Month: December 2020

MMS • RSS
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

As 2020 is coming to an end, we created this article listing some of the best posts published this year. This collection was hand-picked by nine InfoQ Editors recommending the greatest posts in their domain. It’s a great piece to make sure you don’t miss out on some of the InfoQ’s best content.
By Leandro Guimarães, Arthur Casals, Charles Humble, Daniel Bryant, Johan Janssen, Manuel Pais, Renato Losio, Shane Hastie, Steef-Jan Wiggers, Thomas Betts

MMS • RSS
Article originally posted on Data Science Central. Visit Data Science Central
In today’s data-driven world, companies across the globe are plunging into the humungous pool of online customer information that is made available through different modes of data collection. More than 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are created each day, and this number just keeps on growing. Moreover, it was found that 67% of customers were willing to give their data for some benefits in terms of discounts.
Online customer data like social media activities, search engine tracking, and purchase history are being generated on a regular basis. This data gives eCommerce companies a peek into customer demographics, preferences & interests thus creating a customer profile useful for targeting specific products based on customer needs, just at the right time. Hence, data collection should be a priority for these companies to create customized marketing strategies.
“Analytical insights from data are only as useful as the quality of data collected.”
This brings us to the simple truth that accurate data collection plays a pivotal role in creating prolific marketing strategies yielding results for eCommerce companies.
Here are four reasons why collecting accurate customer data is useful for eCommerce companies:
- Promote relevant products through multiple communication channels like email, SMS, push & pull notifications, etc.
- Better customer segmentation by accurately dividing customers based on their behavior, preferences, and interests.
- Developing customized marketing campaigns to give a personal touch using information such as birthday, locality, age group, etc.
- Increasing customer lifetime value by predicting customer requirements based on purchase history information.
To ensure these strategies fall through as desired, you need to follow the basic principles of data collection.
“The basic principles of data collection include keeping things as simple as possible; planning the entire process of data selection, collection, analysis, and use from the start; and ensuring that any data collected is valid, reliable, and credible. It is also important that ethical issues are considered.”
The process and principles of data collection have been around for a long time; remember creating questionnaires and asking customers to fill them? Be it offline or online data collection, principles applied to remain the same.
Let’s have a look at the four principles of data collection one should follow from an online data collection perspective.
Principle 1: Identify the data you need to collect (Get the right data)
This principle simply states that the data needed for analysis should be fixed from the beginning of the data collection process. Do not collect data without figuring out how it will be analyzed or be useful. In such scenarios, it is highly likely you will end up with loads of data that is not useful. For e.g. auto part dealers need information about customer’s car models whereas fashion store owners need information about the customer’s age.
How to go about it?
The customer data you need depends on the type of business you run and the products you are selling. Hence, it is critical to understand what sort of data you need. Businesses usually collect the following type of data based on their requirement:
- Behavioral data
This data tells you how customers behave when they interact with your company. This data is measurable, analyzing it helps you improve your customer’s interaction with your company & increase conversion rates
Data types: Transactional data, communication data, online activity, customer relations
- Identity data
This data usually consists of customer demographics thereby helping you create an ideal customer profile. Thus, playing a vital role in forming customized marketing strategies.
Data types: Name, email, phone number, DOB, gender, birth date, social media profile, company’s name, position
- Descriptive data
This data consists of personal information apart from identity data. This data helps you understand the customer at a personal level and create appropriate strategies aimed at offering additional products and services e.g. a person buying a new car and being interested in music can help you cross-sell car speakers.
Data types: marital status, number of kids, lifestyle, hobbies, pets
- Qualitative data
This type of data is usually acquired through surveys. They include customer preferences, desirability, and sentiments. This data provides insight into the customer’s perception of your company.
Data types: Any kind of customer survey.
Principle 2: Authenticate your source of data (Get data the right way)
Getting data the right way encompasses the source of data. If the source is flawed, the data is meant to give you insignificant or irrelevant analytical insights, ultimately leading to a flawed marketing strategy. Hence, you need to choose the source of the required data very wisely.
How to go about it?
Here are a few sources you may need:
- Website analytical tools
If you are looking to analyze the behavioral data of your customer, a web analytic tool is an answer. Analyzing parameters such as bounce rates, page views, etc. can give you better insights into your customer’s interests.
- Online surveys
The requirement of consent and approval of the participant makes it the most authentic source of data collection. It gives you an in-depth analysis of customers’ opinions and sentiments. Ideal source for qualitative and descriptive data
- Customer interviews & feedback
It can be done through post-purchase feedback forms, call or video call interviews, or focus group meetings. It gives critical insight into customer’s preferences and opinions. It is ideal for identity, descriptive and qualitative data.
- Social media engagements
Customers present their unbiased views and preferences on social media platforms. Social listening can help you identify and analyze consumer’s interests, opinions, and experiences. It is ideal for identity and qualitative data.
Based on the data that you need to gather, a mixed-use of all these sources can help you create a successful marketing strategy.
Principle 3: Validate the data you collect for errors and reduce them (Get the data right)
No matter how authentic the source, there is still a minor possibility of errors based on the type of tools used for data collection. As the success of your marketing efforts depends on accuracy, following a proper data validation process is essential. For e.g. a customer marks his preference for a red shoe over a blue shoe in an online survey but social media listening may suggest that their favorite color is blue when it comes to outfits.
How to go about it?
Especially, when it comes to identity data like name, email, phone number, etc. accuracy and completeness are highly critical, and hence, validation is non-negotiable. Data validation and enrichment call for the implementation of data cleansing techniques.
Principle 4: Get current and updated data (Get the data right away)
Data degrades over time and leads to inaccurate and incorrect insights. Data such as email, phone number, company, position, and addresses of customers change over time. Even preferences and interests are associated with factors such as age, marital status, etc. hence bound to change. At this juncture, it is essential to ensure that the data collected is current and updated.
How to go about it?
Select data collection techniques and sources that can provide you with the latest information on your consumers. For e.g. government records have a high probability of containing obsolete data whereas customer interviews provide you with the latest information. Avoiding data degradation can also be done with the help of thorough cleansing and efficient data management.
Conclusion
Today, the data-oriented approach has left us with a massive amount of information at our disposal. Hence, the need to select the right data to collect, from an authentic source, with high accuracy is indispensable. As a business person or marketer, it is your prime responsibility to facilitate high-quality data collection, gain critical insights, and create impeccable marketing strategies customized according to the needs and wants of the customer.

MMS • RSS
Article originally posted on Data Science Central. Visit Data Science Central
Introduction and Motivation
In this blog, let’s explore the key functionalities of blockchain to serve as a data governance framework and see it with an example using Google Cloud Platform
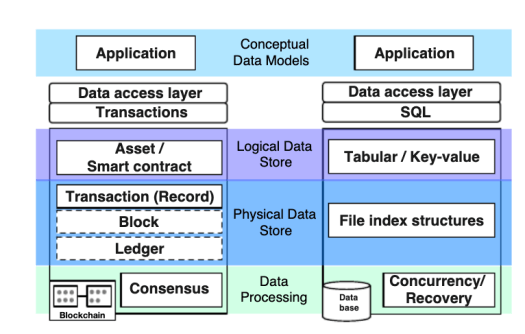
Applications that utilize blockchain technology are:
Blockchain As Data Governance Accelerator
- MDM and blockchain can reap benefits from mutual integration.
- MDM can utilize blockchain for Data Distribution and Data Governance, leaving access to great master data to blockchain technology.
- Access to third-party controls, with enhanced risk management Decentralized ledger systems with full auditing features
- Timely alerts and notifications informing changes
- Acts as a guarantor for the integrity of a digital representation of a physical entity.
- Acts as a Data Chain of Custody
- Helps in the reinterpretation of Events
- Source of Truth and Doubt
- Ability to create blockchain-based data escrow by a combination of cryptographic techniques like secret sharing with smart contracts, where the encrypted and published data is available to a critical number of stakeholders.
One of the use of blockchain in the supply chain industry as DG is where certificates are given to food products to ensure their authenticity. The metadata about the certificates could be stored on a blockchain, and a buyer can verify the purchased product through verifying the certificates with the metadata stored on the blockchain.
BlockChain Data Governance with GCP
GCP makes it easy to get the basics of security right. Google Cloud goes above and beyond to protect data, infrastructure, and services from external threats, while internally, the permission model integrated with Google Workspace gives granular control over access rights.
Blockchain limitations
- Latency in establishing consensus.
- Sensitive data needs to be forgotten.
- Due to high storage volume, features like auto-deletion beyond a certain volume of data has to be incorporated. However, they make other blockchain functions complex.
- Network governance could break down.
- Monopoly or single organizations controlling data ecosystem (generation, access, and regulation of all data, a blockchain) limits its value. Hence it should encourage the involvement and participation of peers in the blockchain networks.
- Reading Blockchain transactions involves reading receipt-based transient synchronous communication, that does not directly return results or indicate whether the transaction was successful.
Future Work & Unanswered Questions
- Better Decision Making with consistency, completeness, and accuracy
- Operational Efficiencies with fact-based decisions that become real-time events.
- Improved data understanding and lineage (removal of confusion, adding clarity and meaning)
- Data alignment leading to Regulatory Compliance
- Increased Revenue obtained by added data confidence and insights sharing.
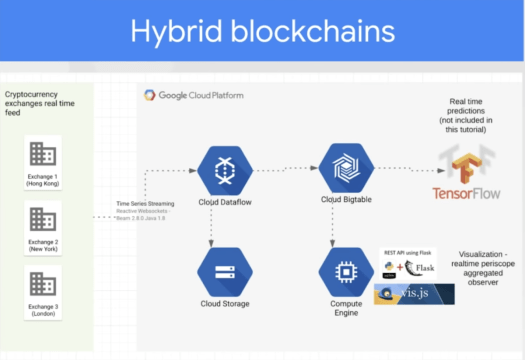
- Strategizing end to end Machine Learning pipelines with Online and Batch/Stream
- Processing events with Blockchain
- Can we integrate AI/ML algorithms with blockchain events (live crypto-currency feed) along with events from disparate data sources ( say Iot)
- How do we ensure the privacy and decentralization of non-blockchain events in the same pipeline?
- In that do, we plan to add Data Catalog and DLP in the architecture.
- How do we assemble and ensure fair data for blockchain (cryptocurrency exchanges) events and build fair ML models?
Role of BlockChain in Machine Learning Model Governance
Note : Blockchain for Data and Model Governance (US20200082302A1, Application US16/128,359)
- Features causing bias, model sensitivity, or target leaks.
- Steps to build the model, datasets used for training, validation, and testing.
- Model interpretability explaining the factors for the Model’s behavior.
- Model explainability and accountability for all use-cases that could alleviate risk and prevent time and effort in Model re-development.
- How can blockchain help to codify accountability?
- By providing the analytic model its own entity, life, structure, and description, with detailed structure and documentation Helping to create Models with more explainability and less bias with an increased focus to deliver Ethical and Explainable AI technology solutions.
- Increasing the scope for future work by creating essential assets for the organization.
- Facilitating analytic tracking document (ATD) and agile model development process which can be used by parties outside the development organization. It also helps regulatory bodies in Model audits.
Conclusion
Blockchain techniques are uniquely suited to data governance systems.
References
- https://www.ibm.com/blogs/journey-to-ai/2020/06/data-governance-the-importance-of-a-modern-machine-learning-knowledge-catalog/
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/solutions/governance/
- https://www.sas.com/content/dam/SAS/en_us/doc/whitepaper1/sas-data-governance-framework-107325.pdf
- https://www.hitachivantara.com/en-us/company/data-management-done-differently/intelligent-data-governance.htmlecid=ps_APAC_dp_en_ss0005sem&utm_source=google_ads_search_apac&utm_medium=paid_search&utm_keyword=data%20governance&gclid=Cj0KCQjwt4X8BRCPARIsABmcnOqsMnMIcpnEyYvBXtD0xjUPbqOyPTOLzR7NQeY9roonXrl85KHRAl4aAu4wEALw_wcB
- https://github.com/topics/data-governance
- https://cloud.google.com/solutions/migration/dw2bq/dw-bq-data-governanceBitcoin Analysis of Data Management in Blockchain-based Systems: From Architecture to Governance
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338144930_Analysis_of_Data_Management_in_Blockchain-based_Systems_From_Architecture_to_Governancehttps://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=8938787
- https://www.cloudtp.com/doppler/12-step-guide-data-governance-cloud-first-world/Blockchain as a Platform for Data Governance 2.0
- https://dataschool.com/data-conversations/blockchain-as-a-platform-for-data-governance-2-0/
- https://cloud.google.com/customers/blockchainhttps://cloud.google.com/blog/products/data-analytics/building-hybrid-blockchain-cloud-applications-with-ethereum-and-google-cloud
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336805100_FaDe_A_Blockchain-Based_Fair_Data_Exchange_Scheme_for_Big_Data_Sharing
- https://www.rtinsights.com/going-beyond-bitcoin-critical-applications-for-blockchain-in-ai/

MMS • RSS
Article originally posted on Data Science Central. Visit Data Science Central
Cyber-attacks have been bothering people lately; however, 2020 shows us that there are no limits for people who are behind these crimes. Hackers used to crack down people’s websites, personal accounts, but now, it is more about getting a bigger fish. The spheres that undergo significant stress from cyberattacks at the moment include small businesses, the world economy, and even politics.
Despite such an issue, malicious programs penetrate governmental and business institutions’ systems and personal computers of the average citizens. It is time to think about your protection in advance. Consider this article to see how software can fit your needs, and seek some information regarding the features you need right now.
These are the options aimed at protection against common risks the business and political spheres experience nowadays. In this regard, let’s give it a more detailed look.
Small Businesses Are at Risk
Returning to the attacked spheres, let us see what meaningful cybercriminals happened lately and how these affected the world. Nearly every organization, whether it is a corporation or a small company, is a target for cyberattacks. Yet, if you own a small business, you should realize that this sector is the most vulnerable and whether you want it or not, you will have to spend some money on durable antivirus software.
The most important thing to keep in mind is that cybercriminals are not standing at one point; the attacks become more sophisticated and sly with every month. Modern antiviruses can detect a damaging file, yet, not all the programs can protect you from a newly created virus. For that reason, it would be fair to conclude that sooner or later, every small company is likely to be attacked.
The devastating effects of the hacking process are also related to the fact that online criminals foresee a particular company’s risks. In other words, they study the organization from the inside, focus on the spots that can be a perfect breach target, and do whatever it takes to hack the security system. Besides, keep in mind that there is always a probability of an insider threat.
Why is the Segment so Luring?
As of the moment of 2020, 28% of the attacks engage small businesses. It seems to be a considerable percentage and makes you wonder what makes the segment so vulnerable in other businesses’ background. The answer was the level of protection. Big corporations cannot close their eyes and keep up with popular antiviruses due to the scope of possible consequences.
Cybercriminals tend to diversify and broaden the field of their activity. So, you should be ready to guard your company, employees, and, of course, your customers. Interestingly, the motives of the criminals are financial (83%), concerned with espionage reasons (8%), and also fun-related (3%). Some of the typical attacks are as follows:
- Spyware – 46%
- Captures of stored data – 34%
- Stolen credit cards usage – 30%
- Export data – 29%
- Backdoor – 28%
- Backdoor and C2 usage – 26%
- Phishing – 22%, etc.
Note that weak passwords are not a good thing for businesses as well, and hackers will use your neglect of the rules. Weak passwords are often an issue that comes from employees’ negligence. All actions that come from the inside of the organization – employees, associates’, or business contractors’ activity – comprise an insider threat.
The insider threat appears when the contributors access sensitive data and use it for the sake of their benefit. On the other hand, data leak may happen due to a person’s inattentiveness and unprofessionalism. You should be aware of similar cases to know the root of the problem in such situations, where an insider brings down the entire company.
Economic Impact
With a growing interest in poorly protected small businesses, global security risks grow as well. Eventually, it poses serious problems for the economy of the entire world. The Global Risks Report 2020 suggests that until 2030, cybercrime will be the second top risk in the global commerce sphere. It sounds odd, considering the technologies people already know. The trouble is that hackers are smart as whips.
Sure, the small companies suffer the most, yet the big corporations also face impactful attacks, and this problem will not disappear. Big organizations have branch offices and sub-companies around the world. And if one of the institutions is affected, then the revenue, reputation, and profits of the entire organization are going to experience tough times.
Public Impact
Another indicator of small business’ vulnerability is the attacks on the public sector and governmental entities. It may seem somehow evident that cyber criminals should be interested in governmental organizations and accounts of politics. The reasons for such breaches vary from personal benefits, like confidential information extortion, to political views.
Lately, the entire world watched the combat between Donald Trump and Joe Biden; one of the discussed topics was the possibility of ransomware attack during the elections. Especially considering the way how high the emotions ran during the debates of both candidates.
The reason for such a concern is related to an incident back in 2016 when ransomware hit the state of Florida election. Despite the recovery, the event left an unpleasant aftertaste, and people realized that it was no joke – cyber attacks were genuine and could undermine the system. If such a public sector is vulnerable, then small businesses are under hit as well.
In this regard, the reaction created by previous ransomware was impressive. Aside from political institutions, Americans saw the issue from a broader perspective: if elections were that easy to compromise, it would be even easier to compromise banking companies, hospitals, etc.
Bottom Line
As you can see, cybercriminals are not a thing to ignore. People could have noticed a more rapid growth in the number of attacks during the last decade. There are three sectors in the limelight of an issue: small businesses, the global economy, and politics. In most cases, the reason for a breach was a human mistake, weak security measures, or unawareness of the problem’s seriousness.

MMS • RSS
Article originally posted on Data Science Central. Visit Data Science Central
Introduction
There are six broad questions which can be answered in data analysis according to an article called “What is the question?” By Jeffery T. Leek, Roger D. Peng. These questions help to frame our thinking of data science problems. Here, I propose that these questions also provide a unified framework for relating statistics to data science.
The six questions according to Jeffery Leek and Roger Peng are
A descriptive question seeks to summarize a characteristic from a dataset. You do not interpret the results. For example: number of fresh fruits and vegetables served in a day.
An exploratory question is a question where you try to find a pattern of a relationship between variables i.e. you aim to generate a hypothesis. At this stage, you do not test the hypothesis. You are merely generating a hypothesis. More generally, you could say that you are proposing a hypothesis which could hold in a new sample from the population.
An inferential question restates the proposed hypothesis in the form of a question that would be answered by analyzing the data. You are validating the hypothesis i.e. does the observed pattern hold beyond the data at hand. Most statistical problems are inferential problems.
A predictive question would be one where you predict the outcome for a specific instance.
A causal question: Unlike the predictive and inferential questions, causal questions relate to averages in a population i.e. how changing the average in one measurement would affect another. Causal questions apply to data in randomized trials and statistical experiments where you try to understand the cause behind an effect being observed by designing a controlled experiment and changing one factor at a time.
A mechanistic question asks what is the mechanism behind an observation i.e. how a change of one measurement always and exclusively leads to a deterministic behaviour in another. Mechanistic questions apply typically to engineering situations.
Implications for Data Science
The six questions framework raise awareness about which question is being asked and aim to reduce the confusion in discussions and media. However, they also help to provide a single framework to co-relate statistics problems to data science.
Re the six questions:
- Descriptive and exploratory techniques are often considered together
- Predictive and Inferential questions can also be combined
So we could consider four questions:
- Exploratory
- Inferential
- Causal
- Mechanistic
Why this framework matters?
That’s because it provides questions which may not have been encountered before. Here are three examples
- Typically, the starting point of data science is ‘big data’. Most data scientists are not used to dealing with small data. When you do not have a large amount of data you need to consider a more statistics driven approach see the difference between statistics and data science big data and inferential statistics
- The significance of causal questions i.e. Corelation vs Causation which I discuss in Correlation does not equal causation but how exactly do you determine causation
- And finally – the mechanistic question which is elaborated more in Why do some traditional engineers not trust data science
Conclusion
The six questions provide rigor and simplicity of analysis. I also find that these questions provide a comprehensive set of questions that link statistics to data science. They help you to think beyond the norm i.e. beyond problems that you encounter to consider all possible problems.
References
What is the question? By Jeffery T. Leek, Roger D. Peng
image source
Presentation: User Stories: Re-Explained – You Think You Know until You Realise You Don't

MMS • Steef-Jan Wiggers
Article originally posted on InfoQ. Visit InfoQ

During the first week of the annual re:invent, AWS introduced the ability to specify AWS Fargate as a computing resource for AWS Batch jobs. With the AWS Batch support for AWS Fargate, customers will have a way to run jobs on serverless compute resources, fully-managed from job submission to completion.
By Steef-Jan Wiggers



