-generation campaign forecasting, inventory analysis, and bid shading solution. With the implementation of Ocient, Basis Technologies says it was able to consolidate 10 workloads on a single cluster, decreasing time to query from 24 hours to minutes or less, and reduce system costs by 30 percent. Basis has 30 billion auction records, over 100 billion rows in the system, and over 5 trillion data points in some columns in its NoSQL database.
…
Kubernetes-native data platform provider Ondat is teaming up with SUSE to deliver management of digital authentication credentials (secrets management) in Kubernetes to protect access to sensitive data for SunnyVision, a data center infrastructure service provider. With SUSE Rancher and built-in Trousseau, SunnyVision can now use the native Kubernetes way to store and access secrets by plugging into Hashicorp Vault using the Kubernetes KMS provider framework. No additional changes or new skills are required.
…
Pure Storage has published its inaugural Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) report, which provides visibility into the company’s current metrics and sets commitments for the future. As part of this ESG report, Pure conducted a product life cycle assessment (LCA) of its portfolio, specifically the FlashArray products, which found that Pure customers achieve up to 80 percent reduction in direct carbon usage by data systems compared to competitive products. Pure said it is committing to several goals to reduce its own carbon footprint, making progress against Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, focused both on company operations and the use phase of Pure products:
- 50 percent intensity reduction in market-based Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions per employee from FY20 to FY30
- Achieve net zero market-based Scope 1 and 2 emissions by FY40
- 66 percent intensity reduction in use of sold products from Scope 3 emissions per effective petabyte shipped from FY20 to FY30
Read the report here.
…
In-memory computing supplier ScaleOut Software has announced support for Redis clients in ScaleOut StateServer Version 5.11 as a community preview. Redis users can use the company’s flagship distributed caching product to connect to a cluster of ScaleOut servers and execute Redis commands. Unlike open-source Redis, ScaleOut StateServer implements fully consistent updates to stored data. In addition, ScaleOut StateServer’s native APIs run alongside Redis commands and incorporate advanced features, such as data-parallel computing, streaming analytics, and coherent, wide-area data replication that are not available on open source Redis clusters.
…
SingleStore has hired Shireesh Thota as senior veep for engineering. Thota will lead the company’s engineering efforts and oversee the design and development of the SingleStore DB product. Yatharth Gupta will head up product management and design as veep of products and growth. Both Thota and Gupta will report directly to CEO Raj Verma. Thota previously ran the engineering ops for Cosmos DB and Postgres Hyperscale (Citus) services at Microsoft, where he worked in multiple roles for more than 15 years.
…
Snowflake today revealed an extension of its relationship with Amazon Web Services intended to improve demand forecasting and delivery for the retail and consumer packaged goods (CPG) industries. The partnership means that retail brands and CPGs can process, analyse and syndicate data from a multitude of sources through Snowflake’s integrated platform, without the delays of traditional methods which require copying and moving data, Snowflake says. Customers will also have access to new data from third-party data providers within Snowflake’s Retail Data Cloud.
…

Taipei-based TEAMGROUP has released its ELITE SO-DIMM DDR5 Standard Memory, which runs at the all-new ultra-high clock speed of 4,800MHz – is up to 50 percent higher than DDR4’s maximum of 3,200MHz. It comes in both single and dual-channel kits. The ELITE SO-DIMM DDR5 Standard Memory is a good choice for laptop users looking for a large performance upgrade without hassle, or so TEAMGROUP says.
From building core systems of Meta, Instagram, Netflix to helping power Web 3.0, the … – YourStory

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts

Prashant Malik, is a known name in the global tech and open source community. As the co-creator of Cassandara, a NoSQL database management system, Prashant is known to have built the system that powers the likes of – Facebook (Meta), Instagram, Netflix, and Apple.
Today, he runs Tykhe Block Ventures, an investment firm founded in 2021 focussed on Web 3.0 organisations.
“Technology is about transformation and change and it is ever evolving. When I came back to India, I built a startup and was mentoring and advising a few blockchain startups and after a few investments I decided to invest in a few startups in the space, and build Tykhe Block Ventures,” Prashant said at YourStory’s Future of Work 2022 summit.
Prashant Malik with the Limeroad team and Neha Dhupia
He explained the world of Web 3.0 is transforming how we look at everything. And that was the cusp for web 2.0 when he along with Avinash Lakshman built Cassandara.
“The idea of building something with NoSQL and later open sourcing it was completely unheard of, and many within the team itself were wary of whether it would work. In fact there was another team working on BigTable, but that couldn’t pan out,” Prashant said.
He explained when the duo were building Cassandara, everything was to be built from scratch. “Nothing like that ever existed, and we didn’t know if it was even manageable and if it could work. But we also knew in our gut it was something new and different. And could change the way we operate, and that is what today Web 3.0 can do.”
The duo had built the database management system to help manage the growing number of users on Meta, then Facebook. After the system was built, the team put it up on the open source network.
“It wasn’t very common to put things on the Open Source. Facebook (Meta), always believed in Open Source. I never realised the scale the platform would take, but then soon everyone needed a database management system that could take in volumes of users,” shared Prashant.
It was his experience of building Cassandara that opened Prashant to the idea of building newer systems and products. “If the product can solve a large enough problem and change the way systems work, it can create a unique method of working and building and also transform what organisations, and consumers can do,” he said.
The idea he added was to open up systems and democratise the database systems making it easy for anyone to build and scale on top of, and that is what the new era of Web 3.0 is all about. It is about creating open environments where people can thrive.
“Within six months of my joining in 2007, we opened Facebook to the world. Anybody with an email ID could now join Facebook. Those were the days when we would end the day with 10 million new users, and begin the next day with 15 to 20 million users. As the days passed, people were coming in hordes, systems kept breaking, and we had to build batches over and over again, every six hours.”
And it is the core on which Facebook (Meta), Instagram, Netflix, and Apple run even today.
“We were a small team then and we didn’t know the scale of what we were building. From the universities the platform had started grabbing eyeballs and was onboarding more users, this meant we needed a database that could accommodate more users,” explained Prashant.
The software database needed to be upgraded in order to accommodate more users. “While there already was Google’s Big Table we knew we needed a database infrastructure that did not follow the rules and norms that were then present.” It was this shift that got him to look at building Cassandra.
At that point in time, there was only MySQL, which didn’t scale that fast. Prashant says Mark kept mentioning there was a need for a system like BigTable, and they started building on a similar architecture.
Soon, Prashant was joined by Avinash Lakshman, who had worked on the Dynamo Project at Amazon, which hadn’t seen production scale, and was theoretical in nature. But the core concepts were strong.
“When both of us got together, something magical happened. We thought why not bring BigTable on top of Dynamo? This led to the beginning of building Cassandra. We had named it after an oracle in Greek mythology. We thought it would become bigger than Oracle. And I don’t think anywhere else in the world we could build that kind of project as nobody would trust two guys to go and build something this big. But Facebook had that DNA – to give people super challenging projects,” reminisced Prashant.
He stressed that a techie’s heart must always be into building and learning continuously.
“The world around us is fast evolving and changing. We need to keep pace with this ever evolving and growing change.”
NoSQL Market Size, Development Data, Growth Analysis & Forecast 2022 to 2028 – Energy Siren

MMS • RSS
Posted on mongodb google news. Visit mongodb google news

The report gives an abstract and quantitative examination of the Global NoSQL .The examination relies upon the division of the NoSQL which focuses on monetary and non-money related factors impacting the NoSQL improvement. The report joins a genuine scene which concludes the market position in the focal parts, including new help offered, thing dispatches, business associations, combinations and acquisitions in the past five years.
Companies operating in the NoSQL
PostgreSQL, Oracle Database, Objectivity, Neo, MySQL, MongoLab, MongoDB, Microsoft SQL Server, MarkLogic, IBM, Hypertable, DynamoDB, Couchbase, CloudDB, Cisco, Basho Technologies, Aerospike
The report highlights of emerging examples, with principal drivers, risks, and likely entryways In the NoSQL. The crucial creators across the world in the worldwide NoSQL are organized in the report. Considering such things introduced in the NoSQL, the around the world NoSQL is ordered Into different segments. The part overpowered the NoSQL and held the greatest piece of around the world NoSQL in the year 2020, and continues to govern the market in 2021 are positive in the report.
We Have Recent Updates of NoSQL in Sample [email protected] https://www.mraccuracyreports.com/report-sample/516883
Considering use, the around the world NoSQL is ordered into different application sections. The application section that is depended upon to drive the slice of the pie of the NoSQL in the next few years are highlighted and thought about in the report. The indispensable components of advancement in this application segment are explained in the report. The areas that addressed the greatest pay part of around the world NoSQL in 2022 are considered in the report. Additionally are depended upon to continue with the edge over its opponents in the regarded time span are considered in the report. The grounded establishment and innumerable Vessel Monitoring System Software associations in these regions are organized in the report.
By the product type, the market is primarily split into:
Key-Value Store, Document Databases, Column Based Stores, Graph Database.
By the end-users/application, this report covers the following segments:
Data Storage, Metadata Store, Cache Memory, Distributed Data Depository, e-Commerce, Mobile Apps, Web Applications, Data Analytics, Social Networking
Elements of the Report:
• New game plans and commitments that market players can imagine are in like manner discussed in the report.
• The possible entryways for business trailblazers and effect of the Coronavirus pandemic are associated with the around the world NoSQL.
• New things and organizations that are thriving in this speedy progressing around the world NoSQL’s monetary environment are discussed in the report.
• The report discusses the how certain advancement things, market frameworks, or game plans could assist with showcasing players.
• The pay open entryways and the growing new game plans are discussed in the report.
• The unquestionable characteristics of each part and market open entryways are explained in the report.
• The powers during the pandemic are relied upon to accelerate the hypothesis pace in the around the world NoSQL are point by point in the report.
• The report gives proposition on the way forward in the around the world NoSQL.
Table of Contents
1.1 Study Scope
1.2 Key Market Segments
1.3 Players Covered: Ranking by Vessel Monitoring System Software Revenue
1.4 Market Analysis by Type
1.4.1 NoSQL Size Growth Rate by Type: 2020 VS 2028
1.5 Market by Application
1.5.1 NoSQL Share by Application: 2020 VS 2028
1.6 Study Objectives
1.7 Years Considered
1.8 Continue…
Inquiry for Buying Report @ https://www.mraccuracyreports.com/checkout/516883
This report tends to a couple of key requests:
• What is the by and large expected advancement of around the world NoSQL after Coronavirus vaccination or treatment is found?
• What are the new essential methodologies that can be executed post-pandemic to remain merciless, agile, client driven, and helpful in the around the world NoSQL?
• Which unequivocal regions are depended upon to drive improvement in the around the world NoSQL?
• What are key government approaches and interventions did by driving around the world NoSQL countries to help with advancing gathering or improvement of Vessel Monitoring System Software.
Article originally posted on mongodb google news. Visit mongodb google news

MMS • RSS
Posted on nosqlgooglealerts. Visit nosqlgooglealerts

Aerospike Inc. today announced that it’s making its managed NoSQL database, the Aerospike Cloud Managed Service, available on Google Cloud.
The company is also simplifying the task of running its software on Red Hat’s OpenShift platform.
Mountain View, California-based Aerospike is a database startup backed by more than $60 million in venture funding. The startup counts major tech firms such as Sony Group Corp. and Adobe Inc. among its customers.
The Aerospike Cloud Managed Service, which Aerospike today made available on Google Cloud, is a managed version of its namesake NoSQL database. The database includes scalability features that allow it to store petabytes of information. It’s used for tasks such as training machine learning models and analyzing sensor logs generated by “internet of things” devices.
One of the core selling points of Aerospike’s database is that it promises faster performance than many competing systems. According to a benchmark test carried out by the startup, its database can carry out 3.6 times more operations per second than the popular Couchbase platform in some cases. Aerospike is also promising up to 15 times faster throughput than Apache Cassandra, another popular NoSQL platform.
One of the contributors to the speed of Aerospike’s database is its so-called hybrid memory architecture.
Aerospike enables companies to create an index, a kind of data shortcut that makes it possible to retrieve information from a database more quickly than would otherwise be possible. This index is kept in RAM rather than on storage drives as is the usual practice. RAM is significantly faster than storage drives, which means that applications can more quickly retrieve information from Aerospike’s database.
The managed version of the database that Aerospike is now bringing to Google Cloud offers a number of additional features. It removes the need for customers to manage the infrastructure on which their deployments run and includes an automated backup tool. Aerospike helps customers of the managed version optimize their database deployments’ hardware usage to reduce costs.
Aerospike today also announced improved compatibility with OpenShift, Red Hat’s distribution of Kubernetes. OpenShift has been certified for use with Aerospike Kubernetes Operator 2.0, a piece of software that makes it easier to run the startup’s NoSQL database on Kubernetes. The update should make it easier for joint Aerospike and Red Hat customers to combine the companies’ respective products.
“With our certification of OpenShift and Aerospike Cloud Managed Services on Google Cloud Platform, customers can easily manage data across multicloud deployments in their operations where previously they were hindered by regulations, cost control and talent availability that stalled innovation,” stated Aerospike Chief Executive Officer Subbu Iyer.
Image: Aerospike
Show your support for our mission by joining our Cube Club and Cube Event Community of experts. Join the community that includes Amazon Web Services and Amazon.com CEO Andy Jassy, Dell Technologies founder and CEO Michael Dell, Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger and many more luminaries and experts.

MMS • Guy Nesher
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

Minze is a modern JavaScript library that abstracts many of the difficulties of writing Web Components with a minimal overhead (2kb minified and compressed) and good developer ergonomics.
Web Components enable developers to create reusable custom HTML elements that encapsulate their design (CSS) and functionality (JavaScript) from the rest of the application.
Since Web Components are framework-agnostic, libraries like Ionic can easily support multiple frameworks (Angular, Vue.js, React) without rewriting their components numerous times.
Minze comes with a simple setup script that takes the developer through a quick installation process:
npm init minze@latest
The initial project contains three simple Web Components that provide a good starting point and show off the significant capabilities of the library.
We will look at a simplified version of the MinzeCounter example to explore how Web Components can be created using Minze.
export class MinzeCounter extends MinzeElement {
html = () => `
<div class="count">
<span>Count is:</span>
${this.count}
</div>
`
css = () => `
.count {
text-align: center;
}
`
reactive = [['count', 0]]
increaseCount = () => this.count++
eventListeners = [['.button', 'click', this.increaseCount]]
}
The “html” and “css” methods return a string containing the component HTML and CSS. Since components should be pretty small, returning template string straight away works well.
Properties defined on a MinzeElement class are considered “non-reactive,” meaning that changing them will not cause the element to re-render.
Reactive properties are defined using the “reactive” property that accepts an array of strings or tuples. Any change to the values defined within the reactive property will trigger a component redraw.
In order, to accept external attributes, developers must use the “attrs” property that works similarly to the “reactive” property with two important caveats:
- “attrs” properties must use dash-case notation
- Developers can use the “observedAttributes” property in combination with the “onAttributeChange” method to track attribute changes. i.e:
attrs = [
'example-attribute'
]
static observedAttributes = ['example-attribute']
onAttributeChange(name, oldValue, newValue) {
console.log(this.exampleAttribute)
}
For developers using TypeScript, accessing properties that were defined as either “reactive” or “attrs” will require an interface that includes these property definitions, as TypeScript does not recognize properties that were not defined directly on the class.
Finally, Minze.define is used to define the new custom elements created. Developers should remember that Custom component names should always consist of at least two words.
Minze is an open-source project published under the MIT license. The source code is available on Minze Github repository, and developers are encouraged to contribute by following the contribution guidelines.